Abstract
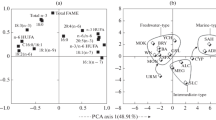
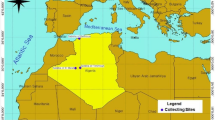
In this study, Artemia salina cysts collected from four Tunisian hypersaline environments were characterized using biometrical, biological and biochemical descriptors. Biometrical analysis revealed that the mean diameter value ranged from 220.25 to 237.76 μm, for the untreated cysts, from 199 to 224.52 μm for decapsulated cysts and that the chorion thickness ranged from 6.62 to 10.58 μm. 48 h after hatching, Artemia from Sebkha El Meleh, Sebha Moknine, Sfax saltworks and Sahline saltworks presented a hatching percentage of 52.7%, 53.75%, 70.16% and 43.74%, respectively. The length of the freshly hatched instar I nauplii varied from 429 to 449.34 μm. The fatty acids profile showed that the n-3 series was strongly dominant in the samples collected from Sebkha Moknine and Sfax saltworks, representing a percentage ranging from 17.92% to 22.45% of the total fatty acids. The data collected in this study can be useful to add new information on biological and biochemical characterization of Artemia strains present in Tunisia. On the basis of fatty acid profile, the Artemia strains collected from Sahline saltworks, Sfax saltworks and Sebkha El Meleh can be as classified as “marine” type, and that from Sebha of Moknine as “freshwater” type.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abatzopoulos T.J., Baxevanis A.D., Triantaphyllidis G.V., Criel G., Pador E.L., Van Stappen G. & Sorgeloos P. 2006. Quality evaluation of Artemia urmiana Günther (Urmia Lake, Iran) with special emphasis on its particular cyst characteristics (International Study on Artemia LXIX). Aquaculture 254(1–4): 442–454. DOI: 10.1016/j.aquacu1ture.2005.11.007
Abatzopoulos T.J., Beardmore J.A., Clegg J.S. & Sorgeloos P. (eds) 2002. Artemia Basic and Applied Biology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, London, Boston, 286 pp. ISBN-10: 1402007469
Abatzopoulos T.J., Zhang B. & Sorgeloos P. 1998. International study on Artemia. LIX Artemia tibetiana: preliminary characterization of a new Artemia species found in Tibet (People’s Republic of China). Int. J. Salt Lake Res 7(1): 41–44. DOI: 10.1023/A:1009073111231
Ayadi H., Abid O., Elloumi J., Bouain A. & Sime-Ngando T. 2004. Structure of the phytoplankton communities in two lagoons of different salinity in the Sfax saltern (Tunisia). J. Plankton Res. 26(6): 669–679. DOI: 10.1093/plankt/fbh047
Baxevanis A.D., Kappas I. & Abatzopoulos T.J. 2006. Molecular phylogenetics and asexuality in the brine shrimp Artemia. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 40(3): 724–738. DOI: 10.1016/j.ympev.2006.04.010
Beck A.D. & Bengtson D.A. 1982. International study on Artemia. XXII. Nutrition in aquatic toxicology: diet quality of geographical strains of Artemia: effect on survival and growth of larval Atlantic silverside Menidia menidia, pp. 249–259. In: Persoone G., Sorgeloos P., Roels D. & Jaspers E. (eds), The Brine Shrimp Artemia, Vol. 1, Morphology, Genetics, Radiobiology, Toxicology, Universa Press, Wettern, Belgium, 318 pp.
Ben Naceur H., Ben Rejeb Jenhani A., El Cafsi M. & Romdhane M.S. 2008a. Determination of biological characteristics of Artemia salina (Crustacea: Anostraca) population from Sabkhet Sijoumi (NE Tunisia). Transit. Waters Bull 2(3): 65–74. DOI: 10.1285/i1825229Xv2n3p65
Ben Naceur H., Ben Rejeb Jenhani A. & Romdhane M.S. 2008b. Valorisation De l’Artemia (Crustacea; Branchiopoda) de la saline de Sahline (Sahel Tunisien) = Development of Artemia (Crustacea; Branchiopoda) from Sahline salt marsh (Sahel of Tunisia). Bull. Soc. Zool. Fr. 133(1–3): 185–192.
Ben Naceur H., Ben Rejeb Jenhani A. & Romdhane M.S. 2009. New distribution record of the brine shrimp Artemia (Crustacea, Branchiopoda, Anostraca) in Tunisia. Check List 5(2): 281–288.
Bengtson D.A., Leger P. & Sorgeloos P. 1991. Use of Artemia as a food source for aquaculture, pp. 255–285. In: Browne R.A., Sorgeloos P. & Trotman C.N.A. (eds), Artemia Biology, CRC Press, Boca Raton. ISBN: 0849367298, 9780849367298
Browne R.A. & MC Donald G. 1982. Biogeography of the brine shrimp Artemia: Distribution of parthenogenetic and sexual populations. J. Biogeogr. 9(4): 331–338.
