Abstract
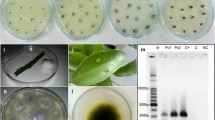
Increased incidence of leaf spots on many tree species, up to the presence of peripheral importance only, including linden trees was noticed recently. First massive and continuous occurence of the fungus Cercospora microsora Sacc. [teleomorph Mycosphaerella millegrana (Cook.) Schröet., Mycosphaerella microsora Syd.], causal agent of anthracnose on linden trees (Tilia cordata Mill.) grown in urban plantings in Slovakia was reported. Along with this, certain of the important growth characteristics of this fungus were studied under laboratory conditions. To specify Cercospora biology mycelial growth of C. microsora in pure hyphal cultures was observed in relation to medium and locality. One-way ANOVA has confirmed a statistically significant influence of both factors, culture medium and locality on growth rate values of C. microsora. The effect of these factors has not proved unambiguously in all cases. In the case of one locality (Nitra), the significant influence of used media has not been proved (P > 0.05). PDAg showed generally as the most suitable medium, inducing the most intensive growth in three localities (41.06 mm/week on average). Comparing three localities, the effect of this factor is not so unambiguous. Growth rate values from the localities Bratislava and Pribeta indicate unsuitability of medium A for the fast radial growth. A Tukey test separately conducted for the factors medium and the locality revealed the significant combinations of means (P ≤ 0.05).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GR:
-
growth rate (mm/week)
- PDAg:
-
potato-dextrose agar enriched with bromcresol green
- MA:
-
malt agar
- A:
-
water agar
References
Berry F.H. 1998. Anthracnose Diseases of Eastern Hardwoods. file://FÄnthracnose%20Diseases%20of%20Eastern%20Hardwoods20%FIDL.htm
Broembsen S.V. 2005. Anthracnose and Other Common Leaf Diseases of Deciduous Shade Trees. pods.dasnr.okstate.edu/docustare/dsweb/Get/Documnet-2831/F-7634web.pdf
Caltrider P.G. 1961. Growth and sporulation of Guignardia bid-wellii. Phytopathol. 51: 860–863.
Chung K. R. 2003. Involvement of calcium/calmodulin signaling in cercosporin toxin biosynthesis by Cercospora nicotianae. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 69: 1187–1196.
Crous P.W. & Braun U. 2003. Mycosphaerella and its anamorphs: 1. Manes published in Cercospora and Passalora. CBS Biodiverzity Series 1, 571pp.
Daub M.E. & Ehrenshaft M. 2000. The photoactivated Cercospora toxin cercosporin: Contributios to plant diesease and fundamental biology. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 38: 461–490.
Donaubauer E. 1999. On the occurrence of some leaf diseases during summer and autum 1999. Forschutz Aktuell, Abstracts, p. 25.
Heimann M.F. & Mahr D.L. 1997. Common foliage diseases of shade trees in Wisconsin. University of Wisconsin-System Board of Regents and University of Wisconsin — Extention, 170 pp.
Juhásová, G. 2002. Škodlivosť parazitických húb na lipách. Zahradnictví 6: 13.
Juhásová G., Ivanová H. & Spišák J. 2006. Biology of fungus Gnomonia leptostyla in agro-ecological environments of Slovakia. Mikologija i Fitopatologija 40: 538–547.
Kaneko R. & Kaneko S. 2004. The effect of bagging branches on levels of endophytic fungal infection in Japanese beech leaves. Forest Pathol. 34: 65–78.
Nix S. 2005. Leaf spot tree disease — Prevention and control. http://forestry.about.com/od/forestdiseases/p/dis-com-1sp.htm
Pataky N.R. 1998. Fungal leaf spot diseases of shade and ornamental trees in the midwest. Plant Disease 648: 1–8.
Pollack F.G. 1987. An annotated compilation of Cercospora names. Mycol. Mem. 12: 1–212.
Stakvilevièienë S. 1999. Influence of environmental conditions on the distribution of the cercosporoid fungi in Lithuania. Bot. Lithuanica Suppl. 3: 87–89.
Sundari K.S. & Adholey A. 2003. Growth profile of ectomycorrhizal fungi mycelium: emphasis on substrate pH influence. J. Microbiol. 83: 209–214.
Zimmermannová-Pastirčáková K. 2002. Occurrence of Horsechestnut leaf blotch and cultural characteristics of its causal agent-fungus Phyllosticta sphaeropsoidea, an anamorph of Guignardia aesculi. Folia oecologica 30: 245–250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernadovičová, S., Ivanová, H. Leaf spot disease on Tilia cordata caused by the fungus Cercospora microsora . Biologia 63, 44–49 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-008-0003-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-008-0003-5