Abstract
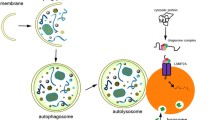
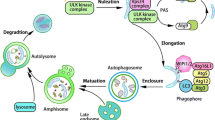
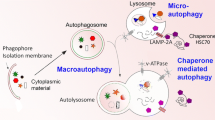
A growing body of research deals with the relationship between the endosomal and autophagic/lysosomal pathways during developmental stages of the central nervous system. This includes their possible influence regarding the onset and progression of specific neurodegenerative disorders. In this review we focus our attention on major alterations affecting two organelles: autophagosomes and multivesicular bodies, both of which are located at the intersection point of their respective pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooney J.R., Hurlburt J.L., Selig D.K., Harris K.M., Fiala J.C., Endosomal compartments serve multiple hippocampal dentritic spines from a widespread rather than a local store of recycling membrane, J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2215–2224
Roizin L., Nishikawa K., Koizumi J., Keoseian S., The fine structure of the multivesicular body and their relationship to the ultracellular constituents of the central nervous system, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 1967, 26, 223–249
Yamamoto T., On the thickness of the unit membrane, J. Cell Biol., 1963, 382, 217–226
Castel M. N., Woulfe J., Wang X., Laduron P. M., Beaudet A., Light and electron microscopic localization of retrogradely transported neurotensin in rat nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons, Neuroscience, 1992, 50, 269–282
Delcroix J. D., Valletta J. S., Wu C., Hunt S. J., Kowal A. S., Mobley W.C., NGF signaling in sensory neurons: evidence that early endosomes carry NGF retrograde signals, Neuron, 2003, 39, 69–84
Kappeller K., Mayor D., An electron microscopic study of the early changes distal to a constriction in sympathetic nerves, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci., 1969, 172, 53–63
Christopher S. Von Bartheld, Amy L. Altick, Multivesicular bodies in neurons: Distribution, protein content, and trafficking function, Prog. Neurobiol., 2011, 93, 313–340
Murphy R. F., Maturation models for endosome and lysosome biogenesis, Trends Cell Biol., 1991, 1, 77–82
van Deurs B., Holm P. K., Kayser L., Sandvig K., Hansen S. H., Multivesicular bodies in HEp-2 cells are maturing endosomes, Eur. J. Cell Biol., 1993, 61, 208–224
Gruenberg J., Griffiths G., Howell K. E., Caracterization of the early endosome and putative endocytic carrier vesicles in vivo and with an assay of vesicle fusion in vitro, J. Cell Biol., 1989, 108, 1301–1316
Mullock, B. M., Bright N. A., Fearon C. W., Gray S. R., Luzio J. P., Fusion of lysosomes with late endosomes produces a hybrid organelle of intermediate density and is NSF dependent, J. Cell Biol., 1998, 140, 591–601
Vonderheit A., Helenius, A., Rab7 associates with early endosomes to mediate sorting and transport of Semliki forest virus to late endosomes, PLoS Biol., 2005, 3, e233
Dunn W.A.Jr., Studies on the mechanisms of autophagy: maturation of the autophagic vacuole, J. Cell Biol., 1990, 110, 1935–1945
Kilionsky D.J., Emr S.D., Autophagy as a regulated pathway of cellular degradation, Science, 2000, 290, 1717–1721
Mizushima N., Levine B., Cuervo A.M., Klionsky D.J., Autophagy fights desease through cellular self-digestion, Nature, 2008, 451, 1069–1075
Yang Z., Klionsky D.J., Eaten alive: a history of macroautophagy, Nat. Cell Biol., 2010, 12, 814–822
Maiuri M.C., Zalckvar E., Kimchi A., Kroemer G., Selfeating and selfkilling: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2007, 8, 741–752
Xie Z., Klionsky D.J., Autophagosome formation: core machinery and adaptations, Nat. Cell Biol., 2007, 9, 1102–1109
He C., Klionsky D.J., Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy, Annu. Rev. Genet., 2009, 43, 67–93
Butowt R., von Bartheld C.S., Sorting of internalized neurotrophins into an endocytic transcytosis pathway via the Golgi system: ultrastructural analysis in retinal ganglion cells, J. Neurosci., 2001, 21, 8915–8930
Chu-Wang I.W., Oppenheim R.W., Uptake, intra-axonal transport and fate of horseradish peroxidase in embryonic spinal neurons of the chick, J. Comp. Neurol., 1980, 193, 753–776
Rind H.B., Butowt R., von Bartheld C.S., Synaptic targeting of retrogradely transported trophic factors in motoneurons: comparison of glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor, brainderived neurotrophic factor, and cardiotrophin-1 with tetanus toxin, J. Neurosci., 2007, 25, 539–549
