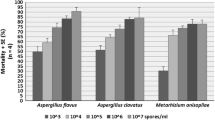
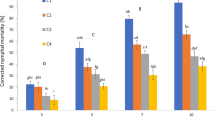
Abstract
Fungi of the order Entomophthorales (Zygomycota, Zygomycetes) constitute a group of mostly insect pathogenic species, which attracts attention of insect pathologists because of their high capacity for use in biological control of pest insects. This work primarily focuses on entomophthoralean species attacking aphids. The Entomophthorales are considered major pathogens of aphids in nature. In fact, the fungi are the only pathogens that regularly and effectively can affect aphid populations in natural ecosystems as well as in agroecosystems. Up to now, 33 entomophthoralean species organized into 9 genera have been recorded in aphid hosts. All fungal species are listed and organised by genus in the work. Descriptions are presented for all the fungal genera and species, including a nomenclature genesis, a geographical distribution, a host specificity/host range, a capability of cultivation in vitro, and possible prospects for their use in biological control strategies. A key to identification of the pathogens is provided as well. A general life cycle outline of the pathogens is followed by fundamental facts on biology and ecology of the fungi and analysis of primary factors that are involved in the study of epizootiology of infectious diseases in insect populations. The abiotic and biotic elements of the environment, which interfere in the pathogen-host interactions, are also underlined. In the last chapter, several examples are reviewed when the Entomophthorales were used against aphids within the four strategies of biological control, namely classical biological control, inoculation biological control, inundation biological control, and conservation biological control. The aim of this review is to cover the present status of knowledge about the natural enemies of aphids and to stimulate an interest of insect pathologists in this group of entomopathogenic fungi.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Mallek, A.Y., Abdel-Rahman, M.A.A. & Hamam, G.H.A. 2003. Survey of Entomopathogenic fungi naturally infecting cereal aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Southern Egypt, p. 2. In: Ehlers, R.U. (ed.) Proceedings of Abstracts of the 9th European Meeting of the IOBC/WPRS Working group “Insect Pathogens and Entomopathogenic Nematodes”, University Kiel, Kiel.
Abdel-Rahman, M.A.A. & Ali, A.M. 2003. Entomopathogenic fungi on cereal aphids in southern Egypt, p. 3. In: Ehlers, R.U. (ed.) Proceedings of Abstracts of the 9th European Meeting of the IOBC/WPRS Working group “Insect Pathogens and Entomopathogenic Nematodes”, University Kiel, Kiel.
Ali-Shtayeh, M.S., Mara’i, A.B.B.M. & Jamous, R.M. 2002. Distribution, occurrence and characterization of entomopathogenic fungi in agricultural soil in the Palestinian area. Mycopathologia 156: 235–244.
Ambethgar, V. 1996. Natural infection of the entomophthoran fungus, Pandora delphacis (Hori) Humber, on the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). J. Entomol. Res. 20: 383–385.
Anderson, S.O. 1985. Sclerotization and tanning of the cuticle, pp. 59–74. In: Kerkut, G.A. & Gilbert, L.I. (eds) Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology, Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Andreadis, T.G. 1987. Transmission, pp. 159–176. In: Fuxa, J.R. & Tanada, Y. (eds) Epizootiology of insect diseases, John Wiley, New York.
Aoki, J. 1981. Pattern of conidial discharge of an Entomophthora species (“grylli” type) (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) from infected cadavers of Mamestra brassicae Linné (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 16: 216–224.
Aoki, J. & Tanada, Y. 1974. Survival of Entomophthora spp. in laboratory cultures. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 9: 80–86.
Aruta, C. & Carvillo, R. 1989. Identification of fungi of the order Entomophthorales in Chile. III. Agro Sur 17(1): 10–14.
Austarå, Ø, Carter, C., Eilenberg, J., Halldórsson, G. & Harding, S. 1997. Natural enemies of the green spruce aphid in spruce plantations in maritime North-West Europe. Icel. Agric. Sci. 11: 113–124.
Bałazy, S. 1993. Flora of Poland. Fungi (Mycota), 24: Entomophthorales. Polish Academy of Science, W. Szafer Institute of Botany, 356 pp.
Bałazy, S., Miętkiewski, R. & Majchrowicz, I. 1990. Mikozy mszyc — ich znaczenie I perspektywy wykorzystania w ochronie roýlin. Zesz. Probl. Post. Nauk Roln. 392: 35–56.
Bałazy, S., Wiśniewski, J. & Kaczmarek, S. 1987. Some noteworthy fungi occurring on mites. Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci., Ser. Sci. Biol. 35: 199–224.
Barr, A.R. 1979. Epidemiological concepts for entomologists. Bull. Entomol. Soc. Am. 25: 129–139.
Barta, M. 2004. Fungi of the order Entomophthorales infecting aphids in Slovakia. PhD. Thesis, Nitra, Slovak University of Agriculture, 189 pp.
Barta, M. & Cagáň, L’. 2002. Prevalence of natural fungal mortality of black bean aphid, Aphis fabae Scopoli, on primary host and two secondary hosts. Acta Fytotechnica et Zootechnica 5: 57–64.
Barta, M. & Cagáň, L’. 2003a. Pandora uroleuconii sp. nov. (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae), a new pathogen of aphids. Mycotaxon 88: 79–86.
Barta, M. & Cagáň, L’. 2003b. Entomophthoralean fungi associated with common nettle aphid (Microlophium carnosum Buckton) and a potential role of nettle patches as reservoirs for the pathogens in landscape. Anz Schadl. J. Pest Sci. 76: 6–13.
Barta, M. & Cagáň, L’. 2004. A potential role of Rhopalosiphum padi (Linnaeus) colonies on winter host, Padus avium Linnaeus, as an inoculum source of fungal diseases of cereal aphids in agricultural landscape. Acta Fytotechnica et Zootechnica 7: 22–25.
Barta, M. & Cagáň, L’. 2006. Observations on the occurrence of Entomophthorales infecting aphids (Aphidoidea) in Slovakia. BioControl 47: 1–14.
Basky, Z. & Hopper, K.R. 2000. Impact of plant density and natural enemy exclosure on abundance of Diurophis noxia (Kurdjumov) and Rhopalosiphum padi (Linné) (Hom., Aphididae) in Hungary. J. Appl. Entomol. 124: 99–103.
Bateman, R. & Chapple, A. 2001. The spray applications of mycopesticide formulations, pp. 289–309. In: Butt, T.M., Jackson, C. & Magan, N. (eds) Fungi as biocontrol agents: Progress, problems and potential, CAB International.
Batko, A. 1962. Notes on Entomophthoraceous fungi in Poland. Entomophaga 2: 129–139.
Batko, A. 1964a. Notes on entomophthoraceous fungi in Poland. Entomophaga 2: 129–131.
Batko, A. 1964b. On the new genera: Zoophthora gen. nov., Triplosporium (Thaxter) gen. nov. and Entomophaga gen. nov. (Phycomycetes: Entomophthoraceae). Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci., Ser. Sci. Biol. 12: 323–326.
Batko, A. 1964c. Some new combinations in the fungus family Entomophthoraceae (Phycomycetes). Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci., Ser. Sci. Biol. 12: 403–406.
Batko, A. 1964d. Remarks on the genus Lamia Nowakowski 1883 vs. Culicicola Nieuwland 1916 (Phycomycetes: Entomophthoraceae). Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci., Ser. Sci. Biol. 12: 399–402.
Batko, A. 1964e. Remarks on the genus Entomophthora Fresenius 1856 non Nowakowski 1883 (Phycomycetes: Entomophthoraceae). Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci., Ser. Sci. Biol. 12: 319–321.
Batko, A. 1966a. A new aphidicolous fungus from Poland, Zoophthora phalloides sp. nov. (Entomophthoraceae). Acta Mycol. 2: 7–13.
Batko, A. 1966b. On the subgenera of the genus Zoophthora Batko 1964 (Entomophthoraceae). Acta Mycol. 2: 15–21.
Batko, A. 1974. Filogeneza a struktury taksonomiczne Entomophthoraceae, pp. 209–305. In: Nowiński, C. (ed.) Ewolucja biologiczna, Szkice teoretyczne i metodologiczne, Polska Akademia Nauk, Warszawa.
Batko, A. & Weiser, J. 1965. On the taxonomic position of the fungus discovered by Strong, Wells, and Apple: Strongwellsea castrans gen. et sp. nov. (Phycomycetes: Entomophthoraceae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 7: 455–463.
Baverstock, J., Roy, H.E., Clark, S.J., Alderson, P.G. & Pell, J.K. 2006. Effect of fungal infection on the reproductive potential of aphids and their progeny. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 91: 136–139.
Beauvias, A., Latgé, J.P., Vey, A. & Prevost, M.C. 1989. The role of surface components of the entomopathogenic fungus Entomophaga aulicae in the cellular immune response of Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera). J. Gen. Microbiol. 135: 489–498.
Bechinger, C., Giebel, K.F., Schnell, M., Leiderer, P., Deising, H.B. & Bastmeyer, M. 1999. Optical measurements of invasive forces exerted by appressoria of a plant pathogenic fungus. Science (Washington, D.C.) 285: 1896–1899.
Behrens, U. 1993. Entomophthora fungi for control of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Växtskyddsnotiser 57: 22–26.
Benz, G. 1987. Environment, pp. 117–242. In: Fuxa, J.R. & Tanada, Y. (eds) Epizootiology of insect diseases, John Wiley, New York.
Ben-Ze’ev, I. 1982. Erynia neopyralidarum sp. nov. and Conidiobolus apiculatus, pathogens of pyralid moths components of misdescribed species Entomophthora pyralidarum (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). Mycotaxon 14: 273–292.
Ben-Ze’ev, I., Bitton, S. & Kenneth, R.G. 1990. Induction and inhibition of germination in Neozygites fresenii (Entomophthorales: Neozygitaceae) zygospores by various time-temperature stimuli. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 55: 1–10.
Ben-Ze’ev, I. & Kenneth, R.G. 1979. Zoopthora erinacea sp. nov. (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae), a fungal parasite of aphids. Mycotaxon 10: 219–232.
Ben-Ze’ev, I. & Kenneth, R.G. 1980. Zoophthora phytonomi and Conidiobolus osmodes (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae), two pathogens of Hypera species (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) coincidental in time and place. Entomophaga 25: 171–186.
Ben-Ze’ev, I. & Kenneth, R.G. 1981. Zoophthora orientalis sp. nov., a fungal pathogen of Aphis citricola (Homoptera: Aphididae), and two new combinations of other species of Entomophthoraceae. Phytoparasitica 9: 33–42.
Ben-Ze’ev, I. & Kenneth, R.G. 1982a. Features-criteria of taxonomic value in the Entomophthorales: I. A revision of the Batkoan classification. Mycotaxon 14: 393–455.
Ben-Ze’ev, I. & Kenneth, R.G. 1982b. Features-criteria of taxonomic value in the Entomophthorales: II. A revision of the genus Erynia Nowakowski 1881 (= Zoophthora Batko 1964). Mycotaxon 14: 456–475.
Ben-Ze’ev, I., Kenneth, R.G., Bitton, S. & Soper, R.S. 1984. The Entomophthorales of Israel and their arthropod hosts: seasonal occurrence. Phytoparasitica 12: 167–176.
Ben-Ze’ev, I., Kenneth, R.G. & Uziel, A. 1987. A reclassification of Entomophthora turbinata in Thaxterosporium gen. nov., Neozygitaceae fam. nov. (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae). Mycotaxon 28: 313–326.
Ben-Ze’ev, I. & Uziel, A. 1979. Monellia costalis (Fitch), a new host for Zoophthora radicans (Brefeld) Batko and Entomophthora planchoniana Cornu (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae) in Israel. Phytoparasitica 7: 159–167.
Bitton, S., Kenneth, R.G. & Ben-Ze’ev, I. 1979. Zygospore overwintering and sporulative germination in Triplosporium fresenii (Entomophthoraceae) attacking Aphis spiraecola on citrus in Israel. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 34: 295–302.
Boguś, M.I. & Scheller, K. 2002. Extraction of an insecticidal protein fraction from the parasitic fungus Conidiobolus coronatus (Entomophthorales). Acta Parasit. 46: 66–72.
Boucias, D.G. & Latgé, J.P. 1988. Nonspecific induction of germination of Conidiobolus obscurus and Nomuraea rileyi with host and non-host cuticle extracts. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 51: 168–171.
Boucias, D.G. & Pendland, J.C. 1991. Attachment of mycopathogens to cuticle: the initial event of mycosis in arthropod hosts, pp. 101–128. In: Cole, G.T. & Hoch, H.C. (eds) The fungal spore and disease initiation in plants and animals, Plenum, New York.
Brady, B.L. 1981. Fungi as parasites of insects and mites. Biocontrol News and Information 4: 281–296.
Brandenburg, R.L. & Kennedy, G.G. 1983. Interactive effects of selected pesticides on the two-spotted spider mite and its fungal pathogen Neozygites floridana. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 34: 240–244.
Brefeld, O. 1870. Entwicklungsgeschichte der Empusa muscae und Empusa radicans. Bot. Ztg. 28: 177–186.
Brey, P.T., Latgé, J.P. & Prévost, M.C. 1986. Integumental penetration of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum by Conidiobolus obscurus (Entomophthoraceae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 48: 34–41.
