Abstract
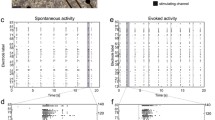
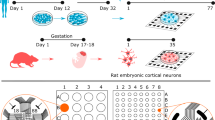
Models of functional connectivity in cortical cultures on multi-electrodes arrays may aid in understanding how cognitive pathways form and improve techniques that aim to interface with neuronal systems. To enable research on such models, this study uses both data- and model-driven approaches to determine what dependencies are present in and between functional connectivity networks derived from bursts of extracellularly recorded activity. Properties of excitation in bursts were analysed using correlative techniques to assess the degree of linear dependence and then two parallel techniques were used to assess functional connectivity. Three models presenting increasing levels of spatio-temporal dependency were used to capture the dynamics of individual functional connections and their consistencies were verified using surrogate data. By comparing network-wide properties between model generated networks and functional networks from data, complex interdependencies were revealed. This indicates the persistent co-activation of neuronal pathways in spontaneous bursts, as can be found in whole brain structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Maeda, H. P. Robinson, and A. Kawana The mechanisms of generation and propagation of synchronized bursting in developing networks of cortical neurons, J. Neurosci., 15(10), (1995), 6834–6845
Y. Jimbo, T. Tateno, and H. P. C. Robinson, Simultaneous induction of pathway-specific potentiation and depression in networks of cortical neurons, Biophysical Journal, 76, (1999), 670–678
G. Shahaf and S. Marom, Learning in networks of cortical neurons, J. Neurosci., 21(22), (2001), 8782
J. van Pelt, P. S. Wolters, Michael A. Corner, W. L. C. Rutten, and Ger J. A. Ramakers, Long-term characterization of firing dynamics of spontaneous bursts in cultured neural networks, IEEE Trans. Bio-med. Eng., 51(11), (2004), 2051–2062
T.B. DeMarse, D.A. Wagenaar, A.W. Blau, and S.M. Potter, The neurally controlled animat: biological brains acting with simulated bodies, Autonomous Robots, 11(3), (2001), 305–310
M.W. Hammond, S. Marshall, J. Downes, D. Xydas, S.J. Nasuto, V.M. Becerra, K. Warwick, and B.J. Whalley, Robust methodology for the study of cultured neuronal networks on MEAs, Baden-Wurttemberg GmbH, Stuttgart, 2008
D. A. Wagenaar, J. Pine, and S. M. Potter, An extremely rich repertoire of bursting patterns during the development of cortical cultures, BMC Neuroscience, 7:11, (2006)
J. van Pelt, I. Vajda, P. S. Wolters, M. A. Corner, and Ger J. A. Ramakers, Dynamics and plasticity in developing neuronal networks in vitro, Prog. Brain Res., 147, (2005), 173–188
D. A. Wagenaar, J. Pine, and S. M. Potter, Searching for plasticity in dissociated cortical cultures on multi-electrode arrays, Journal of Negative Results in Biomedicine, 5:16, (2006)
M. Chiappalone, A. Novellino, I. Vaida, A. Vato, S. Martinoia, and J. Van Pelt, Burst detection algorithms for the analysis of spatiotemporal patterns in cortical networks of neurons, Neurocomputing, 65–66, (2005), 653–662
E. Bullmore and O. Sporns, Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems, Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10(3), (2009), 186–198
C. J. Honey, R. Kötter, M. Breakspear, and O. Sporns, Network structure of cerebral cortex shapes functional connectivity on multiple time scales, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 104(24), (2007), 10240–10245
R. Madhavan, Z. C. Chao, and S. M. Potter, Plasticity of recurring spatiotemporal activity patterns in cortical networks, Physical Biology, 4(3), (2007), 181–193
M. Kaiser, Hierarchy and dynamics of neural networks, Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 4(August), 10–12, 2010
A. Minerbi, R. Kahana, L. Goldfeld, M. Kaufman, S. Marom, and N. E. Ziv, Long-term relationships between synaptic tenacity, synaptic remodeling, and network activity, PLoS Biology, 7(6), (2009), e1000136
J. D. Victor, Spike train metrics, Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 15(5), (2005), 585–592
E. Pereda, Q. R. Quiroga, and J. Bhattacharya, Nonlinear multivariate analysis of neurophysiological signals, Progress in Neurobiology, 77(1–2), (2005), 1–37
D. J. Watts and S. H. Strogatz, Collective dynamics of ’small-world’ networks, Nature, 393, (1998), 440–442
P. Borgnat, E. Fleury, J. L. Guillaume, C. Magnien, C. Robardet, and A. Scherrer, Evolving networks, In Françoise Fogelman-Soulié, Domenico Perrotta, Jakub Piskorski, and Ralf Steinberg, editors, Proceedings of NATO Advanced Study Institute on Mining Massive Data Sets for Security, 198–204. IOS Press, 2008
S. Boccaletti, V. Latora, Y. Moreno, M. Chavez, and D. Hwang, Complex networks: Structure and dynamics, Physics Reports, 424(4–5), (2006), 175–308
M. C. Spencer, D. Xydas, J. H. Downes, M. W. Hammond, V. M. Becerra, K. Warwick, B. J. Whalley, and S. J. Nasuto, Investigation of spatio-temporal dependencies in neuronal functional connectivity, In: 9th IEEE Int. Conf. Cyber. Intel. Sys., 2010
U. Egert, D. Heck, and A. Aertsen, Two-dimensional monitoring of spiking networks in acute brain slices, Experimental Brain Research, 142(2), (2002), 268–274
D. A. Wagenaar and T. B. DeMarse, Meabench: A toolset for multi-electrode data acquisition and on-line analysis, Proc. 2nd Int. IEEE EMBS Conf. Neural Eng., 2005
S. Grün, Data-driven significance estimation for precise spike correlation, Journal of Neurophysiology, 101(3), (2009), 1126–1140
A. R. C. Paiva, I. Park, and J. C. Príncipe, A comparison of binless spike train measures, Neural Computing & Applications, 19(3), (2010), 405–419
P. Grindrod and D. J. Higham, Evolving graphs: dynamical models, inverse problems and propagation, Proc. Roy. Soc. A, 466(2115), (2009), 753–770
R. Albert and A. L. Barabási, Statistical mechanics of complex networks, Reviews of Modern Physics, 74(1), (2002), 47–97
T. Kreuz, D. Chicharro, M. Greschner, and R. G. Andrzejak, Timeresolved and time-scale adaptive measures of spike train synchrony, J. Neurosci. Methods, 195(1), (2010), 92–106
M. C. Spencer, J. H. Downes, D. Xydas, M. W. Hammond, V. M. Becerra, K. Warwick, B. J. Whalley, and S. J. Nasuto, Multi-scale evolving complex network model of functional connectivity in neuronal cultures, IEEE Trans. Bio-med. Eng., (2011), 1–5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Spencer, M.C., Downes, J.H., Xydas, D. et al. Spatio-temporal dependencies in functional connectivity in rodent cortical cultures. Paladyn 2, 156–163 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13230-012-0002-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13230-012-0002-7