Abstract
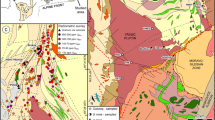
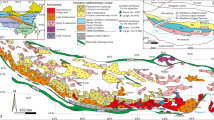
The Channagiri Mafic-Ultramafic Complex occupies lowermost section of the Neoarchaean Shimoga supracrustal group in the Western Dharwar Craton. It is a segmented body occupying the interdomal troughs of granitoids. The magnetite deposits occur in the northeastern portion; typically occupying the interface zone between gabbro and anorthositic. Mineralogically, the deposits are simple with abundant magnetite and ilmenite. Hogbomite is a consistent minor mineral. Magnetites are typically vanadiferous (0.7–1.25% V2O5). Ilmenite consistently analyses more MgO and MnO than coexisting magnetite. Chlorite, almost the only silicate present; lies in the range of ripidolite, corundophilite and sheridanite. The chromiferous suit occupying eastern side of Hanumalapur block (HPB) contains Fe-Cr-oxide analysing 37.8–11.9% Cr2O3 and 40.5–80% FeOt. In these too, chlorite, typically chromiferous (0.6–1.2% Cr2O3), is the most dominant silicate mineral. Geochemistry of V-Ti-magnetite is dominated by Fe, Ti and V with Al, Si, Mg and Mn contributing most of the remaining. Cr, Ni, Zn, Co, Cu, Ga and Sc dominate trace element geochemistry. The Cr-magnetite is high in Cr2O3 and PGE. Two separate cycles of mafic magmatism are distinguished in the CMUC. The first phase of first cycle, viz., melagabbro-gabbro, emplaced in the southeastern portion, is devoid of magnetite deposits. The second phase, an evolved ferrogabbroic magma emplaced in differentiated pulses, occupying northeastern portion of the complex, consists of melagabbro→gabbro-anorthosite→V-Ti magnetite→ferrogabbro sequence. Increase in oxygen fugacity facilitated deposition of V-Ti magnetite from ferrogabbroic magma pulse emplaced in late stages. The second cycle of chromiferous PGE mineralized suite comprises fine-grained ultramafite→alternation of pyroxinite-picrite→Crmagnetite sequence formed from fractionation of ferropicritic magma. HPB also includes >65m thick sill-like dioritic phase at the base of the ferriferous suit and a sinuous band of coarse-grained ultramafite enclosed within the chromiferous suit; both unrelated to the two mafic magmatic cycles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smeeth W.F and Sampath Iyengar P., Mineral resources of Mysore, Bull Mysore. Geol. Dept. 7, 1916.
Vasudev V.N and Ranganathan N., Vanadium and sulphide bearing titaniferous magnetite bodies in Western Dharwar Craton, In Geokarnataka: Ravindra B.M and Ranganathan N., (Eds) Karnataka Asst. Geologist Association, Bangalore, 1994, 168–181
IBM, Indian Minerals Yearbook 2011, Part II, 50th Ed., Vanadium, 2012, 77-1–5, State review. 11–14, 1–16
Dry R.J., Bates C.P and Price D.P., HIsmelt-the future in direct iron making, Proc 58th Iron making Conference, Chicago, 21–24 March, 1999, 361 p
Forge Resources: Qtly Rep. for the period 1 July–30 Sept 2012, Bolla Bolla V-Ti-magnetite project aided at producing (1) pig iron, (2) ferrovanadium and (3) titanium slag.
Pilote J., HIsmelt, Adapted technology for Ti/V magnetite: Non-blast furnace forum in Panzhihua City, Nov 2010.
Pilote J., Future of HIsmelt In India: Appropriate technology for the available resource of the country, 2010.