Brobyn, P.J., Clark, S.J. & Wilding, N. 1988. The effect of fungus infection of Metopolophium dirhodum (Homoptera: Aphididae) on the oviposition behaviour of the aphid parasitoid Aphidius rhopalosiphi (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae). Entomophaga 33: 333–338.
Brobyn, P.J. & Wilding, N. 1977. Invasive and developmental processes of Entomophthora species infecting aphids. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 69: 349–366.
Brobyn, P.J., Wilding, N. & Clark, S.J. 1985. The persistence of infectivity of conidia of the aphid pathogen E. neoaphidis on leaves in the field. Ann. Appl. Biol. 107: 365–376.
Brobyn, P.J., Wilding, N. & Clark, S.J. 1987. Laboratory observations on the effect of humidity on the persistence of infectivity of conidia of the aphid pathogen Erynia neoaphidis. Ann. Appl. Biol. 110: 579–584.
Burger, G.F. & Swain, A.F. 1918. Observations on a fungus enemy of the walnut aphis in southern California. J. Econ. Entomol. 11: 278–288.
Butt, T.M. 1987. A fluorescence microscopy method for the rapid localization of fungal spores and penetration sites on insect cuticle. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 50: 72–74.
Butt, T.M., Beckett, A. & Wilding, N. 1981. Protoplasts in the in vivo life cycle of Erynia neoaphidis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 127: 417–421.
Butt, T.M., Beckett, A. & Wilding, N. 1990. A histological study of the invasive and developmental processes of the aphid pathogen Erynia neoaphidis (Zygomycotina: Entomophthorales) in the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris. Can. J. Bot. 68: 2153–2163.
Butt, T.M. & Goettel, M.S. 2000. Bioassay of entomogenous fungi, pp. 141–195. In: Navon, A. & Ascherp, K.R.S. (eds) Bioassays of Entomopathogenic Microbes and Nematodes, CAB International.
Butt, T.M. & Heath, I.B. 1988. The changing distribution of acting and nuclear behaviour during the cell cycle of the mite pathogenic fungus Neozygites sp. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 46: 499–505.
Butt, T.M. & Humber, R.A. 1989. An immunofluorescence study of mitosis in a mite-pathogen, Neozygites sp. (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). Protoplasma 151: 115–123.
Butt, T.M., Wraight, S.P., Galaini-Wraight, S., Humber, R.A., Roberts, D.W. & Soper, R.S. 1988. Humoral encapsulation of the fungus Erynia radicans (Entomophthorales) by the potato leafhopper Empoasca fabae (Homoptera: Cicadellidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 52: 49–56.
Byford, W.J. & Reeve, G.J. 1969. Entomophthora species attacking aphids in England, 1962–1966. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 52: 342–346.
Cagáñ L’. & Barta M. 2001. Seasonal dynamics and entomophthoralean infection of pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris, in southwestern Slovakia. Plant Prot. Sci. 37: 17–24.
Cappuccino, N. 1988. Spatial patterns of golden-rod aphids and the response of enemies to patch density. Oecologia 76: 607–610.
Carruthers, R.I. & Soper, R.S. 1987. Fungal diseases, pp. 357–416. In: Fuxa, J.R. & Tanada, Y. (eds) Epizootiology of insect diseases, John Wiley, New York.
Carruthers, R.I., Whitfield, G.H. & Haynes, D.L. 1985. Pesticide-induced mortality of natural enemies of the onion maggot Delia antiqua (Dip.: Anthomyiidae). Entomophaga 30: 151–161.
Cheng, C.C. & Long, H.R. 1987. A study on control of aphids with Entomophthora virulenta. Microbiology 14: 97–100.
Chen, C. & Feng, M.G. 2004a. Observation on the initial inoculum source and dissemination of Entomophthorales-caused epizootics in populations of cereal aphids. Sci. China Ser. C Life Sci. 7: 39–44.
Chen, C. & Feng, M.G. 2004b. Sitobion avenae alatae infected by Pandora neoaphidis: their flight ability, post-flight colonization, and mycosis transmission to progeny colonies. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 86: 117–123.
Chen, C. & Feng, M.G. 2006. Probability model for the post-flight fecundity of viviparous alatae infected preflight by the obligate aphid pathogen Pandora neoaphidis. Biol. Control 39: 26–31.
Chudare, Z.P. 1982. Pathogenicity of entomophthoraceous fungi. Izv. Akad. Nauk Latv. SSR 10: 88–105.
Chudare, Z.P. 1990. Biologicheskie svoĭstva entomoftorovykh gribov. Zinatne, Riga, 198 pp.
Chudare, Z.P. 2001. Ultrastructure of the resting spore wall of the insect pathogen Conidiobolus thromboides. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci. Sect. B 55(4): 177–182.
Clarkson, J.M. & Charnley, A.K. 1996. New insights into the mechanisms of fungal pathogenesis in insects. Trends in Microbiology 4: 197–203.
Cohn, F. 1855. Empusa muscae und die Krankheit der Stubenfliegen. Verh. Keiserl. Leopold-Carol. Akad. Naturforsch. 25: 299–360.
Cohn, F. 1870. Über eine neue Krankheit der Erdraupen. Beitr. Biol. Pflanz. 1: 58–86.
Cooke, R.C. & Whipps, J.M. 1993. Ecophysiology of fungi. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 352 pp.
Coremans-Pelseneer, J. 1974. Biologie des champignons du genere Basidiobolus Eidam 1886. Saprophytisme et pourvoir pathogen. Acta Zool. Pathol. Antverpiensia 60: 7–137.
Coremans-Pelseneer, J. 1981. Importance of zygospores in natural and experimental infection of aphids, pp. 107–117. In: Vanbreuseghem, R. (ed.) Sexuality and pathogenicity of fungi, Proc. III. Int. Coll. Med. Mycol., The Prince Leopold Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp.
Coremans-Pelseneer, J., Villers, S. & Matthys, V. 1983. Entomophthorales found on wheat aphids, in soil and air on the same field. Four years compared results. Med. Fac. Landbouw. Rijksuniv. Cent. 48: 207–213.
Cornu, M. 1873. Note sur une nouvelle espèce d’Entomophthora (E. planchoniana). Bull. Soc. Bot. Fr. 20: 189–190.
Courtois, P. & Latteur, G. 1984. Étude quantitative de la survie des crops hyphaux d’Erynia neoaphidis Remaudière et Hennebert (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae) en fonction de la température et de l’humidité relative. Parasitica 40: 211–220.
Dara, S.K. & Semtner, P.J. 1998. Influence of substrate type and temperature on the developmental morphology of Pandora neoaphidis (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales), a pathogen of the tobacco aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 72: 112–118.
Dara, S.K. & Semtner, P.J. 2001. Incidence of Pandora neoaphidis (Rem. et Henn.) Humber (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) in the Myzus persicae Sulzer complex (Homoptera: Aphididae) on three species of Brassica in the fall and winter. J. Entomol. Sci. 36: 152–161.
D’XXXarcy, C., Burnett, P.A. & Heurings, A.D. 1981. Detection, biological effects, and transmission of a virus of the aphid Rhopalosiphum padi. Virology 114: 268–272.
Dean, G.J.W. & Wilding, N. 1971. Entomophthora infecting the cereal aphids Metopolophium dirhudum and Sitobion avenae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 18: 169–176.
Dedryver, C.A. 1978. Facteurs de limitation des populations d’Aphis fabae dans l’Quest de la France. III. Répartition et incidence des différentes espèces d’Entomophthora dans les populations. Entomophaga 23: 137–151.
Dedryver, C.A. 1979. Déclenchement en serre d’une épizootie à Entomophthora fresenii Nowak. sur Aphis fabae Scop. par introduction dinoculum et regulation de l’humidité relative. Entomophaga 24: 443–453.
Dedryver, C.A. 1981. Biologie des pucerons des céréales dans l’Quest de la France. II. Répartition spatio — temporelle et action limitative de trois espèces d’Entomophthoraceae. Entomophaga 26: 381–393.
Dedryver, C.A. 1983. Field pathogenesis of three species of Entomophthorales of cereal aphids in Western France, pp. 11–19. In: Cavalloro, R. (ed.) Aphid antagonists, A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam.
Delalibera, I., Jr. 1996. Producao in vitro de Neozygites sp. (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) patogeno de Mononychellus tanajoa (Acari: Tetranychidae), p. 171. In: Proceedings Simposio Controle Biologico, Foz do Iguacu, Brasil.
Drechsler, C. 1953. Three new species of Conidiobolus isolated from leaf mold. J. Wash. Acad. Sci. 43: 29–43.
Drechsler, C. 1954. Two species of Conidiobolus with minutely ridged zygospores. Am. J. Bot. 41: 567–575.
Dromph, K.M., Eilenberg, J. & Esbjerg, P. 2001. Natural occurrence of entomophthoralean fungi pathogenic to collembolans. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 78: 226–231.
Dromph, K.M., Pell, J.K. & Eilenberg, J. 1997. Sporulation of Erynia neoaphidis from alate Sitobion avenae. Insect Pathogens and Parasitic Nematode. IOBC/WPRS Bulletin 21: 91–94.
Duetting, P.S., Ding, H., Neufeld, J. & Eigenbrode, S.D. 2003. Plant waxy bloom on peas affects infection of pea aphids by Pandora neoaphidis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 84: 149–158.
Dumas, J.L. & Papierok, B. 1989. Virulence of Zoophthora radicans (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) against adults of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Entomophaga 34: 321–330.
Dunphy, G.B. & Nolan, R.A. 1982. Cellular immune response of spruce budworm larvae to Entomophthora egressa protoplasts and other test particles. J. Inverebr. Pathol. 39: 261–263.
Dustan, A.G. 1927. The artificial culture and dissemination of Entomophthora sphaerosperma Fres., a fungous parasite for the control of the European apple sucker (Psyllia mali Schmidb.). J. Econ. Entomol. 20: 68–75.
Ege, O. 1965. Ein Beitrag zur Biologie einiger aphidivorer Entomophthoraceen. Arch. Microbiol. 52: 20–48.
Egina, Ya. & Shagunina, V. 1977. A study of the effectiveness of the fungus Basidiobolus sp., pp. 72–77. In: Shagunina, V. (ed.) Entomopathogenic microorganisms and their use in the control of plant pests, Zinatne, Riga.
Egina, K.Ya., Strazdinya, A.A., Chudare, Z.P., Yakshevits, M.R., Tsinovskii, Ya.P. & Shagunina, V. 1977. Entomophthoroses of aphids in the Latvian SSR, pp. 5–13. In: Shagunina, V. (ed.) Entomopathogenic microorganisms and their use in the control of plant pests, Zinatne, Riga.
Eilenberg, J. 2002. Biology of fungi from the order Entomophthorales with emphasis on the genera Entomophthora, Strongwelsea and Eryniopsis. D.Sc. Thesis, The Royal Veterinary and Agricultural University, Copenhagen, 407 pp.
Eilenberg, J., Bresciani, J. & Latgé, J.P. 1986. Ultrastructural studies of primary spore formation and discharge in the genus Entomophthora. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 48: 318–324.
Eilenberg, J., Bresciani, J., Olesen, U. & Olson, L. 1995. Ultrastructural studies of secondary spore formation and discharge in the genus Entomophthora. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 65: 179–185.
Eilenberg, J., Hajek, A. & Lomer, C. 2001. Suggestions for unifying the terminology in biological control. BioControl 46: 387–400.
Elkassabany, N.M., Steinkraus, D.C., Mcleod, P.J., Correll, J.C. & Morelock, T.E. 1992. Pandora neoaphidis (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) a potential biological control agent against Myzus persicae Sulzer (Homoptera: Aphididae) on spinach. J. Kansas Entomol. Soc. 62: 196–199.
Elkinton, J.S., Hajek, A.E., Boettner, G.H. & Simons, E.E. 1991. Distribution and apparent spread of Entomophaga maimaiga (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) in gypsy moth (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) populations in North America. Environ. Entomol. 20: 1601–1605.
Elliot, S.L., Moraes, G.J., Delalibera, I., Da Silva, C.A.D., Tamai, M.A. & Mumford, J.D. 2000. Potential of the mite-pathogenic fungus Neozigites floridana Fischer (Entomophthorales: Neozygitaceae) for control of the cassava green mite Monoychellus tanajore (Bondar) (Acari: Tetranychidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 90: 191–200.
Elliot, S.L., Moraes, G.J. & Mumford, J.D. 2002. Importance of ambient saturation deficits in an epizootic of the fungus Neozygites floridana in cassava green mites (Mononychellus tanajoa (Bondar)). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 27: 11–25.
Evans, H.C. 1989. Mycopathogens of insects of epigeal and aerial habitats, pp. 205–238. In: Wilding, M., Collins, N.M., Hammond, P.M. & Webber, J.F. (eds) Insect-Fungus interactions. Academic Press, London.
Fan, M.Z., Guo, Ch. & Li, Z.Z. 1991. New species and new record of the genus Erynia in China. Acta Mycol. Sin. 10(2): 95–100.
Fargues, J. & Rodriguez-Rueda, D. 1979. Sensibilité des oeufs des Noctuides Mamestra brassica et Spodoptera littoralis aux Hyphomycetes Paecilomyces fumuso-roseus et Nomuraea rileyi. C. R. Acad. Sci. 290: 65–68.
Feng, M.G. & Chen, C. 2002. Incidence of infected Myzus persicae alatae trapped in flight imply place-to-place dissemination of entomophthoralean fungi in aphid populations through migration. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 81: 53–56.
