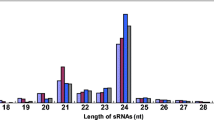
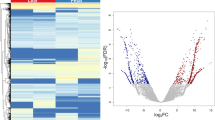
Abstract
In recent years, the prevalence of peanut pod rot in northern China has increased, thereby severely threatening peanut yield and quality. The purpose of this study is to identify and analysis miRNAs during the process of peanut responding to pod rot, providing theoretical basis for improving the disease resistance of peanut by genetic engineering. The DNA libraries were diluted and quantified for sequencing through the Small RNA sequencing technology using Illumina HiSeq 2000. The raw reads were clean after quality trimming. The expression profiles of miRNAs were constructed and its target genes were analysis by quantitative real time PCR. The validation of miR156 targets were conducted by the 5’ RACE PCR. The present study identified 334 peanut miRNAs, of which 97 were down regulated and 27 were up regulated. The expression of 15 miRNAs was performed by qRT-PCR. Target gene prediction shown 1,998 target genes and 2,646 target loci were predicted for 303 miRNAs. A total of 152 target genes were predicted for the 119 differentially expressed miRNAs. Correlation analysis of transcriptome sequencing results identified 14 genes, which are regulated by 10 miRNAs. Negative regulatory relationships were observed between four miRNAs and their respective putative target genes. Many different miRNAs were involved in the molecular regulation of peanut responding to pod rot by negatively regulating target genes. These miRNAs showed different expression trends, the same miRNA might target multiple genes and have multiple target sites.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- miRNAS:
-
microRNAs
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction
- TIR1:
-
Transport inhibitor response 1
- AFB2:
-
Auxin signaling F-box 2
- AFB3:
-
Auxin signaling F-box 3
- PAGE:
-
Denatured polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- CDS:
-
Coding sequence
- FC:
-
Fold Change
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
References
Ahmed F, Senthil-Kumar M, Lee S, Dai X, Mysore KS, Zhao PX (2014) Comprehensive analysis of small RNA-seq data reveals that combination of microRNA with its isomiRs increase the accuracy of target prediction in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA Biol 11(11):1414–1429. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2014.996474
Abdel-Fattah MG, Elsayed Abdalla M (2000) Influence of the endomycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae on the development of peanut pod rot disease in Egypt. Mycorrhiza 10 (1):29–35
Arai T, Fuse M, Goto Y, Kaga K, Kurozumi A, Yamada Y, Sugawara S, Okato A, Ichikawa T, Yamanishi T, Seki N (2018) Molecular pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis based on microRNA expression signature: miR-320 family-regulated molecular pathways and targets. J Hum Genet 63(5):543–554. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-018-0419-x
Brussaard L, De Ruiter PC, Brown GG (2007) Soil biodiversity for agricultural sustainability. Agric Ecosyst Environ 121:233–244. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2006.12.013
Chi X, Yang Q, Chen X, Wang J, Pan L, Chen M, Yang Z, He Y, Liang X, Yu S (2011) Identification and characterization of microRNAs from peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) by high-throughput sequencing. PLoS One 6(11):e27530. doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027530
Cilliers AJ (2001) Resistance in new groundnut breeding lines to black pod rot caused by Chalara elegans. S Afr J Plant Soil 18:174–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/02571862.2001.10634426
Fabra A, Castro S, Tauriani T (2010) Interaction among Arachis hypogaea L. (peanut) and beneficial soil microorganisms: how much is it known? Crit Rev Microbiol 36:179–194. doi:https://doi.org/10.3109/10408410903584863
Fahlgren N, Hill ST, Carrington JC, Carbonell A (2016) P-SAMS: a web site for plant artificial microRNA and synthetic trans-acting small interfering RNA design. Bioinformatics 32(1):157–158. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv534
Ferreira e Silva GF, Silva EM, Azevedo Mda S, Guivin MA, Ramiro DA, Figueiredo CR, Carrer H, Peres LE, Nogueira FT (2014) microRNA156-targeted SPL/SBP box transcription factors regulate tomato ovary and fruit development. Plant J 78(4):604–618. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12493
Gao C, Wang P, Zhao S, Zhao C, Xia H, Hou L, Ju Z, Zhang Y, Li C, Wang X (2017) Small RNA profiling and degradome analysis reveal regulation of microRNA in peanutembryogenesis and early pod development. BMC Genom 18(1):220. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3587-8
Itaya A, Bundschuh R, Archual AJ, Joung JG, Fei Z, Dai X, Zhao PX, Tang Y, Nelson RS, Ding B (2008) Small RNAs in tomato fruit and leaf development. Biochim Biophys Acta 1779(2):99–107. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2007.09.003
Jian XY, Zhang L, Li GL, Zhang L, Wang XJ, Cao XF, Fang XH, Chen F (2010) Identification of novel stress-regulated microRNAs from Oryza sativa L. Genomics 95:47–55. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2009.08.017
Jones JD, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05286
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S (2014) miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D68-73. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1181
Kurtoglu KY, Kantar M, Lucas SJ, Budak H (2013) Unique and conserved microRNAs in wheat chromosome 5D revealed by next-generation sequencing. PLoS One 8(7):e69801. doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069801
Li XG, Ding CF, Zhang TL, Wang XX (2014) Fungal pathogen accumulation at the expense of plant-beneficial fungi as a consequence of consecutive peanut monoculturing. Soil Biol Biochem 72:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.01.019
