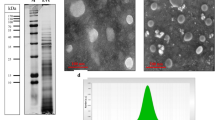
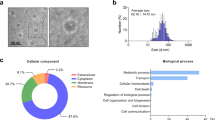
Abstract
Recently, the effect of intestinal microbiota on the lungs has been reported in several studies as the gut-lung axis, which interferes with inflammatory processes through the translocation of bacterial products across the gastrointestinal tract barrier into blood vessels. In numerous studies, the anti-inflammatory properties of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strains have been reported both in vivo and in vitro. In this process, the secretion of bioactive molecules with anti-inflammatory effects is one of the strategies that the bacterium uses. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have drawn the attention of scientists due to their role in cell-to-cell communication either locally or over long distances. In this study, we evaluated the effects of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii supernatant and EVs on the expression profile of cytokines and chemokines by using lung cancer cell line (A549). Principal analysis showed that the bacterial supernatant and derived EVs were able to dysregulate the expression of some specific cytokines. However, the response of bacterium-secreted EVs was more significant compared to the bacterial supernatant for some key cytokines. The secreted EVs significantly could upregulate anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, TGF-β2 and IL-1Ra). On the other hand, F. prausnitzii EVs could downregulate some of the important pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α and TNF-β.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IBS:
-
irritable bowel syndrome
- MAM:
-
microbial anti-inflammatory molecule
- EV:
-
extracellular vesicles
- OMV:
-
outer membrane vesicles
- MV:
-
membrane vesicles
- EPM:
-
Extracellular Polymeric Matrix
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- DSS:
-
Dextran Sodium Sulfate
- hPBMCs:
-
human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- hDCs:
-
human monocyte-derived dendritic cells
- Tregs:
-
regulatory T cells
- BMDCs:
-
bone marrow-derived dendritic cells
- ADIPOQ:
-
Adiponectin, C1Q and collagen domain containing
- BMP2:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 2
- BMP4:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 4
- BMP6:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 6
- BMP7:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 7
- C5:
-
Complement component 5
- CCL1:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 1
- CCL11:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 11
- CCL13:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 13
- CCL17:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 17
- CCL18:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 (pulmonary and activation-regulated)
- CCL19:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19
- CCL2:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2
- CCL20:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20
- CCL21:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21
- CCL22:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 22
- CCL24:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 24
- CCL3:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3
- CCL5:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5
- CCL7:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7
- CCL8:
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 8
- CD40LG:
-
CD40 ligand
- CNTF:
-
Ciliary neurotrophic factor
- CSF1:
-
Colony stimulating factor 1 (macrophage)
- CSF2:
-
Colony stimulating factor 2 (granulocyte-macrophage)
- CSF3:
-
Colony stimulating factor 3 (granulocyte)
- CX3CL1:
-
Chemokine (C-X3-C motif) ligand 1
- CXCL1:
-
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha)
- CXCL10:
-
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10
- CXCL11 :
-
(Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 11
- CXCL12:
-
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12
- CXCL13:
-
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13
- CXCL16:
-
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16
- CXCL2:
-
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2
- CXCL5:
-
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 5
- CXCL9:
-
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9
- FASLG:
-
Fas ligand (TNF superfamily, member 6)
- GPI:
-
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase
- IFNA2:
-
Interferon, alpha 2
- IFNG:
-
Interferon, gamma
- IL10:
-
Interleukin 10
- IL11:
-
Interleukin 11
- IL12A:
-
Interleukin 12A (natural killer cell stimulatory factor 1, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 1, p35)
- IL12B:
-
Interleukin 12B (natural killer cell stimulatory factor 2, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 2, p40)
- IL13:
-
Interleukin 13
- IL15:
-
Interleukin 15
- IL16:
-
Interleukin 16
- IL17A:
-
Interleukin 17A
- IL17F:
-
Interleukin 17F
- IL18:
-
Interleukin 18 (interferon-gamma-inducing factor)
- IL1A:
-
Interleukin 1, alpha
- IL1B:
-
Interleukin 1, beta
- IL1RN:
-
Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist
- IL2:
-
Interleukin 2
- IL21:
-
Interleukin 21
- IL22:
-
Interleukin 22
- IL23A:
-
Interleukin 23, alpha subunit p19
- IL24:
-
Interleukin 24
- IL27:
-
Interleukin 27
- IL3:
-
Interleukin 3 (colony-stimulating factor, multiple)
- IL4:
-
Interleukin 4
- IL5:
-
Interleukin 5 (colony-stimulating factor, eosinophil)
- IL6:
-
Interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2)
- IL7:
-
Interleukin 7
- CXCL8:
-
Interleukin 8
- IL9:
-
Interleukin 9
- LIF:
-
Leukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor)
- LTA:
-
Lymphotoxin alpha (TNF superfamily, member 1)
- LTB:
-
Lymphotoxin beta (TNF superfamily, member 3)
- MIF:
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (glycosylation-inhibiting factor)
- MSTN:
-
Myostatin
- NODAL:
-
Nodal homolog (mouse)
- OSM:
-
Oncostatin M
- PPBP:
-
Pro-platelet basic protein (chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 7)
- SPP1:
-
Secreted phosphoprotein 1
- TGFB2:
-
Transforming growth factor, beta 2
- THPO:
-
Thrombopoietin