Feng, M.G., Chen, C. & Chen, B. 2004. Wide dispersal of aphid-pathogenic Entomophthorales among aphids relies upon migratory alates. Environ. Entomol. 6: 510–516.
Feng, M.G. & Hua, L. 2005. Factors affecting the sporulation capacity during long-term storage of the aphid-pathogenic fungus Pandora neoaphidis grown on broomcorn millet. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 245: 205–211.
Feng, M.G. & Johnson, J.B. 1991. Bioassay of four Entomophthoralean fungi (Entomophthorales) against Diuraphis noxia and Metopolophium dirhodum (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 20: 338–345.
Feng, M.G., Johnson, J.B. & Halbert, S.E. 1991. Natural control of cereal aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) by entomopathogenic fungi (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) and parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae and Encyrtidae) on irrigated spring wheat in southwestern Idaho. Environ. Entomol. 20: 1699–1710.
Feng, M.G., Johnson, J.B. & Kish, L.P. 1990. Survey of entomopathogenic fungi naturally infecting cereal aphids (Homoptera, Aphididae) of irrigated grain crops in southwestern Idaho. Environ. Entomol. 19: 1534–1542.
Feng, M.G. & Li, H.P. 2003. Experimental epizootiology of Zoophthora anhuiensis (Entomophthorales) against Myzus persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae) with a description of a modified Gompertz model for aphid epizootics. Environ. Entomol. 5: 1203–1211.
Feng, M.G., Liu, C.L., Xu, J.H. & Xu, Q. 1998. Modelling and biological implication of time-dose-mortality data for the entomophthoralean fungus, Zoophthora anhuiensis, on the green peach aphid Myzus persicae Sulzer. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 72: 246–251.
Feng, M.G. & Nowierski, R.M. 1991. Entomopathogenic fungi (Zygomycotina: Entomophthorales) infecting cereal aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Montana. Pan-Pacific Entomologist 67: 55–64.
Feng, M.G. & Nowierski, R.M. 1992. Spatial patterns and sampling plans for cereal aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) killed by entomophthoralean fungi and hymenopterous parasitoids in spring wheat. Entomophaga 37: 265–275.
Feng, M.G., Nowierski, R.M., Johnson, J.B. & Poprawski, T.J. 1992a. Epizootics caused by entomophthoralean fungi (Zygomycetes, Entomophthorales) in populations of cereal aphids (Homoptera, Aphididae) in irrigated small grains of southwestern Idaho, USA. J. Appl. Entomol. 113: 376–390.
Feng, M.G., Nowierski, R.M., Klein, R.E., Scharen, A.L. & Sands, D.C. 1992b. Spherical hyphal bodies of Pandora neoaphidis (Remaudière et Hennebert) Humber (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) on Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera: Aphididae): a potential overwintering form. Pan-Pacific Entomologist 68: 100–104.
Feng, M.G., Poprawski, T.J., Nowierski, R.M. & Zeng, Z. 1999. Infectivity of Pandora neoaphidis (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) to Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hom., Aphididae) in response to varying temperature and photoperiod regimes. J. Appl. Entomol. 123: 29–35.
Ferrari, J., Müller, B.C., Kraaijeveld, A.R. & Godfray, H.C. 2001. Clonal variation and covariation in aphid resistance to parasitoids and a pathogen. Evolution 55: 1805–1814.
Freimoser, F.M., Grundschober, A., Tuor, U. & Aebi, M. 2003. Regulation of hyphal growth and sporulation of the insect pathogenic fungus Entomophthora thripidum in vitro. FEMS Microbiol. Letters 222: 281–287.
Freimoser, F.M., Jensen, A.B., Tuor, U., Aebi, M. & Eilenberg, J. 2001. Isolation and in vitro cultivation of the aphid pathogenic fungus Entomophthora planchoniana. Can. J. Bot. 47: 1082–1087.
Fresenius, G. 1856. Notiz, Insecten-Pilze betreffend. Bot. Ztg. 14: 882–883.
Fresenius, G. 1858. Über die Pilzgattung Entomophthora. Abh. Senckenb. Natforsch. Ges. 2: 201–210.
Fritz, R. 1976. The action of some fungicides on the mycelial growth of three species of Entomophthorales. Entomophaga 21: 239–249.
Fuentes-Contreras, E., Pell, J.K. & Niemeyer, H.M. 1998. Influence of plant resistance at the third trophic level: interactions between parasitoids and Entomopathogenic fungi of cereal aphids. Oecologia 117: 426–432.
Funk, C.J., Ramoska, W.A. & Bechtel, D.B. 1993. Histopathology of Entomophaga grylli pathotype 2 infections in Melanoplus differentialis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 61: 196–202.
Furlong, M.J. & Pell, J.K. 1996. Interactions between the fungal entomopathogen Zoophthora radicans Brefeld (Entomophthorales) and two hymenopteran parasitoids attacking the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella Linné. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 68: 15–21.
Furlong, M.J. & Pell, J.K. 1997. The influence of environmental factors on the persistence of Zoophthora radicans conidia. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 69: 223–233.
Furlong, M.J. & Pell, J.K. 2000. Conflicts between a fungal entomopathogen, Zoophthora radicans Brefeld (Entomophthorales), and two larval parasitoids of the diamondback moth. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 76: 85–94.
Fuxa, J.R. & Tanada, Y. 1987. Epidemiological concepts applied to insect epizootiology, pp. 3–21. In: Fuxa, J.R. & Tanada, Y. (eds) Epizootiology of insect diseases, John Wiley, New York.
Gabriel, B.P. 1968. Enzymatic activities of some entomophthoraceous fungi. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 11: 70–81.
Giard, A. 1888. Fragments biologigues XI. Sur quelques entomophthorées. Bull. Sci. Fr. Belg. 19: 298–309.
Gillespie, A.T. & Claydon, N. 1989. The use of entomogenous fungi for pest control and the role of toxins in pathogenesis. Pestic. Sci. 27: 203–215.
Gindin, G. & Ben-Ze’ev, I. 1994. Natural occurrence of and inoculation experiments with Conidiobolus coronatus and Conidiobolus sp. in glasshouse populations of Bemisia tabaci. Phytoparasitica 22: 197–208.
Glare, T.R., Chilvers, G.A. & Milner, R.J. 1985. Capilliconidia as infective spores in Zoophthora phalloides (Entomophthorales). Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 85: 463–470.
Glare, T.R., Chilvers, G.A. & Milner, R.J. 1986a. The effect of environmental factors on the production, discharge, and germination of primary conidia of Zoophthora phalloides Batko. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 48: 275–283.
Glare, T.R. & Milner, R.J. 1991. Ecology of entomopathogenic fungi, pp. 547–612. In: Arora, D.K., Ajello, L. & Mukerji, K.G. (eds) Handbook of applied mycology, Vol. 2, Humans, Animals, and Insects, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Glare, T.R., Milner, R.J. & Chilvers, G.A. 1986b. Influence of temperature on the mortality of Myzus persicae (Sulzer) due to the fungal pathogen Zoophthora phalloides Batko. J. Aust. Entomol. Soc. 25: 63–64.
Glare, T.R., Milner, R.J., Chilvers, G.A., Mahon, R.J. & Brown, W.V. 1987. Taxonomic implications of intraspecific variation amongst isolates of the aphid-pathogenic fungi Zoophthora radicans Brefeld and Zoophthora phalloides Batko (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae). Aust. J. Bot. 35: 49–67.
Goettel, M.S., Poprawski, T.J., Vandenberg, J.D., Li, Z. & Roberts, D.W. 1990. Safety to nontarget invertebrates of fungal biocontrol agents, pp. 209–231. In: Laird, M., Lacey, L.A. & Davidson, E.W. (eds) Safety of microbial insecticides, CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Gökçe, A. & Er, M.K. 2003. First description of the disease by Conidiobolus osmodes on Tipula paludosa larvae with the report of a natural epizootic. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 84: 83–89.
Götz, P. 1986. Encapsulation in arthropods, pp. 153–170. In: M. Brehélin (ed.) Immunity in invertebrates, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Gray, S.N. & Markham, P. 1997. A model to explain the growth kinetics of the aphid-pathogenic fungus Erynia neoaphidis in liquid culture. Mycol. Res. 101: 1475–1483.
Gray, S.N., Robinson, P., Wilding, N. & Markham, P. 1990. Effect of oleic acid on vegetative growth of the aphidpathogenic fungus Erynia neoaphidis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 68: 131–136.
Gres, J.A. & Koval’, E.Z. 1982. New species Entomophthra terrestris sp. nov. affecting the sugar beet root aphid. J. Microbiol., Kiew 44(2): 64–69.
Griggs, M.H., Vandenberg, J.D. & Sawyer, A.J. 1999. Effect of relative humidity on viability of primary conidia of Zoophthora radicans. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 73: 315–320.
Grobler, J.H., Macleod, D.M. & Delyzer, A.J. 1962. The Empusa aphidis Hoffman parasitic on the woolly pine needle aphid, Schizolachnus pini-radiatae (Davidson). Can. Entomol. 94: 46–49.
Grundschober, A., Tuor, U. & Aebi, M. 1998. In vitro cultivation and sporulation of Neozygites parvispora (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 21: 461–469.
Gustafsson, M. 1965. On species of the genus Entomophthora Fres. in Sweden. I. Classification and distribution. Lantburkshögskolans Annaler 32: 102–212.
Gustafsson, M. 1969. On species of the genus Entomophthora Fres. in Sweden. III. Possibility of usage in biological control. Lantburkshögskolans Annaler 35: 235–274.
Hajek, A.E. 2001. Larval behaviour in Limantria dispar increases risk of fungal infection. Oecologia 126: 285–291.
Hajek, A.E., Bauer, L., Mcmanus, M.L. & Vheeler, M.M. 1998. Distribution of resting spores of the Lymantria dispar pathogen Entomophaga maimaiga in soil and on bark. Bio-Control 43: 189–200.
Hajek, A.E., Davis, C.I., Eastburn, C.C. & Vermeylen, F.M. 2002a. Deposition and germination of conidia of the entomopathogen Entomophaga maimaiga infecting larvae of gypsy moth, Lymantria dispar. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 79: 37–43.
Hajek, A.E. & Eastburn, C.C. 2001. Effect of host insects on activation of Entomophaga maimaiga resting spores. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 77: 290–291.
Hajek, A.E., Filotas, M.J. & Ewing, D.C. 2002b. Formation of appressoria by two species of lepidopteran-pathogenic Entomophthorales. Can. J. Bot. 80: 220–225.
Hajek, A.E. & Humber, R.A. 1997. Formation and germination of Entomophaga maimaiga azygospores. Can. J. Bot. 75: 1739–1747.
Hajek, A.E., Humber, R.A. & Elkington, J.S. 1995. Mysteriuos origin of Entomophaga maimaiga in North America. Amer. Entomol. 41: 31–42.
Hajek, A.E., Jensen, A.B., Thomsen, L., Hodge, K.T. & Eilenberg, J. 2003. PCR-RFLP is used to investigate relations among species in the entomopathogenic genera Eryniopsis and Entomophaga. Mycologia 95: 262–268.
Hajek, A.E., Shimazu, M. & Knoblauch, B. 2000. Isolating a species of Entomophthorales using resting spore-bearing soil. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 75: 298–300.
Hajek, A.E. & St. Leger, R.J. 1994. Interactions between fungal pathogens and insect hosts. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 39: 293–322.
Hall, I.M., Lowe, A.D. & Given, B.B. 1976. New record of aphid hosts of Entomophthora aphidis and Entomophthora planchoniana in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Zool. 3: 111–112.
Hall, R.A. 1984. Epizootic potential for aphids of different isolates of the fungus, Verticillium lecanii. Entomophaga 29: 311–321.
Hall, I.M. & Bell, J.V. 1963. The synonymy of Empusa thaxteriana Petch and Entomophthora ignobilis Hall and Dunn. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 5: 182–186.
Hall, I.M. & Dunn, P.H. 1957. Entomophthorous fungi parasitic on the spotted alfalfa aphid. Hilgardia 27: 159–165.
Hall, I.M. & Dunn, P.H. 1958. Artificial dissemination of Entomophthorous fungi pathogenic to the spotted alfalfa aphid in California. J. Econ. Entomol. 51: 341–344.
Hall, R.A. & Papierok, B. 1982. Fungi as biological control agents of arthropods of agricultural and medical importance. Parasitology 84: 205–240.
Harper, D.J., Herbert, D.A. & Moore, R.E. 1984. Trapping patterns of Entomophthora gammae (Weiser) (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) conidia in a soybean field infested with the soybean looper, Pseudoplusia includens (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ. Entomol. 13: 1186–1190.
Harris, M.R. 1948. A phycomycete parasitic on aphids. Phytopathology 38: 118–122.
Hatting, J.L., Humber, R.A., Poprawski, T.J. & Miller, R.M. 1999a. A survey of fungal pathogens of aphids from South Africa, with special reference to cereal aphids. Biol. Control 16: 1–12.
Hatting, J.L., Poprawski, T.J. & Miller, R.M. 1999b. Managing the entomopathogenic fungus Conidiobolus thromboides in Russian wheat aphid cultures. Southwest. Entomol. 24: 99–106.
Hatting, J.L., Poprawski, T.J. & Miller, R.M. 2000. Prevalences of fungal pathogens and other natural enemies of cereal aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) in wheat under dryland and irrigated conditions in South Africa. BioControl 45: 179–199.
