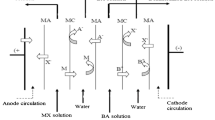
Abstract
Limiting current density of ammonium nitrate solution in laboratory-, pilot-, and industrial-scale electrodialysis modules were determined to provide a method for the prediction of the limiting current density of ammonium nitrate solutions at any conditions. The current-voltage curve was measured in each case and the limiting current density was evaluated using the dependence of the derivative, dI/dU, on the electric current, I. The limiting current was determined as a current at which the derivative dI/dU equals zero. The developed method enables not only the prediction of the limiting current density but the limiting cut and limiting flux can be determined concurrently at any linear flow velocity of the diluate and inlet ammonium nitrate concentration. It could help to prevent working in the overlimiting region and to avoid undesirable decrease of current efficiency and pH changes. The limiting cut is the maximal cut that can be obtained at certain linear flow velocity and module geometry irrespective of the inlet ammonium nitrate concentration and it is very useful information when designing a new electrodialysis unit for specific application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barragán, V. M., & Ruíz-Bauzá, C. (1998). Current-voltage curves for ion-exchange membranes: A method for determining the limiting current density. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 205, 365–373. DOI: 10.1006/jcis.1998.5649.
Davis, T. A., Grebenyuk, V., & Grebenyuk, O. (2001). Electromembrane processes. In S. Pereira Nunes, & K. V. Peinemann (Eds.), Membrane technology: in the chemical industry (pp. 222–267). Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH. DOI: 10.1002/3527600388.ch12.
Gonçalves, F., Fernandes, C., Cameira dos Santos, P., & de Pinho, M. N. (2003). Wine tartaric stabilization by electrodialysis and its assessment by the saturation temperature. Journal of Food Engineering, 59, 229–235. DOI: 10.1016/s0260-8774(02)00462-4.
Jaime Ferrer, J. S., Laborie, S., Durand, G., & Rakib, M. (2006). Formic acid regeneration by electromembrane processes. Journal of Membrane Science, 280, 509–516. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2006.02.012.
Kaláb, J., & Palaty, Z. (2012). Electrodialysis of oxalic acid: batch process modeling. Chemical Papers, 66, 1118–1123. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-012-0232-5.
Kinčl, J., Bobák, M., Diblíková, L., & Čurda, L. (2012). Characteristics of demineralization of salty whey. In Book of Abstracts of ELMEMPRO 2012, August 26–29, 2012 (pp. 62–63). Česk’y Krumlov, Czech Republic.
Krol, J. J., Wessling, M., & Strathmann, H. (1999). Concentration polarization with monopolar ion exchange membranes: current-voltage curves and water dissociation. Journal of Membrane Science, 162, 145–154. DOI: 10.1016/s0376-7388(99)00133-7.
Lee, H. J., Strathmann, H., & Moon, S. H. (2006). Determination of the limiting current density in electrodialysis desalination as an empirical function of linear velocity. Desalination, 190, 43–50. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2005.08.004.
Machuča, L., Tvrzník, D., & Kysela, V. (2012). Conception of electromembrane processes for reuse of waste water containing ammonium nitrate. Waste Forum, 4, 222–228. (in Czech)
Marek, J. (2012). Zkušenosti z úpravy vody pomocí membránovych technologií. Energie kolem nás, 2012(4), 22–24.
Meng, H., Deng, D. Y., Chen, S. J., & Zhang, G. J. (2005). A new method to determine the optimal operating current (I lim’) in the electrodialysis process. Desalination, 181, 101–108. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2005.01.014.
Mulder, M. (1996). Basic principles of membrane technology. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Nikonenko, V. V., Pismenskaya, N. D., Istoshin, A. G., Zabolotsky, V. I., & Shudrenko, A. A. (2008). Description of mass transfer characteristics of ED and EDI apparatuses by using the similarity theory and compartmentation method. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 47, 1118–1127. DOI: 10.1016/j.cep.2007.12.005.
Ponce-de-León, C., & Field, R. W. (2000). On the determination of limiting current density from uncertain data. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 30, 1087–1090. DOI: 10.1023/a:1004015617522.
Ponce-de-León, C., Low, C. T. J., Kear, G., & Walsh, F. C. (2007). Strategies for the determination of the convectivediffusion limiting current from steady state linear sweep voltammetry. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 37, 1261–1270. DOI: 10.1007/s10800-007-9392-3.
Rapp, H. J., & Pfromm, P. H. (1998). Electrodialysis for chloride removal from the chemical recovery cycle of a Kraft pulp mill. Journal of Membrane Science, 146, 249–261. DOI: 10.1016/s0376-7388(98)00122-7.
Strathmann, H. (1991). Electrodialysis. In R. W. Baker (Ed.), Membrane separation systems (pp. 396–448). Park Ridge, NJ, USA: Noyes Data Corporation.
Šímová, H., Kysela, V., & Černín, A. (2010). Demineralization of natural sweet whey by electrodialysis at pilot-plant scale. Desalination and Water Treatment, 14, 170–173. DOI: 10.5004/dwt.2010.1023.
Valerdi-Pérez, R., & Ibáñez-Mengual, J. A. (2001). Current—voltage curves for an electrodialysis reversal pilot plant: determination of limiting currents. Desalination, 141, 23–37. DOI: 10.1016/s0011-9164(01)00386-1.
Vera, E., Ruales, J., Dornier, M., Sandeaux, J., Sandeaux, R., & Pourcelly, G. (2003). Deacidification of clarified passion fruit juice using different configurations of electrodialysis. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 78, 918–925. DOI: 10.1002/jctb.827.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Káňavová, N., Machuča, L. & Tvrzník, D. Determination of limiting current density for different electrodialysis modules. Chem. Pap. 68, 324–329 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-013-0456-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-013-0456-z