Liu HH, Tian X, Li YJ, Wu CA, Zheng CC (2008) Microarray-based analysis of stress-regulated microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA 14:836–843. doi:https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.895308
Liu J, Cheng X, Liu P, Sun J (2017) miR156-Targeted SBP-Box Transcription Factors Interact with DWARF53 to Regulate TEOSINTE BRANCHED1 and BARREN STALK1 Expression in Bread Wheat. Plant Physiol 174(3):1931–1948. doi:https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00445
Lombard L, Rodas CA, Crous PW, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ (2009) Clonectria (Cyindrocladium) associated with dying Pinus cuttings. Persoonia 23:41–47. doi:https://doi.org/10.3767/003158509X471052
Lombard L, Crous PW, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ (2010) Species concepts in calonectria (Cyindrocladium). Stud Mycol 66:1–14. doi:https://doi.org/10.3114/sim.2010.66.01
Mi S, Cai T, Hu Y, Chen Y, Hodges E, Ni F, Wu L, Li S, Zhou H, Long C, Chen S, Hannon GJ, Qi Y (2008) Sorting of small RNAs into Arabidopsis argonaute complexes is directed by the 5’ terminalnucleotide. Cell 133(1):116–127. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.034
Mueth NA, Ramachandran SR, Hulbert SH (2015) Small RNAs from the wheat stripe rust fungus (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici). BMC Genom 16:718. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1895-4
Navarro L, Dunoyer P, Jay F, Arnold B, Dharmasiri N, Estelle M, Voinnet O, Jones JD (2006) A plant microRNAs contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing auxin signaling. Science 312:436–439. doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aae0382
Rajagopalan R, Vaucheret H, Trejo J, Bartel DP (2006) A diverse and evolutionarily fluid set of microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev 20:3407–3425. doi:https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1476406
Subodh KC, Satyabrata N, Ellojita R, Jatindranath M, Rukmini M, Kumar J (2016) Identification and characterization of microRNAs in turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) responsive to infection with the pathogenic fungus Pythium aphanidermatum. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 93:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2016.01.010
Varkonyi-Gasic E, Wu R, Wood M, Walton EF, Hellens RP (2007) Protocol: a highly sensitive RT-PCR method for detection and quantification of microRNAs. Plant Methods 3:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4811-3-12
Wang K, Wang X, Li M, Shi T, Yang P (2017a) Low genetic diversity and functional constraint of microRNA genes participating pollen-pistil interaction in rice. Plant Mol Biol 95(1–2):89–98. doi:10.1007/s11103-017-0638-0
Wang M, Chen M, Yang Z, Chen N, Chi X, Pan L, Wang T, Yu S, Guo X (2017b) Influence of Peanut Cultivars and Environmental Conditions on the Diversity and Community Composition of Pod Rot Soil Fungi in China. Mycobiology 45(4):392–400. doi:10.5941/MYCO.2017b.45.4.392
Wheeler TA, Russell SA, Anderson MG, Serrato-Diaz LM, French-Monar (2016) RD,Wood ward JE.Management of peanut pod rot I : Disease dynamics and sampling. Crop Prot 79:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2015.10.010
Yao YY, Guo GG, Ni ZF, Sunkar R, Du JK, Zhu JK, Sun QX (2007) Cloning and characterization of microRNAs from wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome Biol 8:67–78. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2007-8-6-r96
Zhang BH, Pan XP, Anderson TA (2006) Identification of 188 conserved maize microRNAs and their targets. FEBS Lett 580:3753–3762. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.05.063
Zhang SL, Liu GK, Janssen T, Zhang SS, Xiao S, Li ST, Couvreur M, Bert W (2014) A new stem nematode associated with peanut pod rot in China: morphological and molecular characterization of Ditylenchus arachis n. sp. (Nematoda: Anguinidae. Plant Pathol 63:1193–1206. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12183
Zhao CZ, Xia H, Frazier TP, Yao YY, Bi YP, Li AQ, Li MJ, Li CS, Zhang BH, Wang XJ (2010) Deep sequencing identifies novel and conserved microRNAs in peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Plant Biol 10:3. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-3
Zhu QH, Spriggs A, Matthew L, Fan L, Kennedy G, Gubler F, Helliwell C (2008) A diverse set of microRNAs and microRNA-like small RNAs in developing rice grains. Genome Res 18(9):1456–1465. doi:https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.075572.107
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from The National ten Thousand Youth Talents Plan of 2014 (W02070268), China Agriculture Research System (CARS-13), Taishan Scholar Project Funding, the Breeding Project from Department Science & Technology of Shandong Province (2017LZGC003), the Natural Science Fund of Shandong Province (ZR2017YL017, ZR2016CM07), Agricultural Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CXGC2016B02, CXGC2018E21), the Basic Research Project of Qingdao (17-1-1-51-jch). We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MW carried out all the data analysis and wrote this manuscript; MC collected the samples from the field; ZY, LP, TW and NC conceived the project and drafted the manuscript; CZ and XG carried out the experiment of qRT-PCR; XC and SY supervised the analysis and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Accessibility
Statistical analysis of the differentially expressed genes in transcriptome sequencing, which had been submitted to BioProject: PRJNA302339 and PRJNA396989; All raw data used in this manuscript have been submitted to BioProject: PRJNA302570, with the number: SAMN04274822 and SAMN04274821 for sample L and C, respectively.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLSX 163 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Zhang, Cx., Pan, Lj. et al. Small RNA profiling reveal regulation of microRNAs in field peanut pod rot pathogen infection. Biologia 75, 1779–1788 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00485-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00485-z