Hemmati, F., Pell, J.K., Mccartney, H.A., Clark, S.J. & Deadman, M.L. 2001a. Conidial discharge in the aphid pathogen Erynia neoaphidis. Mycol. Res. 105: 715–722.
Hemmati, F., Pell, J.K., Mccartney, H.A. & Deadman, M.L. 2001b. Airborne concentrations of conidia of Erynia neoaphidis above cereal fields. Mycol. Res. 105: 485–489.
Holdom, D.G. 1983. In vitro culture of the aphid pathogenic fungus Entomophthora planchoniana Cornu (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). J. Aust. Entomol. Soc. 22: 188.
Holdom, D.G., Taylor, P.S., Mackay-Wood, R.J., Ramos, M.E. & Soper, R.S. 1989. Field studies on rice planthoppers (Homoptera, Delphacidae) and their natural enemies in Indonesia. J. Appl. Entomol. 107: 118–129.
Hollingsworth, R.G., Steinkraus, D.C. & Mcnew, R.W. 1995. Sampling to predict fungal epizootics in cotton aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 24: 1414–1421.
Hori, S. 1906. Entomogenous fungi in Japan. Kontyu-gaku Zassi 3: 81–83.
Humber, R.A. 1978. Entomophthora ignobilis, the correct name for a common fungal pathogen of aphids. Mycologia 70: 208–210.
Humber, R.A. 1981. An alternative view of certain taxonomic criteria used in the Entomophthorales (Zygomycetes). Mycotaxon 13: 191–240.
Humber, R.A. 1983. Species complex in the Entomophthorales: New problems for old species, pp. 44–45. In: SIP 16th Annual Meeting, Cornell University, Ithaca.
Humber, R.A. 1984. Eryniopsis, a new genus of the Entomophthoraceae (Entomophthorales). Mycotaxon 21: 257–264.
Humber, R.A. 1987. Revised familial and generic criteria for a phylogenetic classification of the Entomophthorales. In: SIP Annual Meeting. Gainesville, Florida, 1987.
Humber, R.A. 1989. Synopsis of a revised classification for the Entomophthorales (Zygomycotina). Mycotaxon 34: 441–460.
Humber, R.A. 1991. Fungal pathogens of aphids, pp. 45–56. In: Peters, D.C., Webster, J.A. & Chlouber, C.S. (eds) Aphid-plant interactions: Populations to molecules, Agricultural Experiment Station, Division of Agriculture, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater.
Humber, R.A. 1997. Fungi: Identification, pp. 153–185. In: Lacey, L.A. (ed.) Manual of techniques in insect pathology, Academic Press, London.
Humber, R.A. 2001. Collection of Entomopathogenic Fungal Cultures: Catalog of strains. U.S. Department of Agriculture Publication ARS, Agricultural Research Service, Ithaca, NY.
Humber, R.A. & Ben-Ze’ev, I. 1981. Erynia (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales): emendation, synonymy and transfers. Mycotaxon 13: 506–516.
Humber, R.A. & Feng, M.G. 1991. Entomophthora chromaphidis (Entomophthorales): the correct identification of an aphid pathogen in the Pacific Northwest and elsewhere. Mycotaxon 41: 497–504.
Humber, R.A., Soper, R.S., Wilding, N. & Remaudière, G. 1977. The identification of certain widely studied strains of Entomophthora pathogenic for aphids. Mycotaxon 5: 307–310.
Hung, S.Y., Boucias, D.G. & Vey, A. 1993. Effect of Beauveria bassiana and Candida albicans on the cellular defense response of Spodoptera exigua. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 61: 179–187.
Hywel-Jones, N.L. & Webster, J. 1986. Mode of infection of Simulium by Erynia conica. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 87: 381–387.
Ingold, C.T. 1971. Fungal spores: Their liberation and dispersal. Clarendon, Oxford, 302 pp.
James, T.Y., Kauff, F. & Schoch, C.L. et al. 2006. Reconstructing the early evolution of Fungi using a six-gene phylogeny. Nature 443: 818–822.
James, T.Y., Porter, D., Leander, C.A., Vilgalys, R. & Longcore J.E. 2000. Molecular phylogenetics of the Chytridiomycota supports the utility of ultrastructural data in chytrid systematics. Can. J. Bot. 78: 336–350.
Jensen, A.B. & Eilenberg, J. 2001. Genetic variation within the insect-pathogenic genus Entomophthora, focusing on the E. muscae complex, using PCR-RFLP of the ITS II and the LSU rDNA. Mycol. Res. 105: 307–312.
Jensen, A.B., Gargas, A., Eilenberg, J. & Rosendahl, S. 1998. Relationships of the insect-pathogenic order Entomophthorales (Zygomycota, Fungi) based on phylogenetic analysis of nuclear small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences (SSU rDNA). Fungal Genet. Biol. 24: 325–334.
Jensen, M.A., Losey, J.E. & Hajek, A.E. 2001. Altered behaviour and distribution of pea aphids, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Homoptera: Aphididae), infected with Pandora neoaphidis (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). BioControl 46: 337–343.
Keller, S. 1986. Investigation on the effect of herbicide on aphid pathogenic Entomophthoraceae, pp. 493–497. In: Junk, W. (ed.) Ecology of aphidophaga, Academia, Prague.
Keller, S. 1987a. Arthropod-pathogenic Entomophthorales of Switzerland. I. Conidiobolus, Entomophaga and Entomophthora. Sydowia 40: 122–167.
Keller, S. 1987b. Observations on the overwintering of Entomophthora planchoniana. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 50: 333–335.
Keller, S. 1991. Arthropod-pathogenic Entomophthorales of Switzerland. II. Erynia, Eryniopsis, Neozygites, Zoophthora and Tarichium. Sydowia 43: 39–122.
Keller, S. 1997. The genus Neozygites (Zygomycetes, Entomophthorales) with special reference to species found in tropical regions. Sydowia 49: 118–146.
Keller, S. 1998. The role of Entomophthorales in a sustainable agriculture. Insect pathogens and insect parasitic nematodes. IOBC/WPRS Bulletin 21: 13–16.
Keller, S. 1999. Identification of arthropod-pathogenic Entomophthorales, IOBC/WPRS Working group “Insect pathogens and insect parasitic nematodes”, University BOKU, Vienna, 41 pp.
Keller, S. 2002. The genus Entomophthora (Zygomycetes, Entomophthorales) with a description of five new species. Sydowia 54: 157–197.
Keller, S. 2006. Entomophthorales attacking aphids with a description of two new species. Sydowia 58: 38–74.
Keller, S., Kessler, P. & Schweizer, C. 2003. Distribution of insect pathogenic soil fungi in Switzerland with special reference to Beauveria brongniartii and Metarhizium anisopliae. BioControl 48: 307–319.
Keller, S. & Petrini, O. 2005. Keys to the identification of the arthropod pathogenic genera of the families Entomophthoraceae and Neozygitaceae (Zygomycetes), with descriptions of three new subfamilies and a new genus. Sydowia 57: 23–53.
Keller, S. & Steenberg, T. 1997. Neozygites sminthuri sp. nov. (Zygomycetes, Entomophthorales), a pathogen of the springtail Sminthurus viridis L. (Collembola, Sminthuridae). Sydowia 49: 21–24.
Keller, S. & Suter, H. 1980. Epizootiologische Untersuchungen über das Entomophthora — Auftreten bei feldbaulich wichtigen Blattlausarten. Acta Oecol. Oecol. Appl. 1: 63–81.
Keller, S. & Zimmermann, G. 1989. Mycopathogens of soil insect, pp. 240–270. In: Wilding, M., Collins, N.M., Hammond, P.M. & Webber, J.F. (eds) Insect-Fungus interactions. Academic Press, London.
Kenneth, R.G. 1977. Entomophthora turbinata sp. nov. a fungal parasite of the peach trunk aphid, Pterochlorides persicae (Lachnidae). Mycotaxon 6: 381–390.
Kenneth, R.G. & Olmert, I. 1975. Entomopathogenic fungi and their hosts in Israel. Israel J. Entomol. 10: 105–112.
Kerwin, J.L. 1982. Chemical control of the germination of asexual spores of Entomophthora culicis, a fungus parasitic on dipterans. J. Gen. Microbiol. 128: 2179–2186.
Kevorkian, A.G. 1937. Studies in the Entomophthoraceae: I. Observations on the genus Conidiobolus. J. Agric. Univ. Puerto Rico 21: 191–200.
Khachatourians, G.G. 1996. Biochemistry and molecular biology of entomopathogenic fungi, pp. 331–363. In: Howard, D.H. & Miller, J.D. (eds) The Mycota VI. Humans and animal relationships, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg.
King, D.S. 1976a. Systematics of Conidiobolus (Entomophthorales) using numerical taxonomy. I. Biology and cluster analysis. Can. J. Bot. 54: 45–65.
King, D.S. 1976b. Systematics of Conidiobolus (Entomophthorales) using numerical taxonomy. II. Taxonomic considerations. Can. J. Bot. 54: 1285–1296.
King, D.S. 1977. Systematics of Conidiobolus (Entomophthorales) using numerical taxonomy. III. Descriptions of recognized species. Can. J. Bot. 55: 718–729.
King, D.S. 1979. Systematics of fungi causing entomophthoramycosis. Mycologia 71: 731–745.
King, D.S. & Humber, R.A. 1981. Identification of Entomophthorales, pp. 105–127. In: Burges, H.D. (ed.) Microbial control of pest and plant diseases 1970–1980, Academic Press, New York/London.
Kirk, P.M., Cannon, P.F., David, J.C. & Staplers, J.A. 2001. Ainsworth and Bisby’s dictionary of the fungi. 9th Edition. CAB International, Egham, 650 pp.
Kish, L.P. & Allen, G.E. 1978. The biology and ecology of Nomuraea rileyi and a program for predicting its incidence on Anticarsia gemmatalis in soybean. Florida Agric. Exp. Stn. Bull. 795, 44 pp.
Kish, L.P., Majchroowicz, I. & Biever, K.D. 1994. Prevalence of natural fungal mortality of green peach aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) on potatoes and nonsolanaceous hosts in Washington and Idaho. Environ. Entomol. 23: 1326–1330.
Klingen, I. & Jaastad, G. 2003. Prevalence of insect pathogenic fungi and parasitoids on the black cherry aphid, Myzus cerasi, p. 5. In: Ehlers, R.U. (ed.) Proceedings of abstracts of the 9th European Meeting of the IOBC/WPRS Working group “Insect Pathogens and Entomopathogenic Nematodes”, University Kiel, Kiel.
Kobayashi, Y., Mogami, K. & Aoki, J. 1984. Ultrastructural studies on the hyphal growth of Erynia neoaphidis in the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae. Trans. Mycol. Soc. Jpn. 25: 425–434.
Kogan, M. 1998. Integrated pest management: historical perspectives and contemporary developments. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 43: 243–270.
Krejzová, R. 1971a. Tests for the infection of larvae of Galleria mellonella Linné and Antheraea pernyi Linné with representatives of the genus Entomophthora. Věst. Českoslov. Zool. Spol. 35: 114–117.
Krejzová, R. 1971b. Resistance and germinability of resting spores of some species of the genus Entomophthora. Česká Mykologie 25(4): 231–238.
Krejzová, R. 1972a. Experimental infections of several species of aphids by specimens of the genus Entomophthora. Věst. Českoslov. Zool. Spol. 36: 17–22.
Krejzová, R. 1972b. The pathogenic effect of Basidiobolus sp. on Coptotermes formosanus (Shiraki) and Reticulitermes lucifugus (Rossi) (Isoptera). Věst. Českoslov. Zool. Spol. 36: 253–255.
Krejzová, R. 1977. Surface structures of three species of the genus Entomophthora. Entomophaga 22: 271–279.
Krejzová, R. 1979. Mycosis of the aphid Phorodon humuli on hop-plants, pp. 95–97. In: Weiser, J. (ed.) Progress in Invertebrate pathology, Proc. Int. Colloquium on Invertebr. Pathol., Prague.
Kůdela, V. & Polák, Z. 1999. Plant health care terminology. 3. Host-pathogen interactions. Plant Prot. Sci. 35: 1–36.
Kuo, M.J. & Alexander, M. 1967. Inhibition of lysis of fungi by melanins. J. Bacteriol. 94: 624–629.
Lacey, L.A., Fprutos, R., Kaya, H.K. & Vail, P. 2001. Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Do they have a future? Biol. Control 21: 230–248.
Lagnaoui, A. & Radcliffe, E.B. 1998. Potato fungicides interfere with entomopathogenic fungi impacting population dynamics of green peach aphid. Am. Potato J. 75: 19–25.
Lakon, G. 1919. Die Insektenfeinde aus der Familie der Entomophthoreen. Z. Angew. Entomol. 5: 161–216.
Lambiase, T.J. & Yendol, W.G. 1977. The fine structure of Entomophthora apiculata and its penetration of Trichoplusia ni. Can. J. Microbiol. 23: 452–464.
Latgé, J.P. 1975. Croissance et sporulation de 6 espèces d’Entomophthorales. I. Influence de la nutrition carboneé. Entomophaga 20: 201–207.
Latgé, J.P. 1980. Sporulation de Entomophthora obscura Hall et Dunn en culture liquide. Can. J. Microbiol. 26: 1038–1048.
Latgé, J.P. 1981. Comparaison des exigences nutritionelles des Entomophthorales. Ann. Microbiol. (Inst. Pasteur) 132B: 299–306.