Ziguo H., Hongcai F., Lian L. and Turner S., Comprehensive utilization of vanadium-titanium magnetite deposits in China has come to the new level, Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 87, 286–287
Slater H.K., Report on the geological survey of portions of Tarikere, Channagiri and Shimoga taluks during the field season 1904–05, Rec. Mysore Geol. Dept., 1905, 6, 5–27
Slater H.K., Report on survey work in Holalkere, Davangere and Channagiri taluks, Mysore Geol. Dept., Rec., 1912, 12, 1–44
Jayaram B., Note on revision of survey in parts of Kadur, Shimoga and Channagiri taluks., Rec. Mysore. Geol. Dept., 1915, 14, 16–107
Channappa B.G. and Subramanya M., Vanadium bearing titaniferous magnetite ores of Ubrani area, Shimoga district, Dept of Mines and Geology, Govt. of Karnataka, Geological studies 1973, 62, 11
Chayapathi N., Geology and ore reserves of Vanidiferous magnetite deposits in Channagiri taluk, Shimoga district, Karnataka, Proc. Symp. Geol. etc. of Ferrous and Ferro-alloy minerals, Bangalore, 1976, 55–60
Chayapathi N., Investigations for Vanadiferrous titanomagnetite and associated copper in the Masanikere, Taverekere and Magyathahalli areas, Channagire taluk, Shimoga district, Karnataka, Geol. Surv. India, Progress Report for the field season, 1984, 74–79
Ramiengar A.S and Chayapathi N., Vanadiferous magnetite deposit near Masanikere, Channagiri taluk, Shimoga district, Karnataka, Indian Minerals, 1977, 31, 1–5
Ramiengar A.S., Chayapathi N., Raghunandan K.R and Rao M.S., Mineralogy and geochemistry of the vanadiferous titanomagnetite deposit and associated copper mineralization in gabbro-anorthosite near Masanikere, Shimoga district, Karnataka, India, In: Archaean Geochemistry: Proceedings of the symposium on Archaean geochemistry, Hyderabad, 1978, 395–406
Channappa B.G. and Subramanya M., Vanadium bearing titaniferous magnetite ore of Taverekere and Gourapur areas, Channagiri taluk, Shimoga district, Dept. of Mines and Geology, Govt. of Karnataka, Geological studies No. 129, 1979, 9p
Jayaraj K.R., V-Ti-Fe deposits of Ubrani, Tavarekere, Masanikere, Devaranarsipur (Shimoga district) and Mulemane (North Kanara district) areas, Karnataka, Ph.D thesis submitted to Karnatak University, Dharwad, Karnataka, India (Unpublished), 1992, 103p
Jayaraj K.R., Khanadali S.D., Devaraju T.C and Spiering B., A study of Hogbomite in the V-Ti-Fe deposits of Karnataka, Jour. Geol. Soc. India, 1995, 45, 57–64
Jayaraj K.R., Khanadali S.D., Devaraju T.C and Spiering B., A study of Chromiferous Magnetite and Titanomagmetite in the V-Ti Magnetite deposits of Magyatahalli, Shimoga district, Karnataka, Indian Mineralogist, 1996, 30, 59–66
Alapieti T.T., Halkoaho T.A.A., Devaraju T.C., Chromite-hosted PGE mineralization in the Channagiri area, Karnataka State, India, VIIth International Platinum Symposium, 1994, 1–4 Aug 1994, Moscow (Abstract), 3–4
Devaraju T.C., Alapieti T.T., Halkoaho T.A.A., Jayaraj K.R., Khanadali S.D., Evidence of PGE mineralization in the Channagiri mafic complex, Shimoga district, Karnataka, Jour. Geol. Soc. India, 1994, 43, 317–318
Alapieti T.T., Devaraju T.C and Kaukonen R.J., PGE mineralization in the late Archaean iron-rich maficultramafic Hanumalapur Complex, Karnataka, India, Mineral & Petrol., 2008, 92, 99–128
Devaraju T.C., Investigations of Archaean layered mafic-ultramafic complexes of Shimoga Schist belt of Karnataka with special reference to evidence of Platinum mineralization. Report (unpublished) submitted to Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, 2000, 66p
Devaraju T.C., Alapieti T.T., Kaukonen R.J and Sudhakara T.C., Petrological and PGE mineralization study of the Channagiri mafic-ultramafic complex, Shimoga Supracrustal belt, Karnataka, Jour. Geol. Soc. India, 2007, 70, 535–556
Chadwick B., Vasudev V.N. & Jayaram S., Stratigraphy and structure of late Archaean Dharwar volcanic and sedimentary rocks and their basement in a part of Shimoga basin east of Bhadravathi, Karnataka, Jour. Geol. Soc. India, 1988, 32, 1–19
Devaraju T.C., Alapieti T.T., Kaukonen R.J., Geochemistry of ultramafic lenses in the granitoids of the southeastern flanks of Shimoga supracrustal belt (Karnataka) with a note on the distribution of platinum-group elements and minerals. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, 2004, 63, 371–386
