Abstract
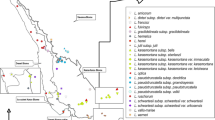
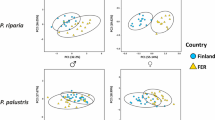
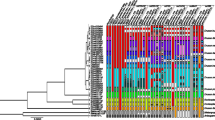
Leech taxonomy is based on unstable morphological characters. The overall level of genetic variability and species differentiation is unknown. Using the RAPD assays genetic diversities and genetic similarities were estimated in twelve species collected in North-Eastern Poland and representing three families and five subfamilies. Ten primers revealed 204 reproducible bands. Genetic diversities varied from 0.099 to 0.219 classifying studied species among variable invertebrates. Total 45 markers comprised 22% of all amplified bands were unique for species thus enabling their identification. Genetic similarities among species (0.528–0.811) evidenced several stages of differentiation, which is mirrored in the current taxonomy. The UPGMA and multidimensional scaling (nMDS) based on our RAPDs are congruent and reflected traditional division into “Rhynchobdellida” and Arhynchobdellida. The RAPD approach proved to be an effective tool in population and evolutionary studies of leeches. For the first time, genetic parameters were estimated enabling to compare leeches with outcomes from other animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams R.P. & Rieseberg L.H. 1998. The effects of non-homology in RAPD bands on similarity and multivariate statistical ordination in Brassica and Helianthus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 97(2): 323–326. DOI: 10.1007/s001220050902
Apakupakul K., Siddall M.E. & Burreson E.M. 1999. Higher level relationships of leeches (Annelida: Clitellata: Euhirudinea) based on morphology and gene sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 12: 350–359. DOI: 10.1006/mpev.1999.0639
Avise J.C. 2004. Molecular Markers, Natural History, and Evolution. 2nd Edition. Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers, Sunderland, Massachusetts, 684 pp. ISBN-10: 0878930418, ISBN-13: 978-0878930418
Baczkiewicz A., Sawicki J., Buczkowska K., Polok K. & Zielinski R. 2008. Application of different DNA markers in studies on cryptic species of Aneura pinguis (Jungermannipsida, Metzgeriales). Cryptogamie Bryol. 29: 3–21.
Bely A.E. & Weisblat D.A. 2006. Lessons from leeches: a call for DNA barcoding in the lab. Evol. Dev. 8(6): 491–501. PMID: 17073933
Boulila A., Bejaoui A., Messaoud C. & Boussaid M. 2010. Genetic diversity and population structure of Teucrium polium (Lamiaceae) in Tunisia. Biochem. Genet. 48(1–2): 57–70. DOI: 10.1007/s10528-009-9295-6
Cichocka J. & Bielecki A. 2008. Biological diversity of leeches (Clitellata: Hirudinida) based on the characteristics of the karyotypes. Wiad. Parazytol. 54(4): 309–314. PMID: 19338221
Dyer A.R., Fowler J.C.S. & Baker G.H. 1998. Detecting genetic variation in exotic eartworms, Aporrectodea spp. (Lumbricidae), in Australian soils using RAPD markers. Soil Biol. Biochem. 30(2): 159–165. DOI: 10.1016/S0038-0717(97)00098-9
Govedich F.R., Blinn D.W., Hevly R.H. & Keim P.S. 1999. Cryptic radiation in erpobdellid leeches in xeric landscapes: a molecular analysis of population differentiation. Can. J. Zool. 77(1): 52–57. DOI: 10.1139/z98-178
Integrated Taxonomic Information System [database on the Internet]. [modified 2009 Dec 24: cited 2010 May 28]. Available from: http://www.itis.gov
Krebs C., Mahy G., Matthies D., Schaffner U., Tiebre M.S. & Bizoux J.P. 2010. Taxa distribution and RAPD markers indicated different origin and regional differentiation of hybrids in the invasive Fallopia complex in central-western Europe. Plant Biol. 12(1): 215–223. DOI: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2009.00219.x
Liu Y.G., Chen S.L. & Li B.F. 2007. Genetic differentiation among common and selected hatchery populations of flounder: evidence from RAPD. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 35(10): 689–695. DOI: 10.1016/j.bse.2007.04.012
Milner M., Bansode A.G., Lawrence A.L., Nevagi S.A., Patwardhan V. & Modak S.P. 2004. Molecular phylogeny in 3-D. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 6(2): 189–200. PMID: 15119827
Morse A.M., Peterson D.G., Islam-Faridi M.N., Smith K.E., Magbanua Z., Garcia S., Kubisiak T.L., Amerson H.V. et al. 2009. Evolution of genome size and complexity in Pinus. PLoSONE 4(2): e4332. DOI: 10.1371.journal.pone.0004332
Nei M. 1987. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. Columbia University Press, New York, Guildford, Surrey, 512 pp. ISBN: 0231063210, 9780231063210
Nei M. & Kumar S. 2000. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, New York, 333 pp. ISBN-10: 0195135857, ISBN-13: 978-0195135855
Nybom H. 2004. Comparison of different nuclear DNA markers for estimating intraspecific genetic diversity in plants. Mol. Ecol. 13(5): 1143–1155. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02141.x
