Abstract
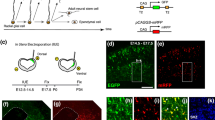
There are three controversial and undetermined models of neurogenesis and gliogenesis from neuroepithelial cells in the early neural tube; the first in which neurons and glia were proposed to originate from a single homogenous population, the second from two separate pools of committed glial and neuronal progenitors, or, lastly, from transit radial glial (RG). Issues concerning embryonic neural lineage development in primates are not well understood due to restrictions imposed by ethics and material sources. In this study, early neural lineage development was investigated in vitro with rhesus monkey embryonic stem cells (rESC) by means of immunofluorescence with lineage specific markers. It was revealed that neural differentiation likely progresses in a sequential lineage restriction pathway from neuroepithelial stem/progenitor cells to neurons and glia via RG and intermediate precursors: neuronal precursors and glial progenitors. In conclusion, our results suggest that the early neural lineage development of rESC in vitro supported the model in which neuroepithelial cells develop into RG capable of generating both neurons and glia. This work should facilitate understanding of the mechanism of development of the nervous system in primates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Copp A.J., Greene N.D., Murdoch J.N., The genetic basis of mammalian neurulation, Nat. Rev. Genet., 2003, 4, 784–793
Sauvageot C.M., Stiles C.D., Molecular mechanisms controlling cortical gliogenesis, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 2002, 12, 244–249
His W., Die Neuroblasten und deren Entstehung im embryonal Mark, Leipzig, DE: S. Hirzel, 1889
Delaunay D., Heydon K., Cumano A., Schwab M.H., Thomas J.L., Suter U., et al., Early neuronal and glial fate restriction of embryonic neural stem cells, J. Neurosci., 2008, 28, 2551–2562
Schaper A., The earliest differentiation in the central nervous system of vertebrates, Science, 1897, 430–431
Sauer F.C., Mitosis in the neural tube, J. Comp. Neurol. 1935, 377–405
Fujita H., Fujita S., [Electron microscopic studies on the histogenesis of nerve cells and neuroglia in domestic flow. II. On neurogia], Kaibogaku Zasshi, 1963, 38, 95–108 (in Japanese)
Williams B.P., Read J., Price J., The generation of neurons and oligodendrocytes from a common precursor cell, Neuron, 1991, 7, 685–693
Udolph G., Prokop A., Bossing T., Technau G.M., A common precursor for glia and neurons in the embryonic CNS of Drosophila gives rise to segment-specific lineage variants, Development, 1993, 118, 765–775
Doe C.Q., Fuerstenberg S., Peng C.Y., Neural stem cells: from fly to vertebrates, J. Neurobiol., 1998, 36, 111–127
Bertrand N., Castro D.S., Guillemot F., Proneural genes and the specification of neural cell types, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2002, 3, 517–530
Fan G., Martinowich K., Chin M.H., He F., Fouse S.D., Hutnick L., et al., DNA methylation controls the timing of astrogliogenesis through regulation of JAK-STAT signaling, Development, 2005, 132, 3345–3356
Malatesta P., Hartfuss E., Gotz M., Isolation of radial glial cells by fluorescent-activated cell sorting reveals a neuronal lineage, Development, 2000, 127, 5253–5263
Alvarez-Buylla A., Garcia-Verdugo J.M., Tramontin A.D., A unified hypothesis on the lineage of neural stem cells, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2001, 2, 287–293
Noctor S.C., Flint A.C., Weissman T.A., Dammerman R.S., Kriegstein A.R., Neurons derived from radial glial cells establish radial units in neocortex, Nature, 2001, 409, 714–720
Rakic P., Developmental and evolutionary adaptations of cortical radial glia, Cereb. Cortex. 2003, 13, 541–549
Evans M.J., Kaufman M.H., Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos, Nature, 1981, 292, 154–156
Thomson J.A., Kalishman J., Golos T.G., Durning M., Harris C.P., Becker R.A., et al., Isolation of a primate embryonic stem cell line, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1995, 92, 7844–7848
Thomson J.A., Itskovitz-Eldor J., Shapiro S.S., Waknitz M.A., Swiergiel J.J., Marshall V.S., et al., Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts, Science, 1998, 282, 1145–1147
Reubinoff B.E., Itsykson P., Turetsky T., Pera M.F., Reinhartz E., Itzik A., et al., Neural progenitors from human embryonic stem cells, Nat. Biotechnol., 2001, 19, 1134–1140
Liour S.S., Yu R.K., Differentiation of radial glia-like cells from embryonic stem cells, Glia, 2003, 42, 109–117
Liour S.S., Kraemer S.A., Dinkins M.B., Su C.Y., Yanagisawa M., Yu R.K., Further characterization of embryonic stem cell-derived radial glial cells, Glia, 2006, 53, 43–56
Gotz M., Barde Y.A., Radial glial cells defined and major intermediates between embryonic stem cells and CNS neurons, Neuron, 2005, 46, 369–372