Camargo W.N., Ely J.S. & Sorgeloos P. 2003. Morphometric characterization of thalassohaline Artemia populations from the Colombian Caribbean. J. Biogeogr. 30(5): 697–702. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2699.2003.00831.x
Camargo W.N., Gabriel C.D., Orlando C.R., Licet C.H., Juan-Carlos G.L., Igor M.M. & Sorgeloos P. 2005. Determination of biological and physicochemical parameters of Artemia franciscana strains in hypersaline environments for aquaculture in the Colombian Caribbean. Saline Syst. 1: 9. DOI: 10.1186/1746-1448-1-9
Cole G.A. & Brown R.J. 1967. Chemistry of Artemia habitats. Ecology 48(5): 858–861. DOI: 10.2307/1933745
Dhont J. & Sorgeloos P. 2002. Applications of Artemia. Chapter 7, pp. 251–272. In: Abatzopolous T.J., Beardmore J.A., Clegg J.S. & Sorgeloos P. (eds), Artemia: Basic and Applied Biology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht. ISBN: 978-1-4020-0746-0
El-Magsodi M.O., El-Ghebli H.M., Hamza M., Van Stappen G.& Sorgeloss P. 2005. Characterization of Libyan Artemia from Abu Camash Sabkha. Libyan J. Mar. Sci. 10: 19–30.
Folch J., Lees M. & Stanley G.H.S. 1957. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226(1): 497–509. PMID: 13428781
Gajardo G., Abatzopoulos T.J., Kappas I. & Beardmore J.A. 2002. Evolution and speciation. Chapter 5, pp. 225–250. In: Abatzopoulos T.J., Beardmore J.A., Clegg J.S., Sorgeloos P. (eds), Artemia: Basic and Applied Biology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht. ISBN-10: 1402007469
Green A.J., Sanchez M.I., Amat F., Figuerola J., Hontoria F., Ruiz O. & Hortas F. 2005. Dispersal of invasive and native brine shrimps Artemia (Anostraca) via waterbirds. Limnol. Oceanogr. 50(2): 737–742. DOI: 10.2307/3597749
Guermazi W., Elloumi J., Ayadi H., Bouain A. & Aleya L. 2008. Coupling changes in fatty acid and protein composition of Artemia salina with environmental factors in the Sfax solar saltern (Tunisia). Aquat. Living Resour. 21(1): 63–73. DOI: 10.1051/alr:2008013
Hontoria F. & Amat F. 1992. Morphological characterization of adult Artemia (Crustacea, Branchiopoda) from different geographical origins. American populations. J. Plankton Res. 14(10): 1461–1471. DOI: 10.1093/plankt/14.10.1461
Kara M.H., Bengraine K.A., Derbal F., Chaoui L. & Amarouayache M. 2004. Quality evaluation of a new Artemia from Chott Marouane (Northeast Algeria). Aquaculture 235(1–4): 361–369. DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.02.016
Lavens P. & Sorgeloos P. 2000. The history, present status and prospects of the availability of Artemia cysts for aquaculture. Aquaculture 181(3–4): 397–403. DOI: 10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00233-1
Lepage G. & Roy C.C. 1984. Improved recovery of fatty acid through direct transesterification without prior extraction or purification. J. Lipid Res. 25(12): 1391–1396. PMID:6530596
Léger P., Bengston D.A., Simpson K.L. & Sorgeloos P. 1986. The use and nutritional value of Artemia as a food source. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 24: 521–623.
Mahdhi A., Chaieb K., Charfeddine R., Laachkar H., Kamoun F. & Bakhrouf A. 2010. Preliminary characterization of two Tunisian Artemia salina populations. Mar. Life 17: 3–11.
Muñoz J., Gómez A., Green A.J., Figuerola J., Amat F. & Rico C. 2008. Phylogeography and local endemism of the native Mediterranean brine shrimp Artemia salina (Branchiopoda: Anostraca). Mol. Ecol. 17(13): 3160–3177. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03818.x PMID: 18510585
Mura G., Zarattini P., Delise M., Fabietti F. & Bocca A. 2000. Seasonal variation of the fatty acid profile in cyst and wild adults of the fairy shrimp Chirocephalus kerkyrensis Pesta, 1936 (Anostraca). Crustaceana 73(4): 479–495. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1163/156854000504453 http://www.jstor.org/pss/20106308
Navarro J.C., Amat F. & Sargent J.R. 1993. The lipids of the cysts of freshwater- and marine-type Artemia sp. populations from Spain. Aquaculture 102(3): 219–230. DOI:m 10.1016/0044-8486(92)90150-J
Sorgeloos P., Bossuyt E., Lavens P., Leger Ph., Vanhaecke P. & Versichele D. 1983. The use of the brine shrimp Artemia in crustacean hatcheries and nurseries, pp. 71–96. In: McVey J. P. (ed.), Mariculture, CRC Handbook of Mariculturem, Vol 1, Crustacean aquaculture, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida. ISBN: 0-8493-0220-x
Sorgeloos P., Lavens P., Leger Ph., Tackaert W. & Versichele D. 1986. Manual for the Culture and Use of Brine Shrimp Artemia in Aquaculture. Laboratory of Mariculture, State University of Ghent, Belgium, 319 pp.