Latgé, J.P., Cole, G., Horisberger, M. & Prévost, M.C. 1986a. Ultrastructure and chemical composition of the ballistospore wall of Conidiobolus obscurus. Exp. Mycol. 10: 99–113.
Latgé, J.P., Fournet, B., Cole, G., Dubourdieu, D. & Tong, N. 1984a. Composition chimique et ultrastructurale des parois des corps hyphaux et des azygospores de Conidiobolus obscurus. Can. J. Microbiol. 30: 1507–1521.
Latgé, J.P., King, D.S. & Papierok, B. 1980. Synonymie de Entomophthora virulenta Hall et Dunn et de Conidiobolus thromboides Drechsler. Mycotaxon 11: 255–268.
Latgé, J.P. & Papierok, B. 1988. Aphid pathogens, pp. 323–335. In: Minks, A.K. & Harrewijn, P. (eds) Aphids. Their biology, natural enemies and control, Vol. 2B, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Latgé, J.P., Papierok, B. & Sampedro, L. 1982. Aggressivité de Conidiobolus obscurus vis-à-vis du puceron du pois. I. Comportement des conidies sur la cuticle avant la pénétration du tube germinatif dans linsecte. Entomophaga 27: 323–330.
Latgé, J.P. & Perry, D.F. 1980. The utilization of an Entomophthora obscura resting spore preparation in biological control experiments against cereal aphids. Bulletin SROP 3: 19–25.
Latgé, J.P., Remaudière, G. & Diaquin, M. 1978a. Un nouveau milieu pour la croissance des champignos Entomophthorales pathogènes d’aphides. Ann. Microbiol. (Inst. Pasteur) 129B: 463–476.
Latgé, J.P., Remaudière, G., Soper, R.S., Madore, C.D. & Diaquin, M. 1978b. Growth and sporulation of Entomophthora virulenta on semidefined media in liquid culture. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 31: 225–233.
Latgé, J.P., Sampedro, L. & Hall, R. 1984b. Aggressivité de Conidiobolus obscurus vis-à-vis du puceron du pois. III. Activités enzymatiques exocellulaires. Entomophaga 29: 185–201.
Latgé, J.P., Sampedro Rosas, L. & Boucias, D.G. 1986b. Aggressiveness of Conidiobolus obscurus against the pea aphid. IV. Electrophoretic and immunoelectrophoretic characterization of aggressive strains. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 48: 159–166.
Latgé, J.P., Silvie, P., Papierok, B., Remaudière, G., Dedryver, C.A. & Rabasse, J.M. 1983. Advantages and disadvantages of Conidiobolus obscurus and of Erynia neoaphidis in the biological control of aphids, pp. 20–32. In: Cavalloro, R. (ed.) Aphid antagonists, A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam.
Latgé, J.P., Soper, R.S. & Madore, C.D. 1977. Media suitable for industrial production of Entomophthora virulenta zygospores. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 19: 1269–1284.
Latteur, G. 1977. Sur la possibilité d’infection directe d’aphides par Entomophthora à partir de sols hébergeants un inoculum naturel. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 284D: 2253–2256.
Latteur, G. 1980. The persistence of infectivity of conidia of Entomophthora obscura at different temperatures on the surface of an unsterilised soil. Acta Oecol. Oecol. Appl. 1: 29–34.
Latteur, G. & Godefroid, J. 1983. Trial of field treatments against cereal aphids with mycelium of E. neoaphidis (Entomophthorales) produced in vitro, pp. 2–10. In: Cavalloro, R. (ed.) Aphid antagonist, A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam.
Latteur, G. & Jansen, J.P. 2002. Effects of 20 fungicides on the infectivity of conidia of the aphid entomopathogenic fungus Erynia neoaphidis. BioControl 47: 435–444.
Latteur, G., Lizen, E. & Oger, R. 1985. Influence de divers facteurs physiques sur la virulence des conidies de l’Entomophthorale Erynia neoaphidis Remaudière et Hennebert envers le puceron du pois Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris). Parasitica 41: 151–162.
Latteur, G. & Randall, L. 1986. The survival of inoculum of conidia of Erynia neoaphidis Remaudière et Hennebert on unsterilized soil. IOBC/WPRS Bulletin 12: 72.
Leatherdale, D. 1970. The arthropod hosts of entomogenous fungi in Britain. Entomophaga 15: 419–435.
Leite, L.G., Alves, S.B., Batista Filho, A. & Roberts, D.W. 2003. Effect of salts, vitamins, sugars and nitrogen sources on the growth of three genera of Entomophthorales: Batkoa, Furia, and Neozygites. Mycol. Res. 107: 872–878.
Li, H.K. 1988. Preliminary observations on Entomophthora delphacis. Int. Rice Res. Newsl. 13: 41.
Li, Z. 1986. Erynia anhuiensis a new pathogen of aphids. Acta Mycol. Sin. 5: 1–6.
Li, H. & Feng, M.G. 2003. New use of broomcorn millets for production of granular cultures of aphid-pathogenic fungus Pandora neoaphidis for high sporulation potential and infectivity to Myzus persicae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 227: 311–317.
Li, W., Xu, W.A., Sheng, C.F., Wang, H.T. & Xuan, W.J. 2006. Factors affecting sporulation and germination of Pandora nouryi (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae), a pathogen of Myzus persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 16: 647–652.
Li, Z., Butt, M., Beckett, A. & Wilding, N. 1993. The structure of dry mycelia of the entomophthoralean fungi Zoophthora radicans and Erynia neoaphidis following different preparatory treatments. Mycol. Res. 97: 1315–1323.
Lizen, E., Latteur, G. & Oger, R. 1985. Sensibilité à infection par l’Entomophthorale Erynia neoaphidis Remaud. et Henn. du puceron Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) selom sa forme, son stade et son âge. Parasitica 41: 163–170.
Lowe, A.D. 1963. The fungus Entomophthora aphidis Hoffman parasitic on the cabbage aphid (Brevicoryne brassicae Linné) in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 6: 314–317.
Lowe, A.D. 1968. The incidence of parasitism and disease in some populations of the cabbage aphid in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 11: 821–828.
Macleod, D.M. 1955. A fungous enemy of the pea aphid, Macrosiphum pisi. Can. Entomol. 11: 503–505.
Macleod, D.M. 1963. Entomophthorales infections, pp. 189–231. In: Steinhaus, E.A. (ed.) Insect pathology, an advanced treatise, Academic Press, New York.
Macleod, D.M. & Müller-Kögler, E. 1970. Insect pathogens: species originally described from their resting spores mostly as Tarichium species (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae). Mycologia 62: 33–66.
Macleod, D.M. & Müller-Kögler, E. 1973. Entomogenous fungi: Entomophthora species with pear-shaped to almost spherical conidia (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae). Mycologia 65: 823–893.
Macleod, D.M., Müller-Kögler, E. & Wilding, N. 1976. Entomophthora species with E. muscae-like conidia. Mycologia 68: 1–29.
Macleod, D.M., Tyrrell, D. & Soper, R.S. 1979. Entomophthora canadensis sp. nov., a fungus pathogenic on the woolly pine-needle aphid, Scizolachnus piniradiatae (Davidson). Can. J. Bot. 57: 2663–2672.
Macleod, D.M., Tyrrell, D. & Welton, M.A. 1980. Isolation and growth of the grasshopper pathogen, Entomophthora grylli. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 36: 85–89.
Magalhães, B.P., Butt, T.M., Humber, R.A., Shields, E.J. & Roberts, D.W. 1990a. Formation of appressoria in vitro by the entomopathogenic fungus Zoophthora radicans (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 55: 284–288.
Magalhães, B.P., Humber, R.A., Shields, E.J. & Roberts, D.W. 1990b. Effects of environment and nutrition on conidial germination and appressorial formation by Zoophthora radicans (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales): a pathogen of the potato leafhopper (Homoptera: Cicadellidae), p. 157. In: Proceedings and abstracts, 4th International Colloquium on Invertebrate Pathology and Microbial Control, University of Adelaide, Australia.
Magalhães, B.P., Lord, J.C., Wraight, S.P., Daoust, R.A. & Roberts, D.W. 1988. Pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana and Zoophthora radicans to the coccinellid predators Coleomegilla maculata and Eriopis connexa. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 52: 471–473.
Magalhães, B.P., St. Leger, R.J., Humber, R.A., Allee, L.L., Shields, E.J. & Roberts, D.W. 1991. Nuclear events during germination and appressorial formation of the entomopathogenic fungus Zoophthora radicans (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 57: 43–49.
Magan, N. 2001. Physiological approaches to improving ecological fitness of fungal biocontrol agents, pp. 239–251. In: Butt, T.M., Jackson, C. & Magan, N. (eds) Fungi as biocontrol agents, CAB International.
Majchrowicz, I. 1979. Entomophthoraceae in populations of Aphis fabae Scopoli in North-Western Poland, pp. 123–124. In: Weiser, J. (ed.) Progress in Invertebrate Pathology, Proceedings of International Colloquium on Invertebr. Pathol. and XIth Annual Meeting, Society for Invertebrate Pathology, Prague.
Majchrowicz, I. 1999. Aphids and entomopathogenic fungi on carrot and lettuce roots in the North-Western Poland, pp. 253–259. In: Mat. Konf. Nauk, PAN, Aphids and other Homopterous Insects, University of Warmia and Masuria, Olsztyn 7.
Majchrowicz, I. 2001. Forecasting of fungal epizootics in aphids infesting agricultural crops, pp. 411–421. In: Mat. Konf. Nauk. PAN, Aphids and other Homopterous Insects, University of Podlasie, Siedlce 8.
Marti, O.G. & Olson, D.M. 2006. Neozygites fresenii (Entomophthorales: Neozygitaceae) prevalence in Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae) in three south central Georgia cotton fields. J. Entomol. Sci. 41: 22–32.
Matanmi, B.A. & Libby, J.L. 1976. The production and germination of resting spores of Entomophthora virulenta (Entomopthorales: Entomophthoraceae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 27: 279–285.
Matsui, T., Sato, H. & Shimazu, M. 1998. Isolation of an entomogenous fungus, Erynia delphacis (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae), from migratory planthoppers collected over the Pacific Ocean. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 33: 545–549.
Mccabe, D.E., Humber, R.A. & Soper, R.S. 1984. Observation and interpretation of nuclear reductions during maturation and germination of entomophthoralean resting spores. Mycologia 76: 1104–1107.
Mcguire, M.R., Maddox, J.V. & Ambrust, E.J. 1987a. Host range studies of an Erynia radicans strain (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) isolated from Empoasca fabae (Homoptera: Cicadellidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 50: 75–77.
Mcguire, M.R., Morris, M.J., Ambrust, E.J. & Maddox, J.V. 1987b. An epizootic caused by Erynia radicans (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae) isolated from Empoasca fabae (Homoptera: Cicadellidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 50: 78–80.
Mcleod, P.J. & Steinkraus, D.C. 1999. Influence of irrigation and fungicide sprays on prevalence of Erynia neoaphidis (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) infections of green peach aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) on spinach. J. Agric. Urban Entomol. 16: 279–284.
Mcleod, P.J., Steinkraus, D.C., Correll, J.C. & Morelock, T.E. 1998. Prevalence of Erynia neoaphidis (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) infections of green peach aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) on spinach in the Arkansas River Valley. Environ. Entomol. 27: 796–800.
Miętkiewski, R., Soper, R.S. & Bałazy, S. 1981. Notes on Zoophthora occidentalis (Thaxter) Batko (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae). Mycotaxon 13: 41–49.
Miętkiewski, R. & Tkaczuk, C. 2005. Insect species used as baits for isolation of entomopathogenic fungi from the soil. IOBC/WPRS 28: 53–61.
Miętkiewski, R. & VAN DER Geest, L.P.S. 1985. Notes on entomophthoraceous fungi infecting insects in the Netherlands. Entomol. Ber. 45: 190–192.
Miller, M.K. & Harper, J.D. 1987. Occurrence of Erynia delphacis in the threecornered alfalfa hopper, Spissistilus festinus Say (Homoptera: Membracidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 50: 81–83.
Millstein, J.A., Brown, G.C. & Nordin, G.L. 1982. Microclimatic humidity influence on conidial production in Erynia sp. (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae), an entomopathogenic fungus of the alfalfa weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ. Entomol. 11: 1166–1169.
Millstein, J.A., Brown, G.C. & Nordin, G.L. 1983. Microclimatic moisture and conidial production in Erynia sp. (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae): in vivo production rate and duration under constant and fluctuating moisture regimes. Environ. Entomol. 12: 1344–1349.
Milner, R.J. 1981a. Recent changes in the nomenclature of entomophthoran pathogens of aphids. J. Aust. Entomol. Soc. 20: 154.
Milner, R.J. 1981b. Patterns of primary spore discharge of Entomophthora spp. from the blue green aphid, Acyrthosiphon kondoi. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 38: 419–425.
Milner R.J. 1982. On the occurrence of pea aphid resistant to isolates of the fungal pathogen Erynia neoaphidis. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 32: 23–27.
Milner, R.J. 1985. Distribution in time and space of resistance to the pathogenic fungus Erynia neoaphidis in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 37: 235–240.
Milner, R.J. 1997. Prospects for biopesticides for aphid control. Entomophaga 42: 227–239.
Milner, R.J. & Bourne, J. 1983. Influence of temperature and duration of leaf wetness on infection of Acyrthosiphon kondoi with Erynia neoaphidis. Ann. Appl. Biol. 102: 19–27.
