Abstract
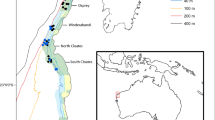
Extensive sampling (450 grabs) was performed all over the inner part of Puck Bay (105 km2 area) in summers of 2007–2009. The GIS-based analysis of samples was performed to assess in detail the distribution of 32 benthic species. The minimum area of occurrence was less than 1 km2 for Lekanosphaera rugicauda and the maximum was 83 km2 for Cerastoderma glaucum. The material reveals that species with the pelagic larval stage were most widespread, with the least distance between individuals and the highest average density (e.g. Cerastoderma glaucum, Hydrobia ventrosa). The most isolated and the least dense species within the studied area were discretely mobile, non-larval crustaceans (e.g. Gammarus oceanicus and Lekanosphaera rugicauda), present at single sites with the largest distance from each other. We conclude that analysis of species distribution helps in understanding the threats to populations of marine invertebrates and marine spatial planning, through locating the isolated species and populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agardy T. (2000). Information needs for marine protected areas: scientific and societal. Bull. Mar. Sci. 66, 875–888.
Agardy T., Bridgewater P., Crosby M.P., Day J., Dayton P.K., Kenchington R., Laffoley D., McConney P., Murray P. A., Parks J.E. & Peau L. (2003). Dangerous targets? Unresolved issues and ideological clashes around marine protected areas. Aquatic Conserv: Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 13, 353–367.
Andrulewicz E., Otręba Z., Węsławski J.M. & Kamińska K. (2012). Disturbances of physical properties of marines pace related to large — scale technical installations. Implications for ecosystem-based management in the Baltic Sea. Marine Management, in press
Baddeley R. & Turner R. (2005). Spatstat: an R package for analyzing spatial point patterns. Journal of Statistical Software. 12, 1–42.
Bell JJ. & Okamura B. (2005). Low genetic diversity in a marine nature reserve: reevaluating diversity criteria in reserve design. Proc. Royal Soc. B, 272, 1067–1074.
Boero F. & Bonsdorff E. (2007). A conceptual framework for marine biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Marine Ecology. 28, 134–145.
Boersma de P. & Parrish J.K. (1999). Limiting abuse: marine protected areas, a limited solution. Ecological Economics. 31, 287–304.
Bologna P.A.X. & Heck, K.L. (2002). Impact of Habitat Edges on Density and Secondary Production of Seagrass-associated Fauna. Estuaries. 25(5), 1033–1044.
Bonsdorff E. (2006). Zoobenthos diversity gradients in the Baltic sea: Continuous post-glacial succession in a stressed ecosystem. Journal of Exp. Marine Biol. And Ecol. 330, 383–391.
Bonsdorff E. & Pearson T. (1999). Variation in the sublittoral macrozoobenthos of the Baltic sea along environmental gradients: a functional group approach. Australian Journal of Ecology. 24, 312–326.
Bostrom C. & Bonsdorff E. (1997). Community structure and spatial variation of benthic invertebrates associated with Zostera marina (L.) beds in the northern Baltic Sea. Journal of Sea Research. 37, 153–166.
Brown J.H. (1984). On the relationship between abundance and distribution of species. The American Naturalist. 124, 255–279.
Dulvy N.K., Sadovy Y. & Reynolds J.D. (2003). Extinction vulnerability in marine populations. Fish and Fisheries. 4, 25–64.
Dziubińska A. (2011). PhD dissertation, University of Gdansk, unpublished manuscript
Elmgren, R. & C. Hill. (1997). Ecosystem function at low biodiversity — the Baltic example. In: Marine Biodiversity. Patterns and Processes. Ormond, R.F.G., Gage, J.D. and Angel, M.V. (eds). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 319–336.
Gic Grusza G., Urbański J., Warzocha J. & Węsławski J.M. (2009). Atlas of marine seabed habitats of Polish Marine Areas. IOPAN, Sopot, 180 pp.
Glockzin M. & Zettler M.L. (2008). Spatial macrozoobenthic distribution patterns in relation to major environmental factors — A case study from the Pomeranian Bay (southern Baltic Sea). Journal of Sea Research. 59, 144–161.
Gray J.S. (2002). Species richness of marine soft sediments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 244, 285–297.
Grzelak K. & Kuklinski P. (2010). Benthic assemblages associated with rocks in a brackish environment of the southernBaltic Sea. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 90, 115–124.
Healey D. & Hovel K.A. (2004). Seagrass bed patchiness: effects on epifaunal communities in San Diego Bay, USA. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology. 313, 155–174.
ICES (2011). Report of the Workshop on the Science for area-based management: Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning in practice (WKCMSP). 1–4 November 2010, Lisbon, Portugal. ICES CM 2011/SSGHIE:01. 25 pp
Janas, U., Zarzycki, T. & Kozik, P. (2004). Palaemon elegans — a new component of the Gulf of Gdańsk macrofauna. Oceanologia. 46, 143–146.
Jazdzewski K. (1973). Ecology of gammarids in the Bay of Puck. Oikos, suppl. 15: 121–126.
