Abstract
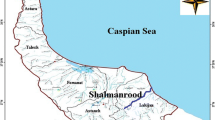
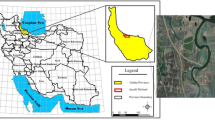
In the present study, the removal of dissolved and colloidal Cd, Co, Cu, Ni and Zn in Arvand River water during estuarine mixing with the Persian Gulf water is investigated. The flocculation process was investigated for a series of mixtures with salinities ranging from 0.48 to 30.3^. The flocculation rates were indicative of the non-conservative behavior of studied metals during estuarine mixing. Rapid flocculation in the low salinity regimes was observed. The order of the final flocculation rate of metals in the river water was as follows: Co (91.2%)> Cd (86.9%)> Zn (83%)> Cu (75.2%)> Ni (74.3%). Salinity, pH, EC and dissolved oxygen do not govern the flocculation of metals during estuarine mixing. The results of the present investigation show that estuarine processes can be considered as an effective mechanism in self purification of colloidal metals that are anthropogenically introduced into the fresh water ecosystem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeLaune R.D., Johnson C.B., Gambrell R.P., Jugsujinda A., Export of dissolved organic carbon from a ponded freshwater marsh receiving diverted Mississippi River water, The Scientific World J., 2008, 8, 1210–1218
Pain G.N., Sanchez A.L., Mehlhorn T.L., The Donana ecological disaster: contamination of a world heritage estuarine marsh ecosystem with acidified pyrite mine waste, Sci. Tot. Environ., 1998, 222, 45–54
Sommerfield P.J., Gee M., Warwick R.M., Benthic community structure in relation to an instantaneous discharge of waste water from a tin mine, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 1994, 28, 363–369
Achterberg E.P., Herzl V.M.C., Braungardt C.B., Millward G.E., Metal behaviour in an estuary polluted by acid mine drainage: the role of particulate matter, Environ. Pollut., 2003, 121, 283–292
Sholkovitz E.R., Boyle E.A., Price N.B., The Removal of Dissolved Humic Acids and Iron During Estuarine Mixing, Earth Planet. Sc. Lett., 1978, 40, 130–136
Forstner U., Wittmann, G.T.W., Metals in Hydrocycle, Springer, Berlin, 1984
Fox L.E., Wofsy S.C., Kinetics of Removal of Iron Colloids from Estuaries, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 1983, 47, 211–216
Hunter K.A., On the estuarine mixing of dissolved substances in relation to Colloidal stability and surface properties, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 1983, 47, 467–473
Zhiqing L., Jianhu Z., Jinsi C., Flocculation of dissolved Fe, Al, Mn, Si, Cu, Pb and Zn during estuarine mixing, Acta Oceanolog. Sin., 1987, 6, 567–576
Featherstone A.M., Ogrady B.V., Removal of Dissolved Copper and Iron at the Freshwater-Saltwater Interface of an Acid Mine Stream, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 1997, 34, 332–337
Saeedi M., Karbassi A.R., Mehrdadi N., Flocculation of dissolved Mn, Zn, Ni and Cu during the mixing of Tadjan River water with Caspian Sea water, Int. J. Environ. Stud., 2003, 60, 575–580
Karbassi A.R., Nouri J., Ayaz G.O., Flocculation of Trace Metals During Mixing ofTalar River Water with Caspian Sea Water, Int. J. Environ. Res., 2007, 1, 66–73
Saeedi M., Karbassi A.R., Estuarine capacity in removal of trace metals from contaminated river water, Southern Caspian Sea, Water Environ. J., 2008, 22, 193–198
Karbassi A.R., Nouri J., Mehrdadi N., Ayaz G.O., Flocculation of heavy metals during mixing of freshwater with Caspian Sea water, Environ. Geol., 2008, 53, 1811–1816
Karbassi A.R., Geochemistry of Ni, Zn, Cu, Pb, Co, Cd, V, Mn, Fe, Al and Ca in sediments of North Western part of the Persian Gulf, Int. J. Environ. Stud., 1998, 54, 205–212
Lance G.N., Williams W.T., A Generalized Sorting for Computer Classifications, Nature, 1966, 212, 218
Anderson A.J.B., Numerical Examination of Multivariate of Soil Samples, Math. Geol., 1971, 3, 1–14
Davis J.C., Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology, Wiley International, New York, 1973
National Research Council Canada, CASS-4 Nearshore Seawater Reference Material for Trace Metals, National Institute for Measurement Standards, Ottawa, Canada, 1999
Karbassi A.R., Nadjafpour Sh., Flocculation of dissolved Pb, Cu, Zn and Mn during Estuarine mixing of river water with the Caspian Sea, Environ. Pollut., 1996, 93, 257–260
Bewers J.M., MacAulay I.D., Sundby B., Trace Metals in theWaters of the Gulf of St Lawrence, Can. J. Earth Sci., 1974, 11, 939–950
Burton J.D., Basic Properties and Processes in Estuarine Chemistry, Academic Press, London, 1976
Duinker J.C., Nolting R.F., Distribution model for particulate trace metals in Rhine estuary, southern bight and Dutch Wadden Sea, Netherlands J. Sea Res., 1976, 10, 71–102
Biati A., Karbassi A.R., Hassani A.H., Monavari S.M., Moattar F., Role of metal species in flocculation rate during estuarine mixing, Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 2010, 7, 327–336
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Karbassi, A., Nabi Bidhendi, G.R., Saeedi, M. et al. Metals removal during estuarine mixing of Arvand River water with the Persian Gulf water. Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 2, 531–536 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2478/v10085-010-0011-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/v10085-010-0011-x