Milner, R.J. & Holdom, D.G. 1986. First record of Neozygites fresenii (Nowakowski) Batko, a fungal pathogen of aphids, in Australia. J. Aust. Entomol. Soc. 25: 85–86.
Milner, R.J., Holdom, D.G. & Glare, T.R. 1984. Diurnal patterns of mortality in aphids infected by entomophthoralean fungi. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 36: 37–42.
Milner, R.J. & Lutton, G.G. 1983. Effect of temperature on Zoophthora radicans (Brefeld) Batko: An introduced microbial control agent of the spotted alfalfa aphid, Therioaphis trifolii (Monell) f. maculata. J. Aust. Entomol. Soc. 22: 167–173.
Milner, R.J. & Mahon, R.J. 1985. Strain variation in Zoophthora radicans, a pathogen of variety of insect hosts in Australia. J. Aust. Entomol. Soc. 24: 195–198.
Milner, R.J., Mahon, R.J. & Brown, W.V. 1983. A taxonomic study of the Erynia neoaphidis Remaudière et Hennebert (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae) group of insect pathogenic fungi, together with a description of the new species of the new species Erynia kondoiensis. Aust. J. Bot. 31: 173–188.
Milner, R.J. & Soper, R.S. 1981. Bioassay of Entomophthora against the spotted alfalfa aphid Therioaphis trifolii f. maculata. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 37: 168–173.
Milner, R.J., Soper, R.S. & Lutton, G.G. 1982. Field release of an Israeli strain of the fungus Zoophthora radicans (Brefeld) Batko for biological control of Therioaphis trifolii (Monell) f. maculata. J. Aust. Entomol. Soc. 21: 113–118.
Milner, R.J., Teakle, R.E., Lutton, G.G. & Dare, F.M. 1980. Pathogens (Phycomycetes: Entomophthoraceae) of the bluegreen aphid Acyrthosiphon kondoi Shinji and other aphids in Australia. Aust. J. Bot. 28: 601–609.
Missonnier, J., Robert, Y. & Thoizon, G. 1970. Circonstences èpidemiologiques semblant favoriser le dèvelopement des mycoses à Entomophthorales chez trios Aphides, Aphis fabae Scop., Capitophorus horni Börner et Myzus persicae Sulz. Entomophaga 15: 169–190.
Morgan, L.W., Boddy, L., Clark, S.J. & Wilding, N. 1995. Influence of temperature on germination of primary and secondary conidia of Erynia neoaphidis (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 65: 132–138.
Møller, A.P. 1993. A fungus infecting domestic flies manipulates sexual behaviour of its hosts. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 33: 403–407.
Nadeau, M.P., Dunphy, G.B. & Boisvert, J.L. 1996a. Development of Erynia conica (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) on the cuticle of the adult black flies Simulium rostratum and Simulium decorum (Diptera: Simuliidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 68: 50–58.
Nadeau, M.P., Dunphy, G.B. & Boisvert, J.L. 1996b. Replicative conidiospore formation and discharge by Erynia conica and Erynia curvispora (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 68: 177–179.
Nagahama, T., Sato, H., Shimazu, M. & Sygiyama, J. 1995. Phylogenetic divergence of the entomophthoralean fungi: Evidence from nuclear 18S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Mycologia 87: 203–209.
Narayanasamy, P., Prabhakar, L.U. & Humber, R.A. 1992. Pandora delphacis (Hori) Humber, pathogen of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), and green leafhopper, Nephotettix virescens (Distant), in India. FAO Plant Protection Bulletin 40: 111–112.
Nielsen, C., Eilenberg, J. & Dromph, K. 2001a. Entomophthorales on cereal aphids. Characterisation, growth, virulence, epizootiology and potential for microbial control. The report of research project No. 53/2001 financed by the Danish EPA, Miljøstyrelsen, 74 pp.
Nielsen, C., Eilenberg, J., Harding, S., Oddsdottir, E. & Halldórsson, G. 2001b. Geographical distribution and host range of Entomophthorales infecting the green spruce aphid Elatobium abietinum Walker in Iceland. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 78: 72–80.
Nielsen, C., Hajek, A.E., Humber, R.A., Bresciani, J. & Eilenberg, J. 2003. Soil as an environment for winter survival of aphid-pathogenic Entomophthorales. Biol. Control 28: 92–100.
Nielsen, C., Hajek, A.E., Humber, R.A. & Eilenberg, J. 1998. Soil — a natural source of entomophthoralean fungi infecting aphids. Bulletin OILB-SROP 21(4): 45–48.
Nowakowski, L. 1883. Entomophthoreae. Przyczynek do znajomości pasorzytnych grzybków sprawiających pomór owadów. Pam. Akad. Umiej. Kraków, Wydz. Mat.-Przyr. 8: 153–179.
Ochoa, L.F., Duque, C.S. & Velez, A. 1996. Rhinoentomophthoromycosis. Report of two cases. J. Laryngol. Otol. 110: 1154–1156.
Oduor, G.I., Yaninek, J.S., Van Der Geest, L.P.S. & De Moraes, G.J. 1996. Germination and viability of capilliconidia of Neozygites floridana (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) under constant temperature, humidity, and light conditions. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 67: 267–278.
Oger, R. & Latteur, G. 1985. Description et precision d’une nouvelle méthode d’estimation de la virulence d’une Entomophthorale pathogène de pucerons. Parasitica 41: 135–150.
Ozino, O.I., Arzone, A. & Alma, A. 1988. Fungal enemies of Sitobion avenae in Piedmontese cereal cultivations. Estratto da Redia 71: 173–183.
Öncüer, C. & Latteur, G. 1979. The effect of 10 fungicides on the infectivity of conidia of Entomophthora obscura Hall et Dunn on the surface of non-sterile soil. Parasitica 35: 3–15.
Pai, M.R., Kini, H. & Kini, U.S. 1993. Rhinoentomophthoromycosis: a report of three cases. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 36: 65–68.
Papierok, B. 1978. Obtention in vivo des azygospores d’Entomophthora thaxteriana Petch, champignon pathogène de pucerons (Homoptères, Aphididae). C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 286D: 1503–1506.
Papierok, B. 1982. Entomophthorales: Virulence and bioassay design, pp. 176–181. In: Invertebrate pathology and microbial control, Proceedings 3rd International Colloquium on Invertebrate Pathology, 15th Annual Meeting of the Society for Invertebrate Pathology, Brighton.
Papierok, B. 1985. Données ècologiques et expérimentales sur les potentialités entomopathogens de l’entomophthorale Conidiobolus coronatus (Constantin) Batko. Entomophaga 30: 303–312.
Papierok, B. 1986. Écologie et comportement entomopathogène des Conidiobolus (Entomophthorales). Bull. Soc. Fr. Mycol. Med. 15: 169–173.
Papierok, B. 1989. On the occurrence of Entomophthorales (Zygomycetes) in Finland. I. Species attacking aphids (Homoptera, Aphididae). Ann. Entomol. Fenn. 55: 63–69.
Papierok, B. & Coremans-Pelseneer, J. 1980. Contribution à l’étude de Conidiobolus osmodes Dreschler (Zygomycètes, Entomophthoraceae), agent occasionnel d’épizooties chez les pucerons (Homoptères, Aphididae). Cryptogamie-Mycologie 1: 111–117.
Papierok, B. & Hajek, A.E. 1997. Fungi: Entomophthorales, pp. 187–212. In: Lacey, L. (ed.) Manual of techniques in insect pathology, Academic Press, San Diego.
Papierok, B. & Havukkala, I. 1986. Entomophthoraceous fungi parasiting cereal aphids in Finland. Ann. Entomol. Fenn. 52: 36–38.
Papierok, B., Rafanomezantsoa-Randriambololona, B.N. & Ziat, N. 1993. Nouvelles données sur I’écologie et le comportement entomopathogène experimental de l’entomophthorale Conidiobolus coronatus (Constantin) Batko (Zygomycètes). Entomophaga 38: 299–312.
Papierok, B., Torres, B.V.L. & Arnault, M. 1984. Contribution a l’ etude de la spécificité parasitairedu champignon entomopathogène Zoophthora radicans (Zygomycètes: Entomophthorales). Entomophaga 29: 109–119.
Papierok, B. & Wilding, N. 1979. Mise en èvidence d’une différence des sensibilité entre 2 clônes du puceron du pois, Acyrthosiphon pisum Harr. (Homoptères, Aphididae), exposés à 2 souches du champignon Phycomycète: Entomophthora obscura Hall et Dunn. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 288D: 93–95.
Papierok, B. & Wilding, N. 1981. Étude du comportement de plusieurs (Zygomycètes: Entomophthoraceae) vis-à-vis des pucerons Acyrthosiphon pisum et Sitobion avenae (Hom.: Aphididae). Entomophaga 26: 241–249.
Pell, J.K., Eilenberg, J., Hajek, A.E. & Steinkraus, D.C. 2001. Biology, ecology and pest management potential of Entomophthorales, pp. 71–153. In: Butt, T.M., Jackson, C. & Magan, N. (eds) Fungi as biocontrol agents, CAB International.
Pell, J.K., Pluke, R., Clark, S.J., Kenward, M.G. & Alderson, P.G. 1997a. Interactions between two aphid natural enemies, the entomopathogenic fungus, Erynia neoaphidis and the predatory beetle, Coccinella septempunctata. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 69: 261–268.
Pell, J.K., Tydeman, C. & Mccartney, H.A. 1997b. Impact of rainfall on the persistence and transmission of Erynia neoaphidis. Insect Pathogens and Insect Parasitic Nematodes, IOBC Bulletin 21: 49.
Pendland, J.C. & Boucias, D.G. 1996. Phagocytosis of lectinopsonized fungal cells and endocytosis of the ligand by insect Spodoptera exigua granular hemocytes: An ultrastructural and immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res. 285: 57–67.
Perry, D.F. 1988. Germination of Erynia bullata resting spores. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 51: 161–162.
Perry, D.F. & Fleming, R.A. 1989. The timing of Erynia radicans resting spore germination in relation to mycosis of Choristoneura funiferana. Can. J. Bot. 67: 1657–1663.
Perry, D.F. & Latgé, J.P. 1982. Dormancy and germination of Conidiobolus obscurus azygospores. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 78: 221–225.
Perry, D.F. & Latgé, J.P. 1983. The effect of eight fungicides on germination of Conidiobolus obscurus resting spores. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 42: 83–86.
Petch, T. 1925. Entomogenous fungi and their use in controlling insect pests. Bull. Dep. Agric. Ceylon 71, 40 pp.
Petch, T. 1932. A list of entomogenous fungi of Great Britain. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 17: 170–178.
Petch, T. 1937. Notes on entomogenous fungi. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 21: 34–67.
Pickering, J., Dutcher, J.D. & Ekbon, B.S. 1989a. An epizootic caused by Erynia neoaphidis and E. radicans (Zygomycetes, Entomophthoraceae) on Acyrthosiphon pisum (Homoptera, Aphididae) on legumes under overhead irrigation. J. Appl. Entomol. 107: 331–333.
Pickering, J., Dutcher, J.D. & Ekbon, B.S. 1989b. The effect of a fungicide on fungal-induced mortality of pecan aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) in the field. J. Econ. Entomol. 83: 1801–1805.
Pickering, J. & Gutierrez, A.P. 1991. Differential impact of the pathogen Pandora neoaphidis (Remaudière et Hennebert) Humber (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) on the species composition of Acyrthosiphon aphids in alfalfa. Can. Entomol. 123: 315–320.
Pilarska, D., Mcmanus, M., Pilarski, P., Georgiev, G., Mirchev, P. & Linde, A. 2006. Monitoring the establishment and prevalence of the fungal entomopathogen Entomophaga maimaiga in two Lymantria dispar L. populations in Bulgaria. J. Pest Sci. 79: 63–67.
Pope, T., Croxon, E., Pell, J.K., Godfray, H.C.J. & Müller, C.B. 2002. Apparent competition between two species of aphid via the fungal pathogen Erynia neoaphidis and its interaction with the aphid parasitoid Aphidius ervi. Ecol. Entomol. 27: 196–203.
Poprawski, T.J., Mercadier, G. & Wraight, S.P. 1992. Interactions between Diuraphis noxia, Zoophthora radicans and Aphelinus asychis — preliminary results of laboratory studies, pp. 180–188. In: Morrison, W.P. (ed.) Proceedings of the 5th Russian Wheat Aphid Workshop, Fort Worth, Great Plains Agricultural Council Publication.
Poprawski, T.J. & Wraight, S.P. 1998. Fungal pathogens of Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae), pp. 209–233. In: Quisenberry, S.S. & Peairs, F.B. (eds) Response model for an introduced pest — Russian wheat aphid, Entomological Society of America, Lanham, Marylend.
Powell, W., Dean, G.J. & Wilding, N. 1986a. The influence of weeds on aphid-specific natural enemies in winter wheat. Crop Prot. 5: 182–189.
Powell, W., Wilding, N., Brobyn, P.J. & Clark, S.J. 1986b. Interference between parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) and fungi (Entomophthorales) attacking cereal aphids. Entomophaga 31: 293–302.
Prasertphon, S. 1963. Conidial formation in Entomophthora coronata (Costantin) Kevorkian. J. Insect. Pathol. 5: 318–335.
Rabasse, J.M. & Robert, Y. 1975. Factuers de limitation des populations d’Aphis fabae dans l’ouest de la France. II. Incidence des mycoses à Entomophthora sur les populations des hôtes primaires et de féverole de printemps. Entomophaga 20: 49–63.