Vitalis T., Laine J., Simon A., Roland A., Leterrier C., Lenkei Z., The type 1 cannabinoid receptor is highly expressed in embryonic cortical projection neurons and negatively regulates neurite growth in vitro, Eur. J. Neurosci., 2008, 28, 1705–1718
Alberts P., Galli T., The cell outgrowth secretory endosome (COSE): a specialized compartment involved in neuronal morphogenesis, Biol. Cell, 2003, 95, 419–424
Alberts P., Rudge R., Irinopoulou T., Danglot L., Gauthier-Rouviere C., Galli T., Cdc42 and actin control polarized expression of TI-VAMP vesicles to neuronal growth cones and their fusion with the plasma membrane, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2006, 17, 1194–1203
Hernandez-Deviez D., Mackay-Sim A., Wilson J.M., A Role for ARF6 and ARNO in the regulation of endosomal dynamics in neurons, Traffic, 2007, 8, 1750–1764
Levine B., Klionsky D.J., Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy, Dev. Cell, 2004, 6, 463–477
Cecconi F., Bartolomeo S.D., Nardacci R., Fuoco C., Corazzari M., Giunta L., et al., A novel role for autophagyin neurodevelopment, Autophagy, 2007, 3, 506–508
Maria Fimia G., Stoykova A., Romagnoli A., Giunta L., Di Bartolomeo S., Nardacci R., et al., Ambra1 regulates autophagy and development of the nervous system, Nature, 2007, 447, 1121–1125
Nixon R. A., Yang D.S., Lee J.H., Neurodegenerative lysosomal disorders: A continuum from developmente too late age, Autophagy, 2008, 4, 590–599
Filimonenko M., Stuffers S., Raiborg C., Yamamoto A., Malerod L., Fisher E.M., et al., Functional multivesicular bodies are required for autophagic clearance of protein aggregates associated with neurodegenerative disease, J. Cell Biol., 2007, 179, 485–500
Lee J.A., Gao F.B., Roles of ESCRT in autophagy-associated neurodegeneration, Autophagy, 2008, 4, 230–232
Parkinson N., Ince P.G., Smith M.O., Highley R., Skibinski G., Andersen P.M., et al., ALS phenotypes with mutations in CHMP2B (charged multivesicular body protein 2B), Neurology, 2006, 67, 1074–1077
Rusten T.E., Filimonenco M., Rodhal L.M., Stenmark H., Simonsen A., ESCRT ing autophagic clearance of aggregating proteins, Autophagy, 2008, 4, 233–236
Skibinski G., Parkinson N.J., Brown J.M., Chakrabarti L., Lloyd S.L., Hummerich H., et al., Mutations in the endosomal ESCRTIII-complex subunit CHMP2B in frontotemporal dementia, Nat. Genet., 2005, 37, 806–808
Truant R., Atwal R.S., Desmond C., Munsie L., Tran T., Huntington’s disease: revisiting the aggregation hypothesis in polyglutamine neurodegenerative diseases, FEBS J., 2008, 275, 4252–4262
Kidd M., Alzheimer’s disease — an electron microscopical study, Brain, 1964, 87, 307–320
Paula-Barbosa M.M., Mota Cardoso R., Faria R., Cruz C., Multivesicular bodies i cortical dendrites of two patients with Alzheimer’s disease, J. Neurol. Sci., 1978, 36, 259–264
Takahashi R.H., Milner T.A., Li F., Nam E.E., Edgar M.A., Yamaguchi H., et al., Intraneuronal Alzheimer abeta42 accumulates in multivesicular bodies and is associated with synaptic pathology, Am. J. Pathol., 2002, 161, 1869–1879
Nixon R.A., Yang D.-S., Autophagy failure in Alzheimer’s diseaselocating the primary defect, Neurobiol. Dis., 2011, 43, 38–45
Winslow A.R., Chen C.W., Corrochiano S., Acevedo-Arozena A., Gordon D.E., et al., Alpha-synuclein impairs macroautophagy: implications for Parkinson’s disease, J.Cell Biol., 2010, 190, 1023–1037
Webb J.L., Ravikumar B., Atkins J., Skepper J.N., Rubinsztein D.C., Alpha-synuclein is degraded by both autophagy and the proteasome, J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278, 25009–13
Cuervo A.M., Stefanis L., Fredenburg R., Lansbury P.T., Sulzer D., Impaired degradation of mutant alpha-synuclein by chaperonemediated autophagy, Science, 2004, 305, 1292–1295
Vogiatzi T., Xilouri M., Vekrellis K., Stefanis L., Wild thype alphasynuclein is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy and macroautophagy in neuronal cells, J. Biol. Chem., 2008, 283, 23542–23556
Anglade P., Vyas S., Javoy-Agid F., Herrero M.T., Michel P.P., Marquez J., et al., Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease, Histol. Histopathol., 1997, 12, 25–31
Lee J.A., Beigneux A., Ahmad S.T., Yang S.G., Gao F.B., ESCRTIII dysfunction causes autophagosome accumulation and neurodegeneration, Curr. Biol., 2007, 17, 1561–1567
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Diana, A. Autophagosomes and multivesicular bodies in neuronal development and degeneration. Translat.Neurosci. 3, 384–387 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-012-0048-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-012-0048-3