Abstract
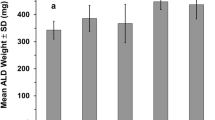
Glucocorticoids help animals respond to stressors but excessive glucocorticoids cause muscle atrophy, while insulin can promote anabolism and growth. In order to compare the glucocorticoids-induced ultrastructural changes between skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, and investigate the preventive effects of insulin on the changes, eighteen male chicks with similar initial weight were randomly divided into three groups. The two test groups were respectively treated with high-dose dexamethasone alone or together with low-dose insulin by intraperitoneal injection, and the control group was treated with an equal volume of saline solution. The experiment lasted for ten days, and then the body weight, muscle size and ultrastructure in skeletal and cardiac muscles of twelve chicks were qualitatively or quantitatively analyzed. The results showed that high-dose dexamethasone induced obvious skeletal and cardiac muscle atrophy. The differences of ultrastructural changes between skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle (such as for the former or the latter, the intermyofibrillar-and-interfilamentary spaces reducing or enlarging, the mitochondria swelling seriously or enlarging lightly, the myofibril filaments compacting or loosing) suggested that dexamethasone induced skeletal and cardiac muscle atrophy by different mechanisms. Low-dose insulin did not affect the dexamethasone-induced decreases of body weight and skeletal muscle size, but alleviated lightly the dexamethasone-induced ultrastructural changes in skeletal muscle. Different from skeletal muscle, low-dose insulin almost resisted the dexamethasone-induced ultrastructural changes in cardiac muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amthor H., Macharia R., Navarrete R., Schuelke M., Brown S.C., Otto A., Voit T., Muntoni F., Vrbóva G., Partridge T., Zammit P., Bunger L. & Patel K. 2007. Lack of myostatin results in excessive muscle growth but impaired force generation. PNAS 104(6): 1835–1840. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0604893104
Auclair D., Garrel D.R., Chaouki Zerouala A. & Ferland L.H. 1997. Activation of the ubiquitin pathway in rat skeletal muscle by catabolic doses of glucocorticoids. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 272(3): C1007–C1016. PMID: 9124503
Azad M.A.K., Kikusato M., Sudo S., Amo T. & Toyomizu M. 2010. Time course of ROS production in skeletal muscle mitochondria from chronic heat-exposed broiler chicken. Comp. Biochem. Phys. A: Mol. Integr. Physiol. 157(3): 266–271. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.07.011
Baehr L.M., David Furlow J. & Bodine S.C. 2010. The Role of MuRF1 in Glucocorticoid Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. FASEB J. 24 (Meeting Abstract Supplement): 989.7. http://www.fasebj.org/cgi/content/meetingabstract/24/1 MeetingAbstracts/989.7
Barazzoni R., Zanetti M., Bosutti A., Stebel M., Cattin L., Biolo G. & Guarnieri G. 2004. Myostatin expression is not altered by insulin deficiency and replacement in streptozotocindiabetic rat skeletal muscles. Clinical Nutrition 23(6): 1413–1417. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2004.06.007
Chen Y.W., Cao L.Z., Ye J.W. & Zhu D.H. 2009. Upregulation of myostatin gene expression in streptozotocininduced type 1 diabetes mice is attenuated by insulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 388(1): 112–116. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.07.129
Cohn R.D., Liang H.Y., Shetty R., Abraham T. & Wagner K.R. 2007. Myostatin does not regulate cardiac hypertrophy or fibrosis. Neuromuscular Disorders 17(4): 290–296. DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2007.01.011
Combaret L., Adegoke O.A.J., Bedard N., Baracos V., Attaix D. & Wing S.S. 2005. USP19 is a ubiquitin-specific protease regulated in rat skeletal muscle during catabolic states. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.288: E693–E700. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00281.2004
