Abstract
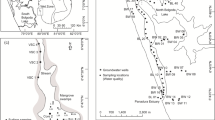
The annual variability of ichthyoplankton in the Yangtze River estuary, located at the junction of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea, on the continental shelf at the western rim of the Pacific Ocean, was studied using vertical tows at twenty stations from August 2002 to August 2009. Basic oceanographic parameters such as temperature and salinity were also measured to evaluate their relationship to the abundance of ichthyoplankton. The eggs or larvae of a total of 34 fish species were present in the samples. Only 8 species were found to occur during every year. Engraulis japonicus and Stolephorus commersonii eggs, as well as Coilia mystus and Stolephorus commersonii larvae, were highly abundant during this period. Additionally, water storage in the Three Gorges Reservoir, which began in June 2003, had significant effects on the abundance of estuarine species, as well as on the composition and diversity of ichthyoplankton; this became evident when these values were compared to the findings from 2002. The number of species (species richness) and abundance of each species varied among the stations relative to the salinity in the estuary during the study period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aimee, A. K., Grace K.M., Jeanne, S.T. & Onge, B. (1999). Abundance and distribution of ichthyoplankton in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island, 1989–1990. Estuaries, 22(1):149–163. DOI:10.2307/1352935.
Alan, J. D., William, J. K., Stephen, G. M., Charles, A., Jamese, Cloern., Thomas, M. P., Jerry, R. S. & Timothy, J. V. (1995). Isohaline position as a habitat indicator for estuarine populations. Ecol Appl, 5(1):272–289. DOI:10.2307/1942069.
Andrés, J.J., Roberto, M., Raul, G. & Carlos, L. (2004). Environmental factors structuring fish communities of the Río de la Plata estuary. Fish Res, 66:195–211. DOI:10.1016/S0165-7836(03)00200-5.
Antonia, G., Annaluce, C. & Roberta, M.(2010). Distribution and abundance of fish larvae in the northern Ionian Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Helgol Mar Res, 65(3):381–398. DOI: 10.1007/s10152-010-0231-2.
Autumn, O. & Scott N. (2008). Increasing nutrient concentrations and the rise and fall of a coastal fishery; a review of data from the Nile Delta, Egypt. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 77(3):308–319. DOI:10.1016/j.ecss.2007.11.028.
Blaber, S.J.M. & T, G. B. (1980). Factors affecting the distribution of juvenile estuarine and inshore fish. J. Fish Biol. 17:143–162. DOI:10.11111/j.1095-8649.1980.tb027 49.x.
Converse, Y.K., Hawkins, C.P. & Valdez R.A. (1998). Habit at relation ships of sub adult hump back chub in the Colorado River through Grand Canyon: spatial variability and implications of flow regulation. Regulated River Research & Management, 14(3):267–284.
Dai, Z.J., Du, J.Z. & Li J.F. (2008). Runoff characteristics of the Changjiang River during 2006: Effect of extreme drought and the impounding of the Three Gorges Dam. Geophysical Research Letters, 35, 401–406, DOI: 10.10291/2008gl03345
Ditty, J.G. (1988). Seasonality and depth distribution of larval fishes in the northern Gulf of Mexico above latitude 26°N. U.S.Fish. Bull. 86: 811–823.
Doreen, M. M.(1992). Seasonality and abundance of ichthyoplankton in Great South Bay, New York. Estuaries, 15(2):230–238. DOI: 10.2307/1352697.
Drinkwater, K.F. & Frank K T. (1994). Effects of river regulation and diversion on marine fish and invertebrates. Aquatic Conservation: Freshwater and Marine. Ecosystems, 4: 135–151.DOI: 10.1002/aqc.3270040205.
Edward, D.H. & Jamie. A. L. (1984). Seasonality of occurrence, foods and food preferences of ichthyoplankton in Biscayne Bay, Florida. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 18: 403–419. DOI:10.1016/0272-7714(84)90080-5.
Garber, A.J., Duncan, T.G., Goodman, A.M., Mills, D.J. & Rohlf, J.L. (1997). Efficacy of Metformin in Type II Diabetes: Results of a Double-Blind, Placebo-controlled, Dose-Response Trial. The American Journal of Medicine, 103(6): 491–497.
Hasan, H. S., Anna, D. G., Levent, B., Recep, B., Mehmet, C., Mehmet, A. & Ahmet, E. K. (2003). Seasonal distribution of fish eggs and larvae off sinop (the southern Black Sea) in 1999–2000. Acta Oecologica, 24:275–280. DOI:10.1016/S1146-609X(03)00022-5.
Jackie K., Jim A. C., & Nelson, D. I. (1998). Linked effects of dam-released floods and water temperature on spawning of the Clanwilliam yellowfish Barbus capensis. Hydrobiologia, 384: 245–265. DOI: 10.1023/A:1003481524320.
James, P. M., Syvitski, C. J., Vörösmarty, A. J. & Kettner, P. G. (2005).Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global Ocean. Science, 308: 376–380. DOI: 10.1126/science.1109454.
Jennifer, A. L., Janet, T. D. A. & Kathryn, L. M. (2005). Ichthyoplankton abundance, distribution, and assemblage structure in the Gulf of Alaska during September 2000 and 2001. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 64:775–785. DOI:10.1016/j.ecss.2005.05.006.
