Abstract
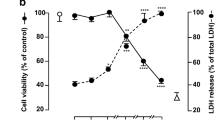
Studies indicate that leptin is involved in not only energy expenditure and food intake, but also in protection against apoptosis, in inflammation and in stimulation of proliferation in many cell types. However, leptin treatment increases the oxidative stress in many cell culture studies. This contradiction evoked a question of whether leptin acts as an oxidant or antioxidant on glial cells. We investigated the effect of leptin on glial cell survival and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced toxicity in vitro. The survival rate of the cells was determined by using 3-(4,5-D-methylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide, thyazolyl blue (MTT) method. The cells obtained from the whole brain of 1–3 day-old rat were treated with 1, 10, 100 and 1000 ng/mL leptin for 24 or 72 h. Either the pretreatment of leptin alone for 5 h or leptin combined simultaneously with H2O2 or well known antioxidant glutathione (GSH) were applied to the cells. Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were measured in cell lysates to which leptin was added for 24 h. The 100 and 1000 ng/mL leptin treatment for 72 h increased the glial viability by 19% and 36%, respectively. The dose of H2O2 that killed 75% of the cells was determined as 100 µM. GSH at different doses was applied as a positive control to the cells and the dose of 500 µM completely eliminated toxic effect of 100 µM H2O2. Either the pretreatment of leptin alone for 5 h or leptin combined simultaneously with H2O2 could not eliminate H2O2-caused toxicity. Furthermore, respective leptin doses did not change the glia MDA level. We suggest that leptin can increase glia survival dose dependently, but can not eliminate H2O2-induced oxidation in primary mixed glial cell culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’ss Medium
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- GHS:
-
glutathione
- iNOS:
-
nitric oxide synthase type II
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- MTT:
-
thyazolyl blue
References
Balasubramaniyan V., Kalaivani S.J. & Nalini N. 2003. Role of leptin on alcohol-induced oxidative stress in swiss mice. Pharmacol. Res. 47: 211–216.
Bouloumie A., Marumo T., Lafontan M. & Buse R. 1999. Leptin induces oxidative stress in human endothelial cells. FASEB J. 13: 1231–1238.
Brown R., Morash B., Ur E. & Wilkinson M. 2005. RNAi-mediated silencing of leptin gene expression increases cell death in C6 glioblastoma cells. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 139: 357–360.
Burguera B., Brunetto A., Garcia-Ocana A., Teijeiro R., Esplen J., Thomas T., Couce M.E. & Zhao A. 2006. Leptin increases proliferation of human osteosarcoma cells through activation of PI(3)-K and MAPK pathways. Med. Sci. Mon. 12: 341–349.
Couce M.E., Burguera B., Parisi J.E., Jensen M.D. & Lloyd R.V. 1997. Localization of leptin receptor in the human brain. Neuroendocrinology 66: 145–150.
Desagher S., Glowinski J. & Prement J. 1996. Astrocytes protect neurons from hydrogen peroxide toxicity. J. Neurosci. 16: 2553–2562.
Erkasap N., Ikizler M., Shneyvays V., Zinman T., Mamedova L.K., Uyar R. & Shainberg, A. 2006. Leptin protects the cardiac myocyte cultures from hypoxic damage. Life Sci. 78: 1098–1102.
Fantuzzi G. & Faggioni R. 2000. Leptin in the regulation of immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 68: 437–446.
Hosoi T., Okuma Y. & Nomura Y. 2000. Expression of leptin receptors and induction of IL-1 β transcript in glial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 273: 312–315.
Huang X.F., Koutcherov I., Lin S., Wang H.Q. & Storlien L. 1996. Localization of leptin receptor mRNA expression in mouse brain. Neuroreport 7: 2635–2638.
Iwata-Ichikawa E., Kondo Y., Miyazaki I., Asanuma M. & Ogawa N. 1999. Glial cells protect neurons against oxidative stress via transcriptional up-regulation of the glutathione synthesis. J. Neurochem. 72: 2334–2344.