Jeczmien W. & Szaniawska A. (2000). Quantitative studies on Gammarus Fabr. genus in Puck Bay (the Baltic Sea). Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiologii. 47(3–4), 561–568.
Laine A.O. (2003). Distribution of soft-bottom macrofauna in the deep open Baltic Sea in relation to environmental variability. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 57, 87–97.
Leeuwen van A., De Roos A.M. & Persson L.(2008). How cod shapes its world. Journal of Sea Research. 60, 89–104.
Levitan D.R. (1991). Influence of body size and population density on fertilization success and reproductive output in a free spawning invertebrate. Biological Bull.(Woods Hole). 181, 261–268.
Mokievsky V.O. (2009). Marine protected areas: theoretical background for design and operation. Russian Journal of Marine Biology. 35, 504–514.
Myers R.A., Barrowman N.J., Hutching J.A. & Rosenberg A.A. (1995). Population dynamics of exploited fish stocks at low population levels. Science. 52227, 1106–1108.
Norse E.A. & Crowder L.B. (2005). Marine Conservation Biology. Island Press; Washington, Covelo, London, 470 pp.
Osowiecki A. (1998). Macrozoobenthos distribution in the coastal zone of the Gulf of Gdansk — autumn 1994 and summer 1995. Oceanological Studies. 27, 123–136.
Petitgas, P. (1998). Biomass-dependent dynamics of fish spatial distributions characterized by geostatistical aggregation curves. ICES Journal of Marine Science. 55, 443–453.
Pliński M. & Florczyk I. (1984). Changes in the phytobenthos resulting from the eutrophication of the Puck Bay. Limnologica (Berlin). 15, 325–327.
Powles H., Bradford M.J., Bradford R.G., Doubleday W.G., Innes S. & Levings C.D. (2000). Assessing and protecting endangered marine species. ICES Journal of Marine Science. 57, 669–676.
Robbins B.D. & Bell S.S. (1994). Seagrass landscapes: a terrestrial approach to the marine subtidal environment. Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 9, 301–304.
Roberts D.A. & Poore A.G.B. (2005). Habitat configuration affects colonization of epifauna in a marine algal bed. Biological conservation. 127, 18–26.
Skov H., Durinck J., Leopold M.F. & Tasker M.L. (2007). A quantitative method for evaluating the importance of marine areas for conservation of birds. Biological conservation. 136, 362–371.
Smoła Z. (2012). MSc dissertation, University of Gdansk
Sumaila U.R. (2002). Marine protected area performance in a model of the fishery. Natural Resource Modelling. 15, 439–451.
Szymelfenig M., Kotwicki L. & Graca B. (2006). Benthic recolonization in post dredging pits in the Puck Bay (Southern Baltic). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science. 68, 489–498.
Tzvetkova, N. L. (1975). Coastal gammarids of the northern and Far Eastern seas of the USSR and adjacent waters. Genera Gammarus, Marinogammarus, Anisogammarus, Mesogammarus (Amphipoda, Gammaridae). Nauka, Leningrad (in Russian).
Virnstein R.W. & Curran M.C. (1986). Colonisation of artificial seagrass versus time and distance from source. Marine Ecol. Progress Ser. 29, 279–288.
Warzocha J. (1995). Classification and structure of of macrofaunal communities in the souhern Baltic. Arch. Fish. Mar. Res. 42, 225–237.
Weslawski J.M., Urbanski J., Kryla-Straszewska L., Andrulewicz E., Linkowski T., Kuzebski E., Meissner W, Otremba Z & Piwowarczyk J. (2010). The different uses of sea space in Polish Marine Areas: is conflict inevitable? Oceanologia. 52, 513–530.
Weslawski J.M., Warzocha J., Wiktor J., Urbanski J., Radtke K., Kryla L., Tatarek A., Kotwicki L. & Piwowarczyk J. (2009). Biological valorisation of the southern Baltic Sea (Polish Exclusive Economic Zone). Oceanologia. 51, 415–435.
Wlodarska-Kowalczuk M., Weslawski J.M., Warzocha J. & Janas U. (2010). Habitat loss and possible effects on local species richness in a speciespoor system — a case study of southern Baltic. Biodivers Conserv. 19, 3991–4002.
Worm B., Lotze H.K. & Sommer U. (2001). Algal propagule banks modify competition, consumer and resource control on Baltic rocky shores. Oecologia. 128, 281–293.
Zschokke S., Dolt C., Rusterholz H., Oggier C., Braschler B., Thommen G.H., Ludin E., Erhardt A. & Baur B. (2000). Short term responses of plants and invertebrates to experimental small-scale grassland fragmentation. Oecologia. 125, 559–572.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Węsławski, J.M., Kryla-Straszewska, L., Warzocha, J. et al. How lonely they are? A degree of isolation among macrozoobenthos species in the Marine Protected Area, the Bay of Puck, the Southern Baltic. Ocean and Hydro 42, 289–295 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13545-013-0085-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13545-013-0085-8