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- TNFRSF11B:
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 11b
- TNFSF10:
-
Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 10
- TNFSF11:
-
Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11
- TNFSF13B:
-
Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b
- VEGFA:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor A
- XCL1:
-
Chemokine (C motif) ligand 1
References
Acevedo R et al (2014) Bacterial outer membrane vesicles and vaccine applications. Front Immunol 5:121. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00121
Bachmann MF, Jennings GT (2010) Vaccine delivery: a matter of size, geometry, kinetics and molecular patterns. Nat Rev Immunol 10:787. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2868
Baker JL, Chen L, Rosenthal JA, Putnam D, DeLisa MP (2014) Microbial biosynthesis of designer outer membrane vesicles. Curr Opin Biotechnol 29:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.02.018
Bauman SJ, Kuehn MJ (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa vesicles associate with and are internalized by human lung epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol 9:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-9-26
Bi Y, Liu G, Yang R (2011) Reciprocal modulation between TH17 and other helper T cell lineages. J Cell Physiol 226:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22331
Bingula R et al (2017) Desired turbulence? Gut-lung axis, immunity, and lung cancer. Journal of oncology 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5035371
Brown L, Wolf JM, Prados-Rosales R, Casadevall A (2015) Through the wall: extracellular vesicles in gram-positive bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi. Nat Rev Microbiol 13:620. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3480
Budden KF, Gellatly SL, Wood DL, Cooper MA, Morrison M, Hugenholtz P, Hansbro PM (2017) Emerging pathogenic links between microbiota and the gut–lung axis. Nat Rev Microbiol 15:55. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.142
Carlsson AH, Yakymenko O, Olivier I, Håkansson F, Postma E, Keita ÅV, Söderholm JD (2013) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii supernatant improves intestinal barrier function in mice DSS colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 48:1136–1144. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2013.828773
Chelakkot C et al (2018) Akkermansia muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicles influence gut permeability through the regulation of tight junctions. Exp Mol Med 50:e450. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2017.282
Chen Q, Xu L, Liang C, Wang C, Peng R, Liu Z (2016) Photothermal therapy with immune-adjuvant nanoparticles together with checkpoint blockade for effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun 7:13193. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13193
Choi C-W, Park EC, Yun SH, Lee S-Y, Kim SI, Kim G-H (2017) Potential usefulness of Streptococcus pneumoniae extracellular membrane vesicles as antibacterial vaccines. J Immunol Res 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7931982
Codemo M, Muschiol S, Iovino F, Nannapaneni P, Plant L, Wai SN, Henriques-Normark B (2018) Immunomodulatory effects of pneumococcal extracellular vesicles on cellular and humoral host defenses. mBio 9:e00559–e00518. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00559-18
De Marco S, Sichetti M, Muradyan D, Piccioni M, Traina G, Pagiotti R, Pietrella D (2018) Probiotic cell-free supernatants exhibited anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity on human gut epithelial cells and macrophages stimulated with LPS. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1756308
Fujita Y, Kadota T, Araya J, Ochiya T, Kuwano K (2018) Extracellular vesicles: new players in lung immunity. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 58:560–565. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb
Gregory AE, Williamson D, Titball R (2013) Vaccine delivery using nanoparticles. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 3:13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2013.00013
Jafari B, Khavari Nejad RA, Vaziri F, Siadat SD (2017) Isolation and characterization of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii extracellular vesicles. Vaccine Research 4:51–54. https://doi.org/10.29252/vacres.4.3.4.51
Jess T, Horváth-Puhó E, Fallingborg J, Rasmussen HH, Jacobsen BA (2013) Cancer risk in inflammatory bowel disease according to patient phenotype and treatment: a Danish population-based cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol 108:1869. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2013.249
Kang C-S et al (2013) Extracellular vesicles derived from gut microbiota, especially Akkermansia muciniphila, protect the progression of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. PLoS One 8:e76520. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076520
Keely S, Talley NJ, Hansbro PM (2012) Pulmonary-intestinal cross-talk in mucosal inflammatory disease. Mucosal Immunol 5:7. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2011.55
Kelly K et al (2001) Randomized phase III trial of paclitaxel plus carboplatin versus vinorelbine plus cisplatin in the treatment of patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer: a southwest oncology group trial. J Clin Oncol 19:3210–3218. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2001.19.13.3210
Khansari N, Shakiba Y, Mahmoudi M (2009) Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress as a major cause of age-related diseases and cancer. Recent Patents Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 3:73–80. https://doi.org/10.2174/187221309787158371
Kim OY et al (2017) Bacterial outer membrane vesicles suppress tumor by interferon-γ-mediated antitumor response. Nat Commun 8:626. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00729-8
Kulkarni HM, Jagannadham MV (2014) Biogenesis and multifaceted roles of outer membrane vesicles from gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology 160:2109–2121. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.079400-0