Dong H., Lin H., Jiao H.C., Song Z.G., Zhao J.P. & Jiang K.J. 2007. Altered development and protein metabolism in skeletal muscles of broiler chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) by corticosterone. Comp. Biochem. Phys. A: Mol. Integr. Physiol. 147(1): 189–195. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.12.034
Du R., An X.R., Chen Y.F. & Qin J. 2007. Some motifs were important for myostatin transcriptional regulation in sheep. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 40(4): 547–553. PMID: 17669271
Fujita S., Rasmussen B.B., Cadenas J.G., Grady J.J. & Volpi E. 2006. Effect of insulin on human skeletal muscle protein synthesis is modulated by insulin-induced changes in muscle blood flow and amino acid availability. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 291(4): E745–E754. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00271.2005
Gilson H., Schakman O., Combaret L., Lause P., Grobet L., Attaix D., Ketelslegers J. M. & Thissen, J. P. 2007. Myostatin gene deletion prevents glucocorticoid-induced muscle atrophy. Endocrinology 148(1): 452–460. DOI: 10.1210/en.2006-0539
Hasselgren P.O. 1999. Glucocorticoids and muscle catabolism. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2(3): 201–205. PMID: 10456248
Hull K.L., Cockrem J.F., Bridges J.P., Candy E.J. & Davidson C.M. 2007. Effects of corticosterone treatment on growth, development, and the corticosterone response to handling in young Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Comp. Biochem. Phys. A: Mol. Integr. Physiol. 148(3): 531–543. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.06.423
Kimball S.R., Horetsky R.L. & Jefferson L.S. 1998. Signal transduction pathways involved in the regulation of protein synthesis by insulin in L6 myoblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 274(1): C221–C228. PMID: 9458731
Kimball S.R., Jurasinski C.V., Lawrence Jr J.C. & Jefferson L.S. 1997. Insulin stimulates protein synthesis in skeletal muscle by enhancing the association of eIF-4E and eIF-4G. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol.272(2): C754–C759. PMID: 9124320
Komamura K., Shirotani-Ikejima H., Tatsumi R., Tsujita-Kuroda Y., Kitakaze M., Miyatake K., Sunagawa K. & Miyata T. 2003. Differential gene expression in the rat skeletal and heart muscle in glucocorticoid-induced myopathy: analysis by microarray. Cardiovasc. Drugs. Ther. 17(4): 303–310. DOI: 10.1023/A:1027352703783
Lang C.H., Silvis C., Nystrom G. & Frost R.A. 2001. Regulation of myostatin by glucocorticoids after thermal injury. FASEB J. 15: 1807–1809. PMID: 11481237
Lin H., Sui S.J., Jiao H.C., Buyse J. & Decuypere E. 2006. Impaired development of broiler chickens by stress mimicked by corticosterone exposure. Comp. Biochem. Phys. A: Mol. Integr. Physiol. 143(3): 400–405. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.12.030
Liu Z.Q., Li G.L., Kimball S.R., Jahn L.A. & Barrett E.J. 2004. Glucocorticoids modulate amino acid-induced translation initiation in human skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 287(2): E275–E281. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00457. 2003
Ma K., Mallidis C., Artaza J., Taylor W., Gonzalez-Cadavid N. & Bhasin S. 2001. Characterization of 5′-regulatory region of human myostatin gene: regulation by dexamethasone in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 281(6): E1128–E1136. PMID: 11701425
Ma K., Mallidis C., Bhasin S., Mahabadi V., Artaza J., Gonzalez-Cadavid N., Arias J. & Salehian B. 2003. Glucocorticoidinduced skeletal muscle atrophy is associated with upregulation of myostatin gene expression. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 285(2): E363–E371. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00487.2002
Marinovic A.C., Zheng B., Mitch W.E. & Price S.R. 2002. Ubiquitin (UbC) expression in muscle cells is increased by glucocorticoids through a mechanism involving Sp1 and MEK1. J. Biol. Chem. 277(19): 16673–16681. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M200501200