Obornik M., Klic M. & Zozka L. 2000. Genetic variability and phylogeny inferred from random amplified polymorphic DNA data reflect life strategy of enthopathogenic fungi. Can J. Bot. 78(9): 1150–1155. DOI: 10.1139/cjb-78-9-1150
Oliver K.R. & Greene W.K. 2009. Transposable elements: powerful facilitators of evolution. BioEssays 31(7): 703–714. DOI: 10.1002/bies.200800219
Pélé J., Abdi H., Moreau M., Thybert D. & Chabbert M. 2011. Multidimensional scaling reveals the main evolutionary pathways of class A G-protein-coupled receptors. PLoS ONE 6(4): e19094. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019094
Pfeiffer I., Brening B. & Kutschera U. 2005. Molecular phylogeny of selected predaceous leeches with reference to the evolution of body size and terrestrialism. Theor. Biosci. 124(1): 55–64. DOI: 10.1016/j.thbio.2005.05.002
Polok K. 2007. Molecular Evolution of the Genus Lolium L. Studio Poligrafii Komputerowej “SQL”, Olsztyn, 317 pp. ISBN: 8388125524, 9788388125522
Polok K., Sawicki J., Kubiak K., Szczecińska M., Korzekwa K., Szandar K. & Zielinski R. 2005a. Evolutionary divergence within Pellia endiviifolia (Dicks.) Dum. from Poland, pp. 241–252. In: Prus-Głowacki W. & Pawlaczyk M.E. (eds), Variability and Evolution: New Perspectives, Wydawnictwo Naukowe UAM, Poznan, 562 pp. ISBN: 83-232-1599-5
Polok K., Urbaniak L., Korzekwa K., Androsiuk P., Ciągło S., Kubiak K. & Zielinski R. 2005b. Genetic similarity of Pinus sylvestris populations on the base of DNA markers, pp. 253–267. In: Prus-Glowacki W. & Pawlaczyk E. (eds), Variability and Evolution: New Perspectives, Wydawnictwo Naukowe UAM, Poznan, 562 pp. ISBN: 83-232-1599-5
Polok K. & Zielinski R. 2011. Mutagenic treatment induces high transposon variation in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Acta Agr. Slov. 97(3): 179–188. DOI: 10.2478/v10014-011-0012-x
Siddall M.E. 2002. Phylogeny of the leech family Erpobdellidae (Hirudinida: Oligochaeta). Invertebr. Syst. 16: 1–6. DOI: 10.1071/IT01011
Siddall M.E, Budinoff R.B. & Borda E. 2005. Phylogenetic evaluation of systematics and biogeography of the leech family Glossiphoniidae. Invertebr. Syst. 19(2): 105–112. DOI: 10.1071/IS04034
Siddall M.E., Min G.-S., Fontanella F.M., Phillips A.J. & Watson S.C. 2011. Bacterial symbiont and salivary peptide evolution in the context of leech phylogeny. Parasitology 138(13): 1815–1827. DOI: 10.1017/S0031182011000539
Sket B. & Trontelj P. 2008. Global diversity of leeches (Hirudinea) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 595(1): 129–137. DOI: 10.1007/s10750-007-9010-8
Sole-Cava A.M. & Thorpe J.P. 1991. High levels of genetic variation in natural populations of marine lower invertebrates. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 44(1): 65–80. DOI: 10.1111/j.1095-8312.1991.tb00607.x
Spiridonova L.N., Korobitsyna K.V., Yakimenko L.V. & Bogdanov A.S. 2008. Genetic differentiation of subspecies of the house mouse Mus musculus and their taxonomic relationships inferred from RAPD-PCR data. Russ. J. Genet. 44(6): 732–739. DOI: 10.1134/S1022795408060148
Szczecinska M., Sawicki J., Polok K., Holdynski Cz. & Zielinski R. 2006. Comparison of three Polygonatum species from Poland based on DNA markers. Ann. Bot. Fenn. 45: 379–388.
Trontelj P., Sotler M. & Verovnik R. 2004. Genetic differentiation between two species of the medicinal leech, Hirudo medicinalis and the neglected H. verbena, based on randomamplified polymorphic DNA. Parasitol. Res. 94(2): 118–124. DOI: 10.1007/s00436-004-1181-x
Utevsky S., Kovalenko N., Doroshenko K., Petrauskiene L. & Klymenko V. 2009. Chromosome numbers for three species of medicinal leeches (Hirudo spp.). Syst. Parasitol. 74(2): 95–102. DOI: 10.1007/s11230-009-9198-2
Verovnik R., Trontelj P. & Sket B. 1999. Genetic differentiation and species status within the snail leech Glossiphonia complanata aggregate (Hirudinea: Glossiphoniidae) revealed by RAPD analysis. Arch. Hydrobiol. 144(3): 327–338.
Williams J.I. & Burreson E.M. 2006. Phylogeny of the fish leeches (Oligochaeta, Hirudinida, Piscicolidae) based on nuclear and mitochondrial genes and morphology. Zool. Scr. 35(6): 627–639. DOI: 10.1111/j.1463-6409.2006.00246.x
Wong C.L., Ng S.M. & Phang S.M. 2007. Use of RAPD in differentiation of selected species of Sargassum (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 19(6): 771–781. DOI: 10.1007/s10811-007-9236-x
Yeh F.C., Yang R.C., Boyle T.B.J., Ye Z.H. & Mao J.X. 2000. POPGENE, the user-friendly shareware for population genetic analysis. Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Centre, University of Alberta, Canada. http://www.ualberta.ca/?fyeh/index.htm http://www.ualberta.ca/?fyeh/popgene.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bielecki, A., Polok, K. Genetic variation and species identification among selected leeches (Hirudinea) revealed by RAPD markers. Biologia 67, 721–730 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-012-0063-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-012-0063-4