Taylor P.N., Chadwick B., Moorbath S., Ramakrishnan M and Vishwanatha M.N., Petrology, chemistry and isotopic ages of Peninsular gneiss, Dharwar acid volcanic rocks and the Chitradurga granite with special reference to the late Archaean evolution of the Karnataka craton, Southern India, Precamb. Res., 1984, 23, 349–375
Wager L.R and Brown G.M., Layered Igneous rocks, Oliver and Boyd, 1968, 588p
Stevens R.E., Compositions of some chromites of the western hemisphere, Am. Mineral., 1944, 29, 1–34
Roach T.A., Roeder P.L., and Hulbert L.J., Composition of chromite in the upper chromitite, Muskox layered intrusion, Northwest territories, Can. Mineralogist, 1998, 36, 117–135
Yong Z, Jian-xing L, Gonf-Jin C, Zhang-Gen L, Mansheng C, Xian-xin X, Experiment study on sintering process optimization of high chromium vanadiumtitanium magnetite (Abstract-p363) In: Characterization of minerals, metals and materials, 2013, Wiley
Himmilberg G.R and Ford A.B., Iron-Titanium oxides of the Dufek intrusion, Antartica, Am. Mineral, 1977, 62, 623–633
Mathison C.I., Magnetites and ilmenites in the Somerset Dam layered basic intrusion, Southeastern Queensland, Lithos, 1975, 8, 93–111
Neumann E.R., The distribution of Mn2+ and Fe 2+ between ilmenites and magnetites in igneous rocks, Am. Jour. Sci., 1974, 274, 1074–1088
Friedman G.M., Study of Hogbomite. Am. Mineral, 1952, 37, 600–608
Zakrzewski M.A., Hogbomite from the Fe-Ti deposit of Liganga (Tanzania). Neues Jahrb Mineral Monatsh, 1977, H8, 373–380
Coolen J.J.M.M.M., Hogbomite and aluminium spinel from some metamorphic rocks and Fe-Ti ores, Neues Jahrbuch fur Mineralogie Monatshifte, 1981, 373–384
Hey M.H., A new review of the chlorites, Mineral Mag., 1954, p277
Barnes S.J., Boyd R., Korneliussen, A., Nillson L.P., Opten M., Pedersen R.B., Robins B., The use of mantle normalization and metal ratios in discriminating between the effects of partial melting, crystal fractionation and sulphide segregation on platinumgroup elements, gold, nickel and copper: examples from Norway. In: Pichard, H.M., Potts P.J., Bowels J.F.W., Cabri S.J. (Eds), Geo-platinum, Amsterdam, 1987, 113–143
Jensen L.S., A new cation plot for classifying subalkaline volcanic rocks, Ontario Dept. Mines Misc, paper No. 66, 1976, 22p
Viljoen, M.J., Viljoen R.P., Pearton T.N., Nature and distribution of Archaean komatiite volcanics in South Africa, In: N.T. Arndt and E.G. Nisbet (Eds.) Komatiites, Allen and Unwin, London, 1982, 53–79
Viljoen, M.J., Viljoen R.P., Evidence for the existence of mobile extrusive peridotite magma from the Komati formation of the Onverwacht Group, Geol. Soc. S. Africa, Sec. pub. 2, Upper Mantle Project, 1969, 87–112
Pearce J.A., Basalt geochemistry used to investigate past tectonic environments, Tectonophysics, 1975, 25, 41–67
Hall A.L., The Bushweld Igneous complex of the central Transvaal, S. African Geol. Sur. Memoir, 1932, 28, Pretoria
Bateman A.M., The formation of late magmatic oxide ores, Eco. Geol., 1951, 46, 404–426
Osborn E.F., The role of oxygen pressure in the crystallization and differentiation of basaltic magma, Am. Jour. Sci., 1959, 257, 609–647
Buddington A.F. and Lindsley D.H., Iron-titanium oxide minerals and their synthetic equivalents, Jour. Petrol, 1964, 5, 310–357
Lister G.F., The composition and origin of selected iron-titanium deposits, Econ. Geol., 1966, 61, 275–310
Collins L.G., Regional crystallization and the formation of magnetite concentration, Dover magnetite district, New Jersey, Econ. Geol., 1969, 64, 17–33
Cawthorn R.G. & Mc Carthy T.S., Bottom crystallization and diffusion control in layered complexes: Evidence from Cr distribution in magnetite from the Bushveld Complex, Geol. Soc. S. Africa. Trans., 1981, 84, 41–50
Cawthorn R.G., Layered Intrusions, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1996, 531p
Duchesne J.C., Fe-Ti deposits in Rogaland anorthosites (South Norway): Geochemical Characteristics and problems of interpretation, Mineralium Deposita, 1999, 34, 182–194
Zhou M.F., Chen W.T., Wang C.Y., Prevec S.A., Liu P.P and Howarth G.H., Two stages of immiscible liquid separation in the formation od Panzhihua-type Fe-Ti-V oxide deposits, SW China, Geoscience Frontiers, 4, 2013, 481–502
Zhou M.F., Robinson P.T., Lesher C.M., Keays R.R., Zhang C.J. and Malpas J., Geochemistry, petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Panzhihua gabbroic layered intrusion and associated Fe-Ti-V oxide deposits, Sichuan Province, SW China, Jour. Petrol., 2005, 46, 2253