Morissette M.R., Cook S.A., Foo S.Y., McKoy G., Ashida N., Novikov M., Scherrer-Crosbie M., Li L., Matsui T., Brooks G. & Rosenzweig A. 2006. Myostatin regulates cardiomyocyte growth through modulation of akt signaling. Circulation Res. 99(1): 15–24. DOI: 10.1161/01.RES.0000231290.45676.d4
O’Connor P.M.J., Kimball S.R., Suryawan A., Bush J.A., Nguyen H.V., Jefferson L.S. & Davis T.A. 2003. Regulation of translation initiation by insulin and amino acids in skeletal muscle of neonatal pigs. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 285(1): E40–E53. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00563.2002
Orellana R.A., Gazzaneo M.C., Wilson F.A., Nguyen H.V., Suryawan A., Almonaci R. & Davis T.A. 2009. Insulin accelerates global and mitochondrial protein synthesis rates in neonatal muscle during sepsis. FASEB J. 23 (Meeting Abstract Supplement): 33.2. http://www.fasebj.org/cgi/content/meeting abstract/23/1 MeetingAbstracts/33.2
Paul M.K. & Mukhopadhyay A.K. 2007. Cancer — the mitochondrial connection. Biologia 62(4): 371–380. DOI: 10.2478/s11756-007-0094-4
Penner G., Gang G., Sun X., Wray C. & Hasselgren, P.O. 2002. C/EBP DNA-binding activity is upregulated by a glucocorticoid-dependent mechanism in septic muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 282(2): R439–R444. DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00512.2001
Qi D. & Rodrigues B. 2007. Glucocorticoids produce whole body insulin resistance with changes in cardiac metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 292(3): E654–E667. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00453.2006
Sandri M., Sandri C., Gilbert A., Skurk C., Calabria E., Picard A., Walsh K., Schiaffino S., Lecker S.H. & Goldberg A.L. 2004. Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell 117(3): 399–412. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00400-3
Schakman O., Gilson H. & Thissen J.P. 2008a. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced myopathy. J. Endocrinol. 197(1): 1–10. DOI: 10.1677/JOE-07-0606
Schakman O., Kalista S., Bertrand L., Lause P., Verniers J., Ketelslegers J.M. & Thissen J.P. 2008b. Role f Akt/GSK-3β/β-Catenin transduction pathway in the muscle anti-atrophy action of insulin-like growth factor-I in glucocorticoid-treated rats. Endocrinology 149(8): 3900–3908. DOI: 10.1210/en.2008-0439
Shah O.J., Kimball S.R. & Jefferson L.S. 2000a. Acute attenuation of translation initiation and protein synthesis by glucocorticoids in skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 278(1): E76–E82.
Shah O.J., Kimball S.R. & Jefferson L.S. 2000b. Among translational effectors, p70S6k is uniquely sensitive to inhibition by glucocorticoids. Biochem. J. 347(Pt2): 389–397. PMID: 10749668
Stump C.S., Short K.R.., Bigelow M.L., Schimke J.M. & Sreekumaran N.K. 2003. Effect of insulin on human skeletal muscle mitochondrial ATP production, protein synthesis, and mRNA transcripts. PNAS 100(13): 7996–8001. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1332551100
Yuan L., Lin H., Jiang K.J., Jiao H.C. & Song Z.G.. 2008. Corticosterone administration and high-energy feed results in enhanced fat accumulation and insulin resistance in broiler chickens. Brit. Poultry Sci. 49(4): 487–495. DOI: 10.1080/00071660802251731
Zheng B., Ohkawa S., Li H., Roberts-Wilson T.K. & Russ Price S. 2010. FOXO3a mediates signaling crosstalk that coordinates ubiquitin and atrogin-1/MAFbx expression during glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. FASEB J. 24(8): 2660–2669. DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-151480
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, J., Du, R., Yang, Y. et al. Effect of insulin on dexamethasone-induced ultrastructural changes in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Biologia 67, 602–609 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-012-0031-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-012-0031-z