Abstract
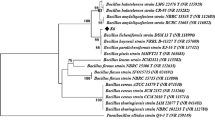
A facultatively anaerobic, thermophilic, xylanolytic bacterium was isolated from a sample collected from the Diyadin Hot Springs, Turkey. According to morphological, biochemical and molecular identification, this new strain was suggested to be representative of the Anoxybacillus pushchinoensis and it was designated as Anoxybacillus pushchinoensis strain A8. It exhibited 97% similarity to 16S rRNA gene sequence of A. pushchinoensis and 77% DNA homology by DNA-DNA hybridization studies. Q-sepharose and CM-sepharose chromatography was used to purify an extracellular xylanase to >90% purity from this species. The enzyme had a molecular mass of approximately 83 kDa. The enzyme showed optimum activity at pH 6.5 and it was 96% stable over a broad pH range of 6.5–11 for 24 hours. The enzyme had optimum activity at 55°C and it was 100% stable at temperature between 50–60°C up to 24 hours. Kinetic characterization of the enzyme was performed at temperature optima (55°C) and Vmax and K m were found to be 59.88 U/mg protein and 0.909 mg/mL, respectively. Oat spelt xylan but not xylooligosaccharides was degraded by the enzyme and xylose was the only product detected from oat xylan degradation. This suggested that the enzyme was an exo-acting xylanase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S., Scopes R.K., Rees G. & Patel B.K.C. 2000. Saccharococcus caldoxylolyticus sp. nov., an obligately thermophilic, xylose-utilizing, endospore-forming bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50: 517–523.
Becker P., Abu-Reesh I. & Markossian S. 1997. Determination of the kinetic parameters during continuous cultivation of the lipase-producing thermophile Bacillus sp. IHI-91 on olive oil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 48: 184–190.
Beffa T., Blanc M., Lyon P.F., Vogt G., Marchiani M., Fischer J.L. & Aragno M. 1996. Isolation of Thermus strains from hot composts (60 to 80°C). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 1723–1727.
Beg O.K., Bhushan B., Kapoor M. & Hoondal G.S. 2000. Production and characterization of thermostable xylanase and pectinase from Streptomyces sp. QG-11-3. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24: 396–402.
Belduz A.O., Dulger S. & Demirbag Z. 2003. Anoxybacillus gonensis sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic, xylose-utilizing, endospore-forming bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53: 1315–1320.
Benson D.A., Karsch-Mizrachi I., Lipman D.J., Ostell J. & Wheeler D.L. 2007. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 35 (Database Issue): D21–D25.
Bergquist P.L. & Morgan H.W. 1992. The molecular genetics and biotechnological application of enzyme from extremely thermophilic eubacteria, pp. 44–75. In: Herbert R.A. & Sharp R.J. (eds), Molecular Biology and Biotechnology of Extremophiles, Chapman & Hall, New York.
Blanco A., Diaz P., Zueco J., Parascandola P. & Pastor F.I.J.A. 1999. A multidomain xylanase from a Bacillus sp. with a region homologous to thermostabilizing domains of thermophilic enzymes. Microbiology 145: 2163–2170.
Brosius J., Palmer M.L., Kennedy P.J. & Noller H.F. 1978. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75: 4801–4805.
Charnock S.J., Bolam D.N., Turkenburg J.P., Gilbert H.J., Ferreira L.M.A., Davies G.J. & Fontes C.M.G.A. 2000. The X6 “thermostabilizing” domains of xylanases are carbohydratebinding modules: structure and biochemistry of the Clostridium thermocellum X6b domain. Biochemistry 39: 5013–5021.
Coutinho P.M. & Henrissat B. 1999b. The modular structure of cellulases and other carbohydrate-active enzymes: an integrated database approach, pp. 15–23. In: Genetics, Biochemistry and Ecology of Cellulose Degradation (Ohmiya K., Hayashi K., Sakka K., Kobayashi Y., Karita S. & Kimura T., eds), Uni Publishers Company, Tokyo.
De Ley J., Cattoir H. & Reynaerts A. 1970. The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur. J. Biochem. 12: 133–142.
Dulger S., Demirbag Z. & Belduz A.O. 2004. Anoxybacillus ayderensi ssp. nov. and Anoxybacillus kestanbolensis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54: 1499–1503.
Dupont C., Roberge M., Shareck F., Morosoli R. & Kluepfel D. 1998. Substratebinding domains of glycanases from Streptomyces lividans: characterization of a new family of xylanbinding domains. Biochem. J. 330: 41–45.
Escara J.F. & Hutton J.R. 1980. Thermal stability and renaturation of DNA in dimethyl sulfoxide solutions: acceleration of the renaturation rate. Biopolymers 19: 1315–1327.
Fernandes A.C., Fontes C.M.G.A., Gilbert H.J., Hazlewood G.P. & Fernandes T.H. 1999. Homologous xylanases from Clostridium thermocellum: evidence for bifunctional activity, synergism between xylanase catalytic modules and the presence of xylan-binding domains in enzyme complexes. Biochem. J. 342: 105–110.
Gasparic A., Martin J., Daniel A.S. & Flint H.J. 1995. A xylan hydrolase gene cluster in Prevotella ruminicola B(1)4: sequence relationships, synergistic interactions, and oxygen sensitivity of a novel enzyme with exoxylanase and β-(1,4)-xylosidase activities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 2958–2964.