Pang K.N., Zhou M.F., Lindsley D., Zhao D and Malpas J., Origin of Fe-Ti oxide ores in the mafic intrusions: Evidence from the Panzhihua intrusion, SW China, Jour. Petrol., 2008, 49, 295–313
Zhang M., Niu Y., Hu P., Volatiles in the mantle lithosphere: modes of occurrence and chemical compositions, In: Anderson J.E and Coates R.W (Eds.) The Lithosphere: Geochemistry, geology and geophysics, Nova Science Publishers Inc, New York, 2009, 171–212
Hou T., Zheng Z., Encarnacion J and Santosh M., Petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Taihe gabbroic intrusion associated with Fe-Ti oxide ores in the Panxi district, Emeishan large igneous province, Ore Geol. Review, 2012, 49, 109–127
Dong H., Xing C and Wang C.Y., Textures and mineral compositions of the Xinjie layered intrusions, SW China: Implications for the origin of magnetite fractionation process of Fe-Ti-rich basaltic magmas, Frontiers, 2013, 4, 503–515
Gross G.A., Grower C.F and Lefebure D.V., Magmatic Ti-Fe ± V oxide deposits, British Columbia Geol. Surv. Geol. Field work Mo44, 1997, 241–1, 241–3
Thy P., Jakobsen N.N. and Wilson J.R., Fine-scale graded layers in the Fongen-Hyllingen gabbroic complex, Norway, Can. Mineral., 1988, 26, 235–243
Dunn J.A and Dey A.K., Vanadium bearing titaniferous iron ores in Singhbhum and Mayurbhanj, India. Trans. Min. Geol. Inst. India, 1937, 31, p30
Kolker A, Mineralogy and geochemistry of Fe-Ti oxide and apatite (nelsonite) deposits and evaluation of liquid immiscibility hypothesis, Econ. Geol., 1982, 77, 1146–1158
Philpotts A.R., Origin of certain iron-titanium oxide and apatite rocks, Econ. Geol., 1967, 62, 303–315
Reynolds I.M., The nature and origin of titaniferous magnetite-rich layers on the upper zone of the Bushveld complex: A review and synthesis, Econ. Geol., 1985, 80, 1089–1108
Hill R and Roeder P., The crystallization of spinel from basaltic liquids as a function of oxygen fugacity, Jour. Geol., 1974, 82, 709–729
Irvine T.N., Crystallization sequence in the Musox intrusion and other layered intrusions — II. Origin of chromitite layers and similar deposits of other magmatic ores. Geochem. Cosmochem. Acta, 1975, 39, 991–1020
Molyneux T.G., The geology of the area in the vicinity of Magnet Heights, east Transvaal, with special reference to the magnetic iron ore, Mineral. Mag., 1972, 38, 863–871
Muan A., Osborn E.F., Phase equlibria at liquidus temperatures in the system MgO-FeO-Fe2O3-SiO2, Am. Ceramic Soc. Jour., 1956, 39, 121–140
Roeder P.L and Osborn E.F., Experimental data for the system MgO-FeO-Fe2O3-CaAl2Si2O2 and their petrologic implications, Am. J. Sci., 1966, 264, 428–480
Mei Y., Zhou M.F., Wang C.Y., Pang K.N., Origin of giant magmatic Fe-Ti-V oxide deposits hosted in layered intrusions in the Pan-Xi area, Sichuan Province, SW China, Mineral deposits research: Meeting the Global Challenge, 2005, 458–461
Zhong H., Zhou X.H., Zhou M.F., Sun M and Liu B.G., Platinum group element geochemistry of the Hongge Fe-V-Ti deposit in the Pan Xi area, southwestern China, Mineral. Deposita, 2002, 37, 226–239
Le Bass M.J., IUGS reclassification of the high-Mg and picritic volcanic rocks, Jour. Petrol., 2000, 41, 1467–1470
Le Maitre R.W., Igneous rocks: A classification and glossary of terms, 2nd Ed. Cambridge University Press, 2002, 236p
Irvine T.N and Barager W.R.A., A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks, Canadian J. Earth Sci., 1971, 8, 523–548
Xing C.M., Wang C.Y., Zhang M., Volatile and C-H-O isotope composition of a giant Fe-Ti-V oxide deposit in the Panxi region and their implications for source of volatiles and the origin of Fe-Ti oxide ores, Science China Earth, China, 2012, http//dz.dn.org/10.10007/s11430-012-4468-2
Zhang M, Niu Y, Su. S., Chemical and stable isotopic constraints on the nature and origin of volatiles in the sub-continental lithospheric mantle beneath China, Lithos, 2007, 96, 55–56
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Devaraju, T.C., Jayaraj, K.R., Sudhakara, T.L. et al. Mineralogy, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the V-Ti-bearing and chromiferous magnetite deposits hosted by Neoarchaean Channagiri Mafic-Ultramafic Complex, Western Dharwar Craton, India: Implications for emplacement in differentiated pulses. cent.eur.j.geo. 6, 518–548 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13533-012-0193-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13533-012-0193-9