Raj, D. & Ramakrishnan, N. 1982. Control of mustard aphid, Lipaphis erysimi Kaltenbach (Homoptera: Aphididae)-feasibility of integrated approach. J. Entomol. Res. 6(2): 123–129.
Ratcliffe, N.A. & Rowley, A.F. 1979. Role of hemocytes in defense against biological agents, pp. 331–414. In: Gupta, A.P. (ed.) Insect hemocytes, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge.
Remaudiére, G. 1977. Sur quelques Aphidoidea de la Polynésie Française. Bull. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 82: 151–155.
Remaudiére, G. 1983. Lutte biologique contre les pucerons des céréales au moyen des champignons Entomophthorales, pp. 227–246. In: Cavalloro, R. & Piavaux, A. (eds) Comm. Eur. Comm Prog. Integr. Biol. Control: Progress Report 1979–1981.
Remaudiére, G. & Hennebert, G.L. 1980. Revision systematique de Entomophthora aphidis Hoffm. in Fres. Description de deux nouveaux pathogènes d’ Aphides. Mycotaxon 11: 269–321.
Remaudiére, G. & Keller, S. 1980. Revision systematique des genres d’Entomophthoraceae a potentialite entomopathogene. Mycotaxon 11: 323–338.
Remaudiére, G., Keller, S., Papierok, B. & Latgé, J.P. 1976a. Considerations systematique et biologiques sur quelque espèces d’ Entomophthora du groupe sphaerosperma pathogènes d’ insectes (Phycomycetes: Entomophthoraceae). Entomophaga 21: 163–177.
Remaudiére, G., Latgé, J.P. & Michel, M.F. 1981. Écologie compareé des entomophthoraceés pathogènes de pucerons en France littorale et continentale. Entomophaga 26: 157–178.
Remaudiére, G., Latgé, J.P. & Papierok, B. 1979. Reconsidération taxonomique de Entomophthora obscura Hall et Dunn. Ann. Microbiol. (Inst. Pasteur) 130A(2): 151–162.
Remaudiére, G., Latgé, J.P., Papierok, B. & Coremans-Pelseneer, J. 1976b. Sur le pouvoir pathogène de quatre espèces d’Entomophthorales occasionnellement isolées d’aphides en France. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 283D: 1065–1068.
Robert, Y., Rabasse, J.M. & Scheltes, P. 1973. Facteurs de limitation des populations d’Aphis fabae Scopoli dans l’Quest de la France. I. Epizootiologie des maladies à Entomophthorales sur féverole de printemps. Entomophaga 18: 61–75.
Roberts, D.W. & Humber, R.A. 1981. Entomogenous fungi, pp. 201–236. In: Cole, G.T. & Kendrick, A. (eds) Biology of conidial fungi 2, Academic Press, New York.
Rockwood, L.P. 1950. Entomogenous fungi of the family Entomophthoraceae in the Pacific Northwest. J. Econ. Entomol. 43: 704–707.
Rohel, E., Couteaudier, Y., Papierok, B., Cavelier, N. & Dedryver, C.A. 1997. Ribosomal internal transcribed spacer size variation correlated with RAPD-PCR pattern polymorphism in the entomopathogenic fungus Erynia neoaphidis and some closely related species. Mycol. Res. 101: 573–579.
Roy, H.E. & Pell, J.K. 2000. Interactions between entomopathogenic fungi and other natural enemies: implications biological control. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 10: 737–752.
Roy, H.E., Pell, J.K. & Alderson, P.G. 1999. Effects of fungal infection on the alarm response of pea aphids. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 74: 69–75.
Roy, H.E., Pell, J.K. & Alderson, P.G. 2001. Targeted dispersal of the aphid pathogenic fungus Erynia neoaphidis by the aphid predator Coccinella septempunctata. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 11: 99–110.
Roy, H.E., Pell, J.K. & Alderson, P.G. 2002. Effect of Erynia neoaphidis infection and coccinellid foraging on the spatial distribution of aphids on plants. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 81: 127–129.
Roy, H.E., Pell, J.K., Clark, S.J. & Alderson, P.G. 1998. Implications of predator foraging on aphid pathogen dynamics. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 71: 236–247.
Rudraiah, M.P. & Usman, S. 1955. An epizootic of the oleander aphids. Sci. Cult. 21: 158–159.
Sajap, A.S., Atim, A.B., Husim, H. & Wahab, Y.A. 1997. Isolation of Conidiobolus coronatus (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) from soil and its effect on Coptotermes curvignathus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Sociobiology 30: 257–262.
Sampedro, L., Uziel, A. & Latgé, J.P. 1984. Agressivité de Conidiobolus obscurus vis-à-vis du puceron du pois. II. Mode de germination in vitro des conidies primaries de souches d’agressivité différente. Mycopathologia 86: 3–19.
Samson, R.A., Evans, H.C. & Latgé, J.P. 1988. Atlas of entomopathogenic fungi. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 127 pp.
Sanchez-Peńa, S.R. 2000. Entomopathogens from two Chihuahuan desert localities in Mexico. BioControl 45: 63–78.
Schmitz, V., Dedryver, C.A. & Pierre, J.S. 1993. Influence of an Erynia neoaphidis infection on the relative rate of increase of the cereal aphid Sitobion avenae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 61: 62–68.
Schofield, G., Pell, J.K. & Harrington, R. 1995. Overwintering of the entomophthoralean fungus Erynia neoaphidis on foliage under field and laboratory conditions, p. 54. In: Program and Abstract, Society for Invertebrate Pathology, 28th Annual Meeting, Cornell University, Ithaca.
Shah, P.A. & Pell, J.K. 2003. Entomopathogenic fungi as biological control agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 61: 413–423.
Shah, P.A., Aebi, M. & Tuor, U. 1998. Method to immobilize the aphid-pathogenic fungus Erynia neoaphidis in an alginate matrix for biocontrol. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 64: 4260–4263.
Shah, P.A., Aebi, M. & Tuor, U. 1999. Production factors involved in the formulation of Erynia neoaphidis as alginate granules. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 9: 19–28.
Shah, P.A., Aebi, M. & Tuor, U. 2000a. Infection of Macrosiphum euphorbiae with mycelial preparations of Erynia neoaphidis in a greenhouse trial. Mycol. Res. 104: 645–652.
Shah, P.A., Aebi, M. & Tuor, U. 2000b. Drying and storage procedures for formulated and unformulated mycelia of the aphid-pathogenic fungus Erynia neoaphidis. Mycol. Res. 104: 440–446.
Shah, P.A., Aebi, M. & Tuor, U. 2002. Effects of constant and fluctuating temperatures on sporulation and infection by the aphid-pathogenic fungus Pandora neoaphidis. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 103: 257–266.
Shah, P.A., Clark, S.J. & Pell, J.K. 2004. Assessment of aphid host range and isolate variability in Pandora neoaphidis (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). Biol. Control 29: 90–99.
Shands, W.A., Simpson, G.W., Hall, I.M. & Gordon, C.C. 1972. Further evaluation of entomogenous fungi as a biological agent of aphid control on potatoes in Northeastern Maine. Maine AES Tech. Bull. 58, 31 pp.
Shimazu, M. 1977. Infectivity of Entomophthora delphacis (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) to the Cotton Aphid, Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 12: 200–201.
Sierotzki, H., Camastral, F., Shah, P.A., Aebi, M. & Tuor, U. 2000. Biological characteristics of selected Erynia neoaphidis isolates. Mycol. Res. 104: 213–219.
Silvie, P., Dedryver, C.A. & Tanguy, S. 1990. Application expérimentale de mycelium d’Erynia neoaphidis (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) dans des populations de pucerons sur laitues en serre maraîchère: etude du suivi de l’inoculum par charactérisation enzymatique. Entomophaga 35: 375–384.
Silvie, P. & Papierok, B. 1991. Les ennemis naturels d’insects du cotonier au Tchad: premières donneés sur les champignons de l’ordre des Entomophthorales. Coton Fibres Tropicale 46: 293–308.
Sivčev, I. 1991. Entomopathogenic fungi of cabbage aphid (Brevicoryne brassicae Linné). Plant Protection (Zast. Bilja) 42: 61–68.
Sivčev, I. 1992. Seasonal dynamics and density of cabbage aphid’s (Brevicoryne brassicae Linné) entomopathogenous fungi. Plant Protection (Zast. Bilja) 43: 181–195.
Sivčev, I. 1993. Influence of temperatures on the sporulation of aphidopathogenous fungi Pandora neoaphidis (Remaudière et Hennebert) Humber. Plant Protection (Zast. Bilja) 44: 133–138.
Sivčev, I. & Draganić, M. 1994. UV rays and Pandora neoaphidis conidia. Plant Protection (Zast. Bilja) 45: 203–207.
Sivčev, I. & Manojlović, B. 1995. Effects of temperature and relative humidity on the germination of aphidopathogenous fungus Pandora neoaphidis conidia. Plant Protection (Zast. Bilja) 46: 51–56.
Six, D.L. & Mullens, B.A. 1996. Distance of conidial discharge of Entomophthora muscae and Entomophthora schizophorae (Zygomycotina: Entomophthorales). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 67: 253–258.
Smith, M.T. & Hardee, D.D. 1996. Influence of fungicides on development of an entomopathogenic fungus (Zygomycetes: Neozygitaceae) in the cotton aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 25: 677–687.
Söderhäll, K. & Ajaxon, R. 1982. Effect of quinones and melanin on mycelial growth of Aphanomyces spp. and extracellular protease of Aphanomyces astaci, a parasite on crayfish. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 39: 105–109.
Soper, R.S., Holbrook, F.R., Majchrowicz, I. & Gordon, C.C. 1975. Production of Entomophthora resting spores for biological control of aphids. Univ. Maine Orono Life Sci. Agric. Exp. Stn. Tech. Bull. 76: 1–15.
Soper, R.S. & Macleod, D.M. 1963. Spore morphology of Entomophthora fresenii Nowakowski. J. Insect Pathol. 5: 478–482.
Soper, R.S. & Macleod, D.M. 1981. Descriptive epizootiology of an aphid mycosis. U.S.D.A. Techn. Bull., No. 1632, 17 pp.
Soper, R.S. & Ward, M.G. 1981. Production, formulation and application of fungi for insect control, pp. 161–180. In: Papavias, G.C. (ed.) Biological control in crop production, Beltsville Agric. Res. Centre, Ottawa.
Srinivasan, M.C. & Thirumalachar, M.J. 1964. On the identity of Entomophthora coronata. Mycopathol. Mycol. Appl. 24: 294–296.
Steenberg, T. & Eilenberg, J. 1995. Natural occurrence of Entomopathogenic fungi on Aphids at an agricultural field site. Czech Mycology 48: 89–96.
Steenberg, T., Eilenberg, J. & Bresciani, J. 1996. First record of a Neozygites species (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) infecting springtails (Insecta: Collembola). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 68: 97–100.
Steinhaus, E.A. 1954. The effects of disease on insect populations. Hilgardia 23: 197–261.
Steinhaus, E.A. 1956. Microbial control: The emergence of an idea. Hilgardia 26: 107–160.
Steinhaus, E.A. 1975. Disease in a Minor Cord. Ohio State Univ. Press, 488 pp.
Steinkraus, D.C. & Boys, G.O. 1997. Update on prediction of epizootics with extension-based sampling service, pp. 1047–1048. In: Proc. Beltwide Cotton Conference, New Orleans: National Cotton Council of America.
Steinkraus, D.C. & Boys, G.O. 2005. Mass harvesting of entomopathogenic fungus, Neozygites fresenii, from natural field epizootics in the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 88: 212–217.
Steinkraus, D.C., Boys, G.O., Bagwell, R.D., Johnson, D.R., Lorenz, G.M., Meyers, H., Layton, M.B. & O’XXXleary, P.F. 1998a. Expansion of extension-based aphid fungus sampling service to Louisiana and Mississippi, pp. 1239–1242. In: Proc. Beltwide Cotton Conference, National Cotton Council of America, San Diego.
Steinkraus, D.C., Boys, G.O., Hollingsworth, R.G., Bacheler, J.S., Durant, J.A., Freeman, B.L., Gaylor, M.J., Harris, F.A., Kuntson, A., Lentz, G.L., Leonard, B.R., Luttrell, R., Parker, D., Powell, J.D., Ruberson, J.R. & Sorenson, C. 1996a. Multistate sampling for Neozygites fresenii in cotton, pp. 735–738. In: Proc. Beltwide Cotton Conference, National Cotton Council of America, Nashville.
Steinkraus, D.C., Boys, G.O. & Rosenheim, J.A. 2002. Classical biological control of Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae) with Neozygites fresenii (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) in California cotton. Biol. Control 25: 297–304.
Steinkraus, D.C., Boys, G.O. & Slaymaker, P.H. 1993. Culture, storage, and incubation period of Neozygites fresenii (Entomophthorales: Neozygitaceae), a pathogen of the cotton aphid. Southwest. Entomol. 18: 197–202.
Steinkraus, D.C., Hollingsworth, R.G. & Boys, G.O. 1996b. Aerial spores of Neozygites fresenii (Entomophthorales: Neozygitaceae): density, periodicity, and potential role in cotton aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) epizootics. Environ. Entomol. 25: 48–57.