Jiang, M., Shen, X.Q. & Chen L.F. (2006). Studies on species of fish eggs and larvae and distribution in changjiang estuary and vicinity waters. ACTA Oceanologica Sinica, 28(2):171–174 (in Chinese)
Kimmerer, W.J. (2002). Physical, biological, and management responses to variable freshwater flow into the San Francisco estuary. Estuaries, 25,(6B):1275–1290. DOI: 10.1007/BF02692224
Liu, S.D. & Xian, W.W., 2009. Temporal and spatial patterns of the ichthyoplankton community in the Yangtze Estuary and its adjacent waters. Biodiversity Science, 17(2): 151–159. (in Chinese)
Liu, R.Y. & Luo, B.Z. (1992). Impacts of the three gorges project on the ecology and environment of the changjiang river estuary and adjacent waters. Studia marina sinica, 33: 1–13. (in Chinese)
Lourdes, V.Y. (2000). Seasonal variation of ichthyoplankton in a western Caribbean bay system. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 58: 379–392. DOI:10.1023/A:1007695717652
Nelson, J.S. (1994). Fishes of the world. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Naimie, C.E., Blain, C.A. & Lynch, D.R. (2001). Seasonal mean circulation in the Yellow Sea, a model-generated climatology. Continental Shelf Research, 21, 667–695. DOI:10.1016/S0278-4343(00)00102-3
Ning, X.R., Shi, J.X., Cai, Y.M. & Liu, C.G. (2004). Biological productivity front in the Changjiang Estuary and the Hangzhou Bay and its ecological effects. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 26(6), 96–106 (in Chinese)
Pombo, L., Elliott, M. & Rebelo J. E. (2002). Changes in the fish faunal of the Ria de Aveiro estuarine lagoon (Portugal) during the twentieth century. Journal of Fish Biology, 61:167–181. DOI: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.2002.tb01769.x.
ai]Richard, A.V., Timothy, L. H., Carole, C. M., Ted, M. & William, C. L. (2001). Effects of a test flood on fishes of the Colorado River in Grand Canyon, Arizona. Ecological Applications, 11(3):686–700. DOI:10.1890/1051-0761(2001)011.
Rogério, N. C., Samara, H.S., David, R.T. & Evoy Z.F.(2010). Distribution and abundance of fish eggs and larvae in three tributaries of the Upper Uruguay River (Brazil). Environ Biol Fish. 1–11. DOI:10.1007/s10641-010-9759-x
Ruple, D.L. (1984). Occurrence of larval fishes in the surf zone of a northern Gulf of Mexico barrier island. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci, 18:191–208. DOI: 10.1016/0272-7714(84)90106-9.
Su, J.L. (1998). Circulation dynamics of the China Seas: north of 181N. In: Robinson, A.R., Brink, K. (Eds.), The Sea, The Global Coastal Ocean: Regional Studies and Syntheses, Vol. 11. Wiley, New York, pp. 483–506.
Tang, D.Q., Yan, D., Jane, S., Gary, M. & Julia, S. (2005). Sea surface temperature and its variability in the Indonesian region. Oceanography, 18(4):50–61.
Uncles, R.J., Bloomer, N. J., Frickers, P. E. Griffiths, M. L., Harris, C., Howland R.J.M., Morris, A.W., Plummer, D.H. & Tappin, A.D. (2000). Seasonal variability of salinity, temperature, turbidity and suspended chlorophyll in the Tweed Estuary. The Science of the total environment, 251–52:115–124.
Wan, R.J., Zhou, F., Shan, X.J. & Sun S. (2010). Impacts of variability of habitat factors on species composition of ichthyoplankton and distribution of fish spawning ground in the Changjiang River estuary and its adjacent waters. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30:155–165. DOI: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2010.04.006
Wang, B.D., Zhan, R. & Zang, J.Y.(2002). Distributions and transportation of nutrients in Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent sea areas. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 24(1):53–58 (in Chinese)
Wang, M., Zhang, L.Z. & Gui Z.S. (2011). Spatial and Temporal Transport of Organic Carbon in Changjiang Mainstream and Influence of Three Gorges Project. Periodical of ocean university of China. 41(1/2):117–124 (in Chinese)
Whitehead, P.J.P., Nelson G.J. & Wongratana, T. (1988). FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 7. Clupeoid fishes of the world (Suborder Clupeoidei). Part 2 -Engraulididae. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(7/2):305–579.
Whiting P.J. (2002). Stream flow necessary for environmental maintenance. Anuual review of Earth And Planetary Sciences, 30:181–206. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.earth.30.083001.161748.
William F.H.J. & Alexander. J.C. (1990). Temporal distribution of ichthyoplankton near Beaufort Inlet, North Carolina. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 68:157–168. DOI:10.3354/meps068157.
Yves, D.E.L. (1990). Distribution and Abundance of Ichthyoplankton in the Manicouagan River Estuary, a Tributary of the Lower St. Lawrence Estuary. Estuaries, 13(1):43–50.
Zar, J.H. (1996). Biostatistical Analysis. Englewood Cliffs. London: Prentice-Hall International, Inc.
Zhou, M.J., Shen, Z.L. & Yu, R.C. (2008). Responses of a coastal phytoplankton community to increased nutrient input from the Changjiang (Yangtze) River. Continental Shelf Research, 28: 1483–1489.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, M., Shen, XQ., Li, L. et al. Annual variability of ichthyoplankton in the Yangtze River estuary of China from August 2002 to 2009. Ocean and Hydro 42, 59–69 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13545-013-0060-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13545-013-0060-4