Lee YK, Mazmanian SK (2010) Has the microbiota played a critical role in the evolution of the adaptive immune system? Science 330:1768–1773. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1195568
Lizotte P, Wen A, Sheen M, Fields J, Rojanasopondist P, Steinmetz N, Fiering S (2016) In situ vaccination with cowpea mosaic virus nanoparticles suppresses metastatic cancer. Nat Nanotechnol 11:295. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2015.292
Manning AJ, Kuehn MJ (2013) Functional advantages conferred by extracellular prokaryotic membrane vesicles. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 23:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1159/000346548
Manuzak J, Dillon S, Wilson C (2012) Differential interleukin-10 (IL-10) and IL-23 production by human blood monocytes and dendritic cells in response to commensal enteric bacteria. Clin Vaccine Immunol 19:1207–1217. https://doi.org/10.1128/CVI.00282-12
Martín R et al (2014) The commensal bacterium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is protective in DNBS-induced chronic moderate and severe colitis models. Inflamm Bowel Dis 20:417–430. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.MIB.0000440815.76627.64
Martín R et al (2017) Functional characterization of novel Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strains isolated from healthy volunteers: a step forward in the use of F. Prausnitzii as a next-generation probiotic. Front Microbiol 8:1226. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01226
Matsuzaki T, Yokokura T, Azuma I (1985) Anti-tumour activity of lactobacillus casei on Lewis lung carcinoma and line-10 hepatoma in syngeneic mice and Guinea pigs. Cancer Immunol Immunother 20:18–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199768
Mayrand D, Grenier D (1989) Biological activities of outer membrane vesicles. Can J Microbiol 35:607–613. https://doi.org/10.1139/m89-097
Nøkleby H, Aavitsland P, O’hallahan J, Feiring B, Tilman S, Oster P (2007) Safety review: two outer membrane vesicle (OMV) vaccines against systemic Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B disease. Vaccine 25:3080–3084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.01.022
Perwez Hussain S, Harris CC (2007) Inflammation and cancer: an ancient link with novel potentials. Int J Cancer 121:2373–2380. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.23173
Qiu X, Zhang M, Yang X, Hong N, Yu C (2013) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii upregulates regulatory T cells and anti-inflammatory cytokines in treating TNBS-induced colitis. J Crohn's Colitis 7:e558–e568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crohns.2013.04.002
Quevrain E et al. (2015) Identification of an anti-inflammatory protein from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, a commensal bacterium deficient in Crohn’s disease. Gut:gutjnl-2014-307649. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307649
Ripert G, Racedo SM, Elie A-M, Jacquot C, Bressollier P, Urdaci MC (2016) Secreted compounds of the probiotic Bacillus clausii strain O/C inhibit the cytotoxic effects induced by Clostridium difficile and Bacillus cereus toxins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:3445–3454. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02815-15
Rossi O et al (2015) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strain HTF-F and its extracellular polymeric matrix attenuate clinical parameters in DSS-induced colitis. PLoS One 10:e0123013. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123013
Rossi O et al (2016) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii A2-165 has a high capacity to induce IL-10 in human and murine dendritic cells and modulates T cell responses. Sci Rep 6:18507. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18507
Shen Y, Torchia MLG, Lawson GW, Karp CL, Ashwell JD, Mazmanian SK (2012) Outer membrane vesicles of a human commensal mediate immune regulation and disease protection. Cell Host Microbe 12:509–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2012.08.004
Sivan A et al (2015) Commensal Bifidobacterium promotes antitumor immunity and facilitates anti–PD-L1 efficacy. Science:aac4255. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac4255
Sokol H et al (2008) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:16731–16736. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804812105
Wan Y et al (2014) Fermentation supernatants of lactobacillus delbrueckii inhibit growth of human colon cancer cells and induce apoptosis through a caspase 3-dependent pathway. Oncol Lett 7:1738–1742. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2014.1959
Wang H et al (2013) Gut-lung crosstalk in pulmonary involvement with inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol: WJG 19:6794. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6794
Zhang M et al (2014) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii inhibits interleukin-17 to ameliorate colorectal colitis in rats. PLoS One 9:e109146. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109146
Zitvogel L et al (1998) Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell derived exosomes. Nat Med 4:594. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0598-594
Acknowledgments
We thank all the personnel of Mycobacteriology and Pulmonary Research Department, Pasteur Institute of Iran for their assistance in this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BJ wrote the manuscript and performed laboratory work. SDS, RAKN and FV supervised the project. SDS designed the project. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
No competing financial and/or non-financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafari, B., Khavari Nejad, R.A., Vaziri, F. et al. Evaluation of the effects of extracellular vesicles derived from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii on lung cancer cell line. Biologia 74, 889–898 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00229-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00229-8