Bonfanti L., Peretto P., Radial glial origin of the adult neural stem cells in the subventricular zone, Prog. Neurobiol., 2007, 83, 24–36
Mujtaba T., Piper D.R., Kalyani A., Groves A.K., Lucero M.T., Rao M.S., Lineage-restricted neural precursors can be isolated from both the mouse neural tube and cultured ES cells, Dev. Biol., 1999, 214, 113–127
Nistor G.I., Totoiu M.O., Haque N., Carpenter M.K., Keirstead H.S., Human embryonic stem cells differentiate into oligodendrocytes in high purity and myelinate after spinal cord transplantation, Glia, 2005, 49, 385–396
Shin S., Dalton S., Stice S.L., Human motor neuron differentiation from human embryonic stem cells, Stem Cells Dev., 2005, 14, 266–269
Takagi Y., Takahashi J., Saiki H., Morizane A., Hayashi T., Kishi Y., Dopaminergic neurons generated from monkey embryonic stem cells function in a Parkinson primate model, J. Clin. Invest., 2005, 102–109
Yue F., Cui L., Johkura K., Ogiwara N., Sasaki K., Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons from primate embryonic stem cells by coculture with sertoli cells, Stem Cells, 2006, 24, 1695–1706
Mizuseki K., Sakamoto T., Watanabe K., Muguruma K., Ikeya M., Nishiyama A., Generation of neural crest-derived peripheral neurons and floor plate cells from mouse and primate embryonic stem cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2003, 100, 5828–5833
Watanabe K., Kamiya D., Nishiyama A., Katayama T., Nozaki S., Kawasaki H., et al., Directed differentiation of telencephalic precursors from embryonic stem cells, Nat. Neurosci., 2005, 8, 288–296
Lazzari G., Colleoni S., Giannelli S.G., Brunetti D., Colombo E., Lagutina I., et al, Direct derivation of neural rosettes from cloned bovine blastocysts: a model of early neurulation events and neural crest specification in vitro, Stem Cells, 2006, 24, 2514–2521
Cazillis M., Rasika S., Mani S., Gressens P., Lelievre V., In vitro induction of neural differentiation of embryonic stem (ES) cells closely mimics molecular mechanisms of embryonic brain development, Pediatr. Res., 2006, 59, 48R–53R
Wolf D.P., Kuo H.C., Pau K.Y., Lester L., Progress with nonhuman primate embryonic stem cells, Biol. Reprod., 2004, 71, 1766–1771
Kuo H.C., Pau K.Y., Yeoman R.R., Mitalipov S.M., Okano H., Wolf D.P., Differentiation of monkey embryonic stem cells into neural lineages, Biol. Reprod., 2003, 68, 1727–1735
Levitt P., Cooper M.L., Rakic P., Coexistence of neuronal and glial precursor cells in the cerebral ventricular zone of the fetal monkey: an ultrastructural immunoperoxidase analysis, J. Neurosci., 1981, 1, 27–39
Levitt P., Cooper M.L., Rakic P., Early divergence and changing proportions of neuronal and glial precursor cells in the primate cerebral ventricular zone, Dev. Biol., 1983, 96, 472–484
Mayer-Proschel M., Kalyani A.J., Mujtaba T., Rao M.S., Isolation of lineage-restricted neuronal precursors from multipotent neuroepithelial stem cells, Neuron, 1997, 19, 773–785
Nat R., Nilbratt M., Narkilahti S., Winblad B., Hovatta O., Nordberg A., Neurogenic neuroepithelial and radial glial cells generated from six human embryonic stem cell lines in serum-free suspension and adherent cultures, Glia, 2007, 55, 385–399
Bystron I., Rakic P., Molnar Z., Blakemore C., The first neurons of the human cerebral cortex, Nat. Neurosci., 2006, 9, 880–886
Anthony T.E., Klein C., Fishell G., Heintz N., Radial glia serve as neuronal progenitors in all regions of the central nervous system, Neuron, 2004, 41, 881–890
Mo Z., Moore A.R., Filipovic R., Ogawa Y., Kazuhiro I., Antic S.D., et al., Human cortical neurons originate from radial glia and neuronrestricted progenitors, J. Neurosci., 2007, 27, 4132–4145
Hansen D.V., Lui J.H., Parker P.R., Kriegstein A.R., Neurogenic radial glia in the outer subventricular zone of human neocortex, Nature, 2010, 464, 554–561
Reinchisi G., Limaye P.V., Singh M.B., Antic S.D., Zecevic N., Neurogenic potential of hESC-derived human radial glia is amplified by human fetal cells, Stem Cell Res., 2013, 11, 587–600
Pinto L., Gotz M., Radial glial cell heterogeneity—the source of diverse progeny in the CNS, Prog. Neurobiol., 2007, 83, 2–23
Li H., Babiarz J., Woodbury J., Kane-Goldsmith N., Grumet M., Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of CNS radial glial cells and their transition to restricted precursors, Dev. Biol., 2004, 271, 225–238
Howard B.M., Mo Z., Filipovic R., Moore A.R., Antic S.D., Zecevic N., Radial glia cells in the developing human brain, Neuroscientist, 2008, 14, 459–473
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Wei, Q., Zhang, J. et al. Neural lineage development in the rhesus monkey with embryonic stem cells. Translat.Neurosci. 4, 378–384 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-013-0135-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-013-0135-0