Abstract
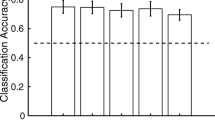
Since the successful demonstration of “brain reading” of fMRI BOLD signals using multivoxel pattern classification (MVPA) techniques, the neuroimaging community has made vigorous attempts to exploit the technique in order to identify the signature patterns of brain activities associated with different cognitive processes or mental states. In the current study, we tested whether the valence and arousal dimensions of the affective information could be used to successfully predict individual’s active affective states. Using a whole-brain MVPA approach, together with feature elimination procedures, we are able to discriminate between brain activation patterns associated with the processing of positive or negative valence and cross validate the discriminant function with an independent data set. Arousal information, on the other hand, failed to provide such discriminating power. With an independent sample, we test further whether the MVPA identified brain network could be used for inter-individual classification. Although the inter-subject classification success was only marginal, we found correlations with individual differences in affective processing. We discuss the implications of our findings for future attempts to classify patients based on their responses to affective stimuli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox D. D., Savoy R. L., Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) “brain reading”: detecting and classifying distributed patterns of fMRI activity in human visual cortex, Neuroimage, 2003, 19, 261–270
Haynes J. D., Rees G., Decoding mental states from brain activity in humans, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2006, 7, 523–534
Haxby J. V., Gobbini M. I., Furey M. L., Ishai A., Schouten J. L., Pietrini P., Distributed and overlapping and representations of faces and objects in ventral temporal cortex, Science, 2001, 293, 2425–2430
Kamitani Y., Tong F., Decoding the visual and subjective contents of the human brain, Nat. Neurosci., 2005, 8, 679–685
Shinkareva S. V., Mason R. A., Malave V. L., Wang W., Mitchell T. M., Just M. A., Using fMRI brain activation to identify cognitive states associated with perception of tools and dwellings, PLoS One, 2008, 3: e1394
Lewis-Peacock J. A., Postle B. R., Temporary activation of long-term memory supports short-term memory, J. Neurosci., 2008, 28, 8765–8771
Hampton A. N., O’Doherty J. P., Decoding the neural substrates of reward-related decision making with functional MRI, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007, 104, 1377–1382
Soon C. S., Brass M., Heinze H. J., Haynes J. D., Unconscious determinants of free decisions in the human brain, Nat. Neurosci., 2008, 11, 543–545
Fung G., Stoeckel J., SVM feature selection for classification of SPECT of Alzheimer’s disease using spatial information, Knowl. Inf. Syst., 2007, 11, 243–258
Gerardin E., Chételat G., Chupin M., Cuingnet R., Desgranges B., Kim H. S., et al., Multidimensional classification of hippocampal shape features discriminates Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment from normal aging, Neuroimage, 2009, 47, 1476–1486
Koutsouleris N., Meisenzahl E. M., Davatyikos C., Bottlender R., Frodl T., Scheuerecker J., et al., Use of neuroanatomical pattern classification to identify subjects in at-risk mental states of psychosis and predict disease transition, Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 2009, 66, 700–712
Hahn T., Marquand A. F., Ehlis A., Dresler T., Kittel-Schneider S., Jarczok T. A., et al., Integrating neurobiological markers of depression, Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 2010, 68, 361–368
Pessoa L., Padmala S., Decoding near-threshold perception of fear from distributed single-trial brain activation, Cereb. Cortex, 2007, 17, 691–701
Rolls E. T., Grabenhorst F., Franco L., Prediction of subjective affective state from brain activations, J. Neurophysiol., 2009, 101, 1294–1308
Ethofer T., De Ville D. V., Scherer K., Vuilleumier P., Decoding of emotional information in voice-sensitive cortices, Curr. Biol., 2009, 19, 1028–1033
Sitaram R., Lee S., Ruiz S., Rana M., Veit R., Birbaumer N., Real-time support vector classification and feedback of multiple emotional brain states, Neuroimage, 2010, 56, 753–765
Peelen M. V., Atkinson A. P., Vuilleumier P., Supramodel representations of perceived emotions in the human brain. J. Neurosci., 2010, 30, 10127–10134
Lang P. J., Bradley M. M., Cuthbert B. N., International affective picture system (IAPS): Affective ratings of pictures and instruction manual, Technical Report A-8, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, 2008
Alorda C., Serrano-Pedraza I., Campos-Bueno J. J., Sierra-Vazquez V., Montoya P., Low spatial frequency filtering modulates early brain processing of affective complex pictures, Neuropsychologia, 2007, 45, 3223–3233
Delplanque S., N’diaye K., Scherer K., Grandjean D., Spatial frequencies or emotional effects? A systematic measure of spatial frequencies for IAPS pictures by a discrete wavelet analysis, J. Neurosci. Methods, 2007, 165, 144–150
Kriegeskorte N., Simmons W., Bellgowan P., Baker C., Circular analysis in systems neuroscience: the dangers of double dipping, Nat. Neurosci., 2009, 12, 535–540
Vul E., Harris C., Winkielman P., Pashler H., Puzzlingly high correlations in fMRI studies of emotion, personality, and social cognition, Perspect. Psychol. Sci., 2009, 4, 274–291
Mak A. K. Y., Hu Z. G., Zhang J. X. X., Xiao Z., Lee T. M. C., Sexrelated differences in neural activity during emotion regulation, Neuropsychologia, 2009, 47, 2900–2908
Talairach J., Tournoux P., Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain: 3-dimensional proportional system: an approach to cerebral imaging, Stuttgart, Thieme Medical Publishers, 1988
Boynton G. M., Engel S. A., Glover G. H., Heeger D. J., Linear systems analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging in human V1, J. Neurosci., 1996, 16, 4207–4221
De Martino F., Valente G., Staeren N., Ashburner J., Goebel R., Formisano E., Combining multivariate voxel selection and support vector machines for mapping and classification of fMRI spatial patterns, Neuroimage, 2008, 43, 44–58
Formisano E., De Martino F., Bonte M., Goebel R., “Who” is saying “What”? Brain-based decoding of human voice and speech, Science, 2008, 322, 970–973
Staeren N., Renvall H., De Martino F., Goebel R., Formisano E., Sound categories are represented as distributed patterns in the human auditory cortex, Curr. Biol., 2009, 19, 498–502
Adolphs R., Neural systems for recognizing emotion, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 2002, 12, 169–177
Phillips M. L., Drevets W. C., Rauch S. L., Land R., Neurobiology of emotion perception I: the neural basis of normal emotion perception, Biol. Psychiatry, 2003, 54, 504–514
Ihssen N., Cox W. M., Wiggett A., Fadardi J. S., Linden D. E., Differentiating heavy from light drinkers by neural responses to visual alcohol cues and other motivational stimuli, Cereb. Cortex, 2011, 21, 1408–1415
Mourão-Miranda J., Oliveira L., Ladouceur C. D., Marquand A., Brammer M., Birmaher B., et al., Pattern recognition and functional neuroimaging help to discriminate healthy adolescents at risk for mood disorders from low risk adolescents, PLoS One 2012, 7: e29482
References
Adolphs R., Neural systems for recognizing emotion, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 2002, 12, 169–177
Phillips M. L., Drevets W. C., Rauch S. L., Land R., Neurobiology of emotion perception I: the neural basis of normal emotion perception, Biol. Psychiatry, 2003, 54, 504–514
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yuen, K.S.L., Johnston, S.J., De Martino, F. et al. Pattern classification predicts individuals’ responses to affective stimuli. Translat.Neurosci. 3, 278–287 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-012-0029-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-012-0029-6