Sorgeloos P., Maeza-Mesa M., Benijts F. & Persoone G. 1976. Current research on the culturing of the brine shrimp Artemia salina.L. at the State University of Ghent, Belgium, pp. 473–495. In: Persoone G. & Japsers E. (eds), Proc. 10th Europe Symp. Mar. Biol. Vol. 1., Research in Mariculture, Universa Press, Wettern, Belgium.
Triantaphyllidis G.V., Abatzopoulos T.J., Miasa E. & Sorgeloos P. 1996. International study on Artemia population from Namibia and Madagascar; cytogenetics, biometry, hatching characteristics and fatty acid profiles. Hydrobiologia 335(2): 97–106. DOI: 10.1007/BF00015271
Triantaphyllidis G.V., Abatzopoulos T.J. & Sorgeloos P. 1998. Review of the biogeography of the genus Artemia (Crustacea, Anostraca). J. Biogeogr. 25(2): 213–226. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2699.1998.252190.x
Triantaphyllidis G.V., Pilla E., Thomas K., Abatzopoulos T.J., Beardmore J.A. & Sorgeloos P. 1994. International study on Artemia: LII. Incubation of Artemia cyst samples at high temperature reveals mixed nature with Artemia franciscana cysts. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 183(2): 273–282. DOI: 10.1016/0022-0981(94)90092-2
Van Ballaer E., Versichele D., Vanhaecke P., Léger P., Abdelkader B.N., Turki S. & Sorgeloos P. 1987. Characterization of Artemia from different localities in Tunisia with regard to their use in local aquaculture, pp. 199–209. In: Sorgeloos P., Bengston D.A., Decleir W. & Jasper E. (eds), Artemia Research and its Application, Vol. 1, Morphology, Genetics, Strain Characterization, Toxicology, Universa Press, Wettern, Belgium.
Van Stappen G. 2002. Zoogeography, pp. 171–224. In: Abatzopoulos T.J., Beardmore J.A., Clegg J.S. & Sorgeloos P. (eds), Artemia: Basic and Applied Biology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht. ISBN: 978-1-4020-0746-0
Van Stappen G., Lavens P. & Sorgeloos P. 1998. Effects of hydrogen peroxide treatment in Artemia cysts of different geographical origin. Arch. Hydrobiol. Spec. Iss. Adv. Limnol 52: 281–296. DOI: 321 http://www.mendeley.com/research/effect-h2o2-treatment-artemia-cystspdf/
Van Stappen G., Sui L., Xin N. & Sorgeloos P. 2003. Characterization of high-altitude Artemia populations from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, PR China. Hydrobiologia 500: 179–192. DOI: 10.1007/978-94-007-1084-912
Vanhaecke P. & Sorgeloos P. 1980. International study on Artemia. IV. The biometrics of Artemia strains from different geographical origin, pp. 393–405. In: Persoone G., Sorgeloos P., Roels O. & Jaspers E. (eds), The Brine Shrimp Artemia, Vol. 3, Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium.
Vanhaecke P., Tackaert W. & Sorgeloos P. 1987. The biogeography of Artemia: an updated review, pp. 129–155. In: Sorgeloos P., Bengston D.A., Decleir W. & Jaspers E. (eds), Artemia Research and its Applications, Vol. 1, Morphology, Genetics, Strain Characterization, Toxicology, Universal Press, Wetteren, Belgium.
Vu Do Q. & Nguyen N.L. 1987. Inoculation of Artemia in experimental ponds in central Vietnam: an ecological approach and a comparison of three geographical strains, pp. 253–269. In: Sorgeloos P., Bengston D.A., Decleir W. & Jaspers E. (eds), Artemia Research and its Applications, Vol. 3, Morphology, Genetics, Strain, Characterization, Toxicology, Universal Press,Wetteren, Belgium.
Watanabe T., Oowa F., Kitajima C. & Fujita S. 1980. Relationship between dietary value of brine shrimp Artemia salina and their content of W3 highly unsaturated fatty acids. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 46: 35–41.
Webster C.D. & Lovell R.T. 1991. Lipid composition of three geographical sources of the brine shrimp nauplii (Artemia sp). Comp. Biochem. Physiol 100(3): 555–559. DOI: 10.1016/0305-0491(91)90219-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahdhi, A., Messina, C., Kamoun, F. et al. Determination of biological characteristics of Tunisian Artemia salina populations. Biologia 67, 143–150 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-011-0149-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-011-0149-4