Jin L., Burguera B.G., Couce M.E., Scheithauer B.W., Lamsan J., Eberhardt N.L., Kulig E. & Lloyd R.V. 1999. Leptin and leptin receptor expression in normal and neoplastic human pituitary: evidence of a regulatory role for leptin on pituitary cell proliferation. Clin. Endocrin. Metab. 84: 2903–2911.
Kitamura Y., Ota T., Matsuoka Y., Tooyama I., Kimura H., Shimohama S., Nomura Y., Gebicke-Haerter P.J. & Taniguchi T. 1999. Hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis mediated by p53 protein in glial cells. Glia 25: 154–164.
Kutlu S., Canpolat S., Aydın M., Yaşar A., Tuzcu M. & Baydas G. 2005. Exogenous leptin increases lipid peroxidation in the mouse brain. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 206: 233–236.
Mattace-Rasso G., Esposito E., Iacono A., Pacilio M., Coppola A., Bianco G., Diano S., Di Carlo R. & Meli R. 2006. Leptin induces nitric oxide synthase type II in C6 glioma cells. Role for nuclear factor-κB in hormone effect. Neurosci. Lett. 396: 121–126.
Mossmann T. 1983. Rapid colorimetric assay of cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assay. J. Immun. Methods 65: 55–63.
Oda A., Taniguchi T. & Yokoyama M. 2001. Leptin stimulates rat aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Kobe J. Med Sci 47: 141–150.
Ohkawa H., Ohishi N. & Yagi K. 1979. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 95: 351–358.
Richter-Landsberg C. & Vollgraf U. 1998. Mode of cell injury and death after hydrogen peroxide exposure in cultured oligodendroglia cells. Exp. Cell Res. 244: 218–229.
Russo V.C., Metaxas S., Kobayashi K, Haris M. & Werther G.A., 2004. Antiapoptotic effects of leptin in human neuroblastoma cells. Endocrinology 145: 4103–4112.
Shioda S., Funahashi H., Nakajo S., Yada T., Maruta O. & Nakai Y. 1998. Immunohistochemical localization of leptin receptor in the rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 243: 41–44.
Souad N. & Sanchez-Margalet V. 2002. Human leptin promotes survival of human circulating blood monocytes prone to apoptosis by activation of P42/44 MAPK pathway. Cell. Immun. 2: 143–149
Takashi N., Waelput W. & Guisez Y. 1999. Leptin is an endogenous protective protein against the toxicity by TNF. J. Exp. Med. 189: 207–212.
Tanabe K., Okuya S., Tanizawa Y. & Matsutani A. 2001. Leptin increases the viability of isolated rat pancreatic islets by suppressing apoptosis. Endocrinology 142: 4827–4830.
Tanabe K., Okuya S., Tanizawa Y., Matsutani A. & Oka Y. 1997. Leptin induces proliferation of pancreatic beta cell line MIN6 through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 241: 765–768.
Watson A.M., Poloyac S.M., Howard G. & Blouin R.A. 1999. Effect of leptin on cytochrome P-450, conjugation, and antioxidant enzymes in the ob/ob mouse. Drug Metab. Dispos. 27: 695–700.
Wiesner G., Vaz M., Collier G., Seals D., Kaye D., Jennings G., Lambert G., Wilkinson D. & Esler M. 1999. Leptin is released from the human brain: influence of adiposity and gender. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 84: 2270–2274.
Xu F.P., Chen M.S., Wang Y.Z., Yi Q., Lin S.B., Chen A.F. & Luo J.D. 2004. Leptin induces hypertrophy via endothelin-1-reactive oxygen species pathway in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Circulation 110: 1269–1275.
Zhang F., Wang S., Signore A.P. & Chen J. 2007. Neuroprotective effects of leptin against ischemic injury induced by oxygenglucose deprivation and transient cerebral ischemia. Stroke 38: 2329–2336.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabadere, S., Kus, G., Uyar, R. et al. The actions of leptin on survival and hydrogen peroxide toxicity in primary mixed glial cells of rat. Biologia 62, 793–797 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-007-0148-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-007-0148-7