Abstract
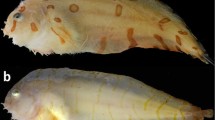
In contrast with the usual coloration of stone crayfish (Austropotamobius torrentium), we newly discovered a rare marble morph in a brook in the Czech Republic (Central Europe). During mark-recapture sessions, we captured by hand 1,103 individuals over the 3 years 2008–2010 from which only 5 were marble-colored. This color morph’s frequency of occurrence was thus less than 1% within the estimated subadult and adult stone crayfish population. Although many biological papers and determination keys regarding crayfish are based upon analysis of exoskeletal coloration, recent studies have asserted that this characteristic provides unreliable guidance when determining species inasmuch as it easily results in errors because many crayfish species exhibit an extensive variety of color morphs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beingesser K.R. & Copp N.H. 1985. Differential diurnal distribution of Procambarus clarkii (Girard) juveniles and adults and possible adaptive value of color differences between them (Decapoda, Astacidea). Crustaceana 49(1–3) 164–172. DOI: 10.1163/156854085X00404
Bubb D.H., Lucas M.C. & Thom T.J. 2002. Winter movements and activity of signal crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus in an upland river, determined by radio telemetry. Hydrobiologia 483(1–3): 111–119. DOI: 10.1023/A:1021363109155
Castillo R., Negre-Sadargues G. & Lenel R. 1982. General survey of the carotenoids in crustacean, pp. 211–224. In: Britton G. & Goodwin T.W. (eds), Carotenoid Chemistry and Biochemistry: proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Carotenoids, Liverpool, UK, 26–31 July 1981, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 399 pp. ISBN: 0080262244, 9780080262246
Finlay J.B., Buhay J.E. & Crandall K.A. 2006. Surface to subsurface freshwater connections: phylogeographic and habitat analyses of Cambarus tenebrosus, a facultative cavedwelling crayfish. Anim. Conserv. 9(4): 375–387. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-1795.2006.0046.x
Fox D.L. 1953. Animal Biochromes and Structural Colours: Physical, Chemical, Distributional & Physiological Features of Coloured Bodies in the Animal World. Cambridge University Press, London and New York, 379 pp.
Füreder L. & Machino Y. 2002. A revised determination key of freshwater crayfish in Europe. Ber. Naturwiss.-Med. Ver. Innsbruck 89: 169–178.
Goddard J.S. & Hogger J.B. 1986. The current status and distribution of freshwater crayfish in Britain. Field Studies 6: 383–396.
Hand C. 1954. A blue crayfish from California. California Fish and Game 40(4): 437–438.
Holdich D.M., Haffner P. & Noël P. 2006. Species files, pp. 50–129. In: Souty-Grosset C., Holdich D.M., Noël P., Reynolds J.D. & Haffner P. (eds), Atlas of Crayfish in Europe, Series: Collection Patrimoines Naturels 64, Muséum national d’Historie naturelle, Paris, 188 pp. ISBN: 2856535798
Kadlecová K., Bíly M. & Maciak M. 2012. Movement patterns of the co-occurring species Astacus astacus (noble crayfish) and Austropotamobius torrentium (stone crayfish). Fund. Appl. Limnol. 180(4): 351–360.
Kent W.J. 1901. The colors of the crayfish. Amer. Natur. 35(419): 933–936.
Kozák P., Ďuriš Z. & Policar T. 2002. The stone crayfish Austropotamobius torrentium (Schrank) in the Czech Republic. Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscicul. 367: 707–713.
Machino Y. & Füreder L. 2005. How to find a stone crayfish Austropotamobius torrentium (Schrank, 1803): A biogeographic study in Europe. Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscicult. 376-377: 507–517.
Momot W.T. & Gall J.E. 1971. Some ecological notes on the blue color phase of the crayfish, Orconectes virilis, in two lakes. Ohio J. Sci. 71(6): 363–371.
Pârvulescu L. 2010. Comparative biometric study of crayfish populations in the Anina Mountains (SW Romania) hydrographic basins. Studia Universitatis Babeş — Bolyai, Biologia, LV. 1: 3–15.
Pöckl M., Pennerstorfer J. & Pekny R. 2003. Flusskrebse in Österreich. Gugler Print & Media, Melk.
Pöckl M. & Streissl F. 2005. Austropotamobius torrentium as an indicator for habitat quality in running waters? Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscicult. 376–377: 743–758.
Schnabel Z.E. 1938. The estimation of total fish population of a lake. Amer. Mathem. Month. 45(6): 348–352.
Sommer T.R., Morrissy N.M. & Potts W.T. 1991. Growth and pigmentation of marron (Cherax tenuimanus) fed a reference ration supplemented with the microalga Dunaliella salina. Aquaculture 99(3–4): 285–295. DOI: 10.1016/0044-8486(91)90249-7
Streissl F. & Hödl W. 2002. Habitat and shelter requirements of the stone crayfish, Austropotamobius torrentium Schrank. Hydrobiologia 477(1–3): 195–199. DOI: 10.1023/A:102109 4309738
Thacker R.W., Hazlett B.A., Esman L.A., Stafford C.P. & Keller T. 1993. Color morphs of the crayfish Orconectes virilis. Amer. Midl. Natur. 129(1): 182–199.
Vlach P., Hulec L. & Fischer D. 2009. Recent distribution, population densities and ecological requirements of the stone crayfish (Austropotamobius torrentium) in the Czech Republic. Knowl. Manage. Aquat. Ecosyst. 394-395: 13. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1051/kmae/2010005
Vogt G., Huber M., Thiemann M., Van den Boogaart G., Schmitz O.J. & Schubart C.D. 2008. Production of different phenotypes from the same genotype in the same environment by developmental variation. J. Exp. Biol. 211(4): 510–523. DOI: 10.1242/jeb.008755
Volpe E.P. & Penn G.H. 1957. Dimorphism of chromatophore patterns in the dwarf crayfish. J. Heredity 48(3): 91–96.
Vorburger C. & Ribi G. 1999. Aggression and competition for shelter between a native and introduced crayfish in Europe. Freshwater Biol. 42(1): 111–119. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2427.1999.00465.x
Walker M.L., Austin C.M. & Meewan M. 2000. Evidence for the inheritance of a blue variant of the Australian fresh-water crayfish Cherax destructor (Decapoda: Parastacidae) as an autosomal recessive. J. Crustacean Biol. 20(1): 25–30. DOI:10.1651/0278-0372(2000)020[0025:EFTIOA]2.0.CO;2
Wolfe D.A. & Cornwall D.H. 1964. Carotenoids of cavernicolous crayfish. Science 144(3625): 1467–1468. DOI: 10.1126/science. 144.3625.1467
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patoka, J., Římalová-Kadlecová, K., Bílý, M. et al. Frequency of new marble-colored morph in wild population of Austropotamobius torrentium (Decapoda: Astacidae). Biologia 68, 707–711 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-013-0208-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-013-0208-0