Steinkraus, D.C., Hollingsworth, R.G. & Slaymaker, P.H. 1995. Prevalence of Neozygites fresenii (Entomophthorales: Neozygitaceae) on cotton aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Arkansas cotton. Environ. Entomol. 24: 465–474.
Steinkraus, D.C., Howard, M.N., Hollingsworth, R.G. & Boys, G.O. 1999. Infection of sentinel cotton aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) by aerial spores of Neozygites fresenii (Entomophthorales: Neozygitaceae). Biol. Control 14: 181–185.
Steinkraus, D.C., Kring, T.J. & Tugwell, N.P. 1991. Neozygites fresenii in Aphis gossypii on cotton. Southwest. Entomol. 16: 118–122.
Steinkraus, D.C., Oliver, J.B., Humber, R.A. & Gaylor, M.J. 1998b. Mycosis of bandedwinged whitefly (Trialeurodes abutilonea) (Homoptera: Aleurodidae) caused by Orthomyces aleyrodis gen. et sp. nov. (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 72: 1–8.
Steinkraus, D.C. & Rosenheim, J. 1995. Biological factors influencing the epizootiology of cotton aphid fungus, pp. 887–889. In: Proc. Beltwide Cotton Conference, National Cotton Council of America, San Antonio.
Steinkraus, D.C. & Slaymaker, P.H. 1994. Effect of temperature and humidity on formation, germination, and infectivity of conidia of Neozygites fresenii (Zygomycetes: Neozygitaceae) from Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 64: 130–137.
Steinkraus, D.C. 2006. Factors affecting transmission of fungal pathogens of aphids. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 92: 125–131.
St. Leger, R.J. 1991. Integument as a barrier to microbial infections, pp. 284–306. In: Binnington, K. & Retnakaran, A. (eds) Physiology of the insect epidermis, CSIRO, Melbourne.
Štalmachová, M. & Cagáň, L. 2000. Entomophtorales as significant natural enemies of cereal aphids infecting maize in Slovakia. Insect Pathogens and Insect Parasitic Nematodes. IOBC WPRS Bulletin 23: 187–191.
Tanabe, Y., O’XXXdonnell, K., Saikawa, M. & Sugiyama, J. 2000. Molecular phylogeny of parasitic Zygomycota (Dimargaritales, Zoopagales) based on nuclear small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 16: 253–262.
Tanada, Y. 1963. Epizootiology of insect diseases, pp. 423–475. In: Steinhaus, E.A. (ed.) Insect pathology: An advanced treatise, Vol. 2., Academic Press, New York.
Tanada, Y. & Fuxa, J.R. 1987. The pathogen population, pp. 113–157. In: Fuxa, J.R. & Tanada, Y. (eds) Epizootiology of insect diseases, John Wiley, New York.
Tehler, A., Little, D.P. & Farris, J.S. 2003. The full-length phylogenetic tree from 1551 ribosomal sequences of chitinous fungi, Fungi. Mycol. Res. 107: 901–916.
Thaxter, R. 1888. The Entomophthoreae of the United States. Mem. Boston Soc. Nat. Hist. 4: 133–201.
Thoizon, A. 1967. Entomophthora pyriformis sp. nov., entomophthorale parasite de puceron. Entomophaga 12: 303–307.
Thoizon, A. 1970. A key to species of Entomophthora infecting aphids. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 6: 517–562.
Thomsen, L., Bresciani, J. & Eilenberg, J. 2001. Formation and germination of resting spores from different strains from the Entomophthora muscae complex produced in Musca domestica. Can. J. Bot. 79: 1076–1082.
Tkaczuk, C. 2006. The effect of selected heavy metal ions on the growth and conidial germination of the aphid pathogenic fungus Pandora neoaphidis (Remaudière et Hennebert) Humber. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 14: 897–902.
Turian, G. 1957. Entomo-mycoses dans la région de Genève. Mitt. Schweiz. Entomol. Ges. 30: 93–98.
Tymon, A.M., Shah, P.A. & Pell, J.K. 2004. PCR-based molecular discrimination of Pandora neoaphidis isolates from related entomopathogenic fungi and development of species-specific diagnostic primers. Mycol. Res. 108: 419–433.
Tyrrell, D. & Macleod, D.M. 1972. A taxonomic proposal regarding Delacroixia coronata (Entomophthoraceae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 20: 11–13.
Uziel, A. & Kenneth, R.G. 1986. In vitro resting spore production in Erynia neoaphidis, p. 230. In: Samson, R.A., Vlak, J.M. & Peters, D. (eds) Fundamental and Applied Aspects of Insect Pathology, Fourth International Colloquium on Invertebrate Pathology, Veldhoven.
Uziel, A. & Kenneth, R.G. 1991. Survival of primary conidia and capilliconidia at different humidities in Erynia (subgen. Zoophthora) spp. and in Neozygites fresenii (Zygomycotina: Entomophthorales), with special emphasis on Erynia radicans. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 58: 118–126.
Uziel, A. & Kenneth, R.G. 1999. Influence of commercially derived lipids and a surfactant on the mode of germination and process of germ-tube formation in primary conidia of two species of Erynia subgenus Neopandora (Zygomycotina: Entomophthorales). Mycopathologia 144: 153–163.
Uziel, A. & Shtienberg, D. 1993. Effect of meteorological variates on persistence of primary conidia and capilliconidia of Erynia radicans (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) under natural conditions. Ann. Appl. Biol. 122: 441–450.
Van Der Plank, J.E. 1975. Principles of plant infections. Academic Press, New York, 210 pp.
Van Driesche, R.G. & Bellows, T.S. 1996. Biological control. Publ. Chapman Hall., 539 pp.
Vey, A. & Fargues, J. 1977. Histological and ultrastructural studies of Beauveria bassiana infection in Leptinotarsa decemlineata larvae during ecdysis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 30: 207–215.
Vey, A., Hoagland, R.F. & Butt, T.M. 2001. Toxic metabolites of fungal biocontrol agents, pp. 311–346. In: Butt, T.M., Jackson, C. & Magan, N. (eds) Fungi as biocontrol agents, CAB International.
Vingaard, M.G., Steinkraus, D.C., Boys, G.O. & Eilenberg, J. 2003. Effects of long-term storage at −14°C on the survival of Neozygites fresenii (Entomophthorales: Neozygitaceae) in cotton aphids (Homopter: Aphididae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 82: 97–102.
Voronina, E.G. 1968. Ecological characteristics of strains of the fungus Entomophthora thaxteriana Petch reared from the pea aphid and the greenhouse thrips. Tr. Vses. Inst. Zashch. Rast. 31: 394–406.
Voronina, E.G. 1971. Entomophthorosis epizootics of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris (Homoptera, Aphidoidea). Entomol. Rev. 50: 444–453.
Voronina, E.G. 1997. Entomoftorovye griby i biopreparaty epizootiynovo i toksicheskovo deĭstviya. Zashch. Karant. Rast. 5: 12–13.
Wallace, D.R., Mcleod, D.M., Sullivan, C.R., Tyrell, D. & De Lyzer, A.J. 1976. Induction of resting spore germination in Entomophthora aphidis by long-day light conditions. Can. J. Bot. 54: 1410–1418.
Watanabe, H. 1987. The host population, pp. 71–112. In: Fuxa, J.R. & Tanada, Y. (eds) Epizootiology of insect diseases, John Wiley, New York.
Waterhouse, G.M. 1973. Entomophthorales, pp. 219–229. In: Ainsworth, G.C., Sparrow, F.K. & Sussman, A.S. (eds) The fungi. An advanced treatise, Vol. IVb, Academic Press, New York.
Waterhouse, G.M. & Brady, B.L. 1982. Key to the species of Entomophthora s. lato. Bull. Br. Mycol. Soc. 16: 113–143.
Weiser, J. & Batko, A. 1966. A new parasite of Culex pipiens L., Entomophthora destruens sp. nov. (Phycomycetes, Entomophthoraceae). Folia Parasit. 13: 144–149.
Wells, M.L., Mcpherson, R.M., Ruberson, J.R. & Herzog, G.A. 2000. Effect of fungicide application on activity of Neozygites fresenii (Entomophthorales: Neozygitaceae) and cotton aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) suppression. J. Econ. Entomol. 93: 1118–1126.
Weseloh, R.M. & Andreadis, T.G. 2002. Detecting the titer in forest soils of spores of the gypsy moth (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) fungal pathogen, Entomophaga maimaiga (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). Can. Entomol. 134: 269–279.
Wilding, N. 1969. Effect of humidity on the sporulation of Entomophthora aphidis and E. thaxteriana. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 53: 126–130.
Wilding, N. 1970a. Entomophthora conidia in the air-spora. J. Gen. Microbiol. 62: 149–157.
Wilding, N. 1970b. The effect of temperature on the infectivity and incubation periods of the fungi Entomophthora aphidis and E. thaxteriana for the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum, pp. 84–88. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Colloquium of Insect Pathology, Maryland.
Wilding, N. 1971. Discharge of conidia of Entomophthora thaxteriana Petch from the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris. J. Gen. Microbiol. 69: 417–422.
Wilding, N. 1973. The survival of Entomophthora spp. in mummified aphids at different temperature and humidities. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 21: 309–311.
Wilding, N. 1975. Entomophthora species infecting pea aphis. Trans. R. Entomol. Soc. 127: 171–183.
Wilding, N. 1981. The effect of introducing aphid-pathogenic Entomophthoraceae into field populations of Aphis fabae Scop. Ann. Appl. Biol. 99: 11–23.
Wilding, N. 1982. The effect of fungicides on field populations of Aphis fabae and on the infection of the aphids by Entomophthoraceae. Ann. Appl. Biol. 100: 221–228.
Wilding, N., Latteur, G. & Dedryver, C.A. 1986a. Evaluation of Entomophthorales for Aphid control: Laboratory and field data, pp. 159–162. In: Samson, R.A., Vlak, J.M. & Peters, D. (eds) Fundamental and Applied Aspects of Invertebrate Pathology, 4th Inter. Coll. Invert. Pathol, Wageningen.
Wilding, N., Mardell, S.K. & Brobyn, P.J. 1986b. Introducing Erynia neoaphidis into a field populations of Aphis fabae: form of the inoculum and effect of irrigation. Ann. Appl. Biol. 108: 373–385.
Wilding, N., Mardell, S.K., Brobyn, P.J., Wratten, S.D. & Lomas, J. 1990. The effect of introducing the aphid pathogenic fungus Erynia neoaphidis into populations of cereal aphids. Ann. Appl. Biol. 117: 683–691.
Wilding, N. & Perry, N.J. 1980. Studies on Entomophthora in populations of Aphis fabae on field beans. Ann. Appl. Biol. 94: 367–378.
Witlaczil, E. 1885. Neozygites aphidis, eine neue gregarine. Arch. Mikrosk. Anat. 24: 599–603.
Wraight, S.P., Butt, T.M., Galaini-Wraight, S., Allee, L.L., Soper, R.S. & Roberts, D.W. 1990. Germination and infection processes of the entomophoralean fungus Erynia radicans on the potato leafhopper, Empoasca fabae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 56: 157–174.
Wraight, S.P., Galaini-Wraight, S., Carruthers, R.I. & Roberts, D.W. 2003. Zoophthora radicans (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) conidia production from naturally infected Empoasca kraemeri and dry-formulated mycelium under laboratory and field conditions. Biol. Control 28: 60–77.
Wraight, S.P, Jackson, M.A. & De Kock, S.L. 2001. Production, stabilization and formulation of fungal biocontrol agents, pp. 253–287. In: Butt, T.M., Jackson, C. & Magan, N. (eds) Fungi as biocontrol agents, CAB International.
Wraight, S.P., Poprawski, W.L., Meyer, W.L. & Peairs, F.B. 1993. Natural enemies of Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) and associated cereal aphid species in spring-planted wheat and barley in Colorado. Environ. Entomol. 22: 1383–1391.
Xu, J.H. & Feng, M.G. 2000. The time-dose mortality modelling and virulence indices for two entomophthoralean species, Pandora delphacis and Pandora neoaphidis, against the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae. Biol. Control 17: 29–34.
Xu, J.H., & Feng, M.G. 2002. Pandora delphacis (Entomophthorales: Entomophthoraceae) infection affects the fecundity and population dynamics of Myzus persicae Sulzer (Homoptera: Aphididae) at varying regimes of temperature and relative humidity in the laboratory. Biol. Control 25: 85–91.
Xu, Q., Feng, M.G., Xu, J.H. & Liu, Z.Q. 2000. High virulence and rapid infection of an aphid-derived isolate of Zoophthora anhuiensis against Myzus persicae. Mycosystema 19: 241–247.
Yendol, W.G. 1968. Factors affecting germination of Entomophthora conidia. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 10: 116–121.
Zimmermann, A. 1901. De dietrlijke Vijanden der Koffiecultuur op. Iava Deel. II Meded. Lands Plantent. 44: 25–27.
Zimmermann, G. 1978. Zur Biologie, Untersuchungsmethodik und Bestimmung von Entomophthoraceen (Phycomycetes: Entomophthorales) an Blattläusen. Z. Angew. Entomol. 85: 241–252.
Zimmermann, G. 1986. Insect pathogenic fungi as pest control agents, pp. 217–231. Franz J.M. (ed.) Biological plant and health protection, Gustav Fischer Verlag.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barta, M., Cagáň, L. Aphid-pathogenic Entomophthorales (their taxonomy, biology and ecology). Biologia 61 (Suppl 21), S543–S616 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-007-0100-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-007-0100-x