Gessesse A. 1998. Purification and properties of two thermostable alkaline xylanases from an alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 3533–3535.
Gessesse A. & Gashe B.A. 1997. Production of alkaline xylanases by an alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. isolated from na alkaline soda lake. J. Appl. Microbiol. 83: 402–406.
Huss V.A.R., Festl H. & Schleifer K.H. 1983. Studies on the spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 4: 184–192.
Johnson J.L. 1985. Determination of DNA base composition. Methods Microbiol. 18: 1–29.
Kalogeris E., Christakopoulos P., Kekos D. & Macris B.J. 1998. Studies on the solid-state production of thermostable endoxylanases from Thermoascus aurantiacus: characterization of two isozymes. J. Biotechnol. 6: 155–163.
Kambourova M., Mandeva R., Fiume I., Maurelli L., Rossi M. & Morana A. 2006. Hydrolysis of xylan at high temperature by co-action of the xylanase from Anoxybacillus flavithermus BC and the β-xylosidase/α-arabinosidase from Sulfolobus solfataricus Oα. J. Appl. Microbiol. 102: 1586–1593.
Khasin A., Alchanati I. & Shoham Y. 1993. Purification and characterization of a thermostable xylanase from Bacillus stearothermophilus T-6. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 1725–1730.
Kubata B.K., Suzuki T., Horitsu H., Kawai K. & Takamizawa K. 1994. Purification and characterization of Aeromonas caviae ME-1 xylanase V, which produces exclusively xylobiose from xylan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 531–535.
Kubata B.K., Takamizawa K., Kawai K., Suzuki T. & Horitsu H. 1995. Xylanase IV, an exoxylanase of Aeromonas caviae ME-1 which produces xylotetraose as the only low-molecular-weight oligosaccharide from xylan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 1666–1668.
Laemmli U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Lee D., Koh Y.S., Kim K.J., Kim B.C., Choi H.J., Kim D.S., Suhartono M.T. & Pyun Y.R. 1999. Isolation and characterization of a thermophilic lipase from Bacillus thermoleovorans ID-1. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 179: 393–400.
Lineweawer H. & Burk D. 1934. The determination of enzyme dissociation constant. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 56: 658–661.
Mandel M. & Marmur J. 1968. Use of ultraviolet absorbance-temperature profile for determining the guanine plus cytosine content of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 12: 195–206.
Miller G.L. 1959. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal. Chem. 31: 426–428.
Pikuta E., Cleland D. & Tang J. 2003. Aerobic growth of Anoxybacillus pushchinensis K1T: emended descriptions of A. pushchinensis and the genus Anoxybacillus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53: 1561–1562.
Pikuta E., Lysenko A., Chuvilskaya N., Mendrock U., Hippe H., Suzina N., Nikitin D., Osipov G. & Laurinavichus K. 2000. Anoxybacillus pushchinensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel anaerobic, alkaliphilic, moderately thermophilic bacterium from manure, and description of Anoxybacillus flavithermus comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50: 2109–2117.
Ratanakhanokchai K., Kyu K.L. & Tanticharoen M. 1999. Purification and properties of a xylan-binding endoxylanase from alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. strain K-1. App. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 694–697.
Sneath P.H.A. 1986. Endospore-forming gram-positive rods and cocci, pp. 1104–1207. In Sneath P.H.A., Mair N.S., Sharpe M.S. & Holt J.G. (eds), Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Vol. 2, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore.
Somogyi M. 1952. Notes on sugar determination. J. Biol. Chem. 195: 19–23.
Sonnleitner B. & Fiechter A. 1983. Advantages of using thermophiles in biotechnological processes: expectations and reality. Trends Biotechnol. 1: 74–80.
Stackebrandt E. & Goebel B.M. 1994. Taxonomic note: a place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int. J. Sys. Bacteriol. 44: 846–849.
Sunna A., Gibbs M.D. & Bergquist P.L. 2000. The thermostabilizing domain, XynA, of Caldibacillus cellulovorans xylanase is a xylan binding domain. Biochem. J. 346: 583–586.
Sunna A., Gibbs M.D. & Bergquist P.L. 2001. Identification of novel β-mannan-and β-glucan-binding modules: evidence for a superfamily of carbohydrate-binding modules. Biochem. J. 356: 791–798.
Teather R.M. & Wood P.J. 1982. Use of Congo red polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from the bovine rumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 43: 777–780.
Touzel J.P., O’Donohue M., Debeire P., Samain E. & Breton C. 2000. Thermobacillus xylanilyticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new aerobic thermophilic xylan-degrading bacterium isolated from farm soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50: 315–320.
Vandamme P., Pot B., Gillis M., De Vos P., Kersters K. & Swings J. 1996. Polyphasic taxonomy, a consensus approach to bacterial systematics. Microbiol. Rev. 60: 407–438.
Wayne L.G., Brenner D.J., Colwell R.R., Grimont P.A.D., Kandler P., Krichevsky M.I., Moore L.H., Moore W.E.C., Murray R.G.E., Stackebrandt E., Starr M.P. & Truper H.G. 1987. International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Sys. Bacteriol. 37: 463–464.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kacagan, M., Canakci, S., Sandalli, C. et al. Characterization of a xylanase from a thermophilic strain of Anoxybacillus pushchinoensis A8. Biologia 63, 599–606 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-008-0134-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-008-0134-8