Abstract
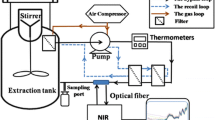
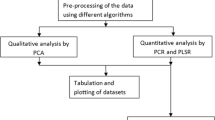
Near-infrared (NIR) imaging systems simultaneously record spectral and spatial information. Near-infrared imaging was applied to the identification of (E,Z)-4-(3-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acryloyl)morpholine (dimethomorph) in both mixed samples and commercial formulation in this study. The distributions of technical dimethomorph and additive in the heterogeneous counterfeit product were obtained by the relationship imaging (RI) mode. Furthermore, a series of samples which consisted of different contents of uniformly distributed dimethomorph were prepared and three data cubes were generated for each content. The spectra extracted from these images were imported to establish the partial least squares model. The model’s evaluating indicators were: coefficient of determination (R 2) 99.42 %, root mean square error of calibration (RMSEC) 0.02612, root mean square error of cross-validation (RMSECV) 0.01693, RMSECVmean 0.03577, relative standard error of prediction (RSEP) 0.01999, and residual predictive deviation (RPD) 15.14. Relative error of prediction of the commercial formulation was 0.077, indicating the predicted value correlated with the real content. The chemical value reconstruction image of dimethomorph formulation products was calculated by a MATLAB program. NIR microscopy imaging here manifests its potential in identifying the active component in the counterfeit pesticide and quantifying the active component in its scanned image.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkshire, I. R., Kenny, P. G., Fletcher, I. W., & Prutton, M. (1996). Quantitative surface microanalysis of samples with extreme topograghy utilising image interpretation by scatter diagrams and principal component analysis. Ultramicroscopy, 63, 193–203. DOI: 10.1016/0304-3991(96)00039-3.
Clarke, F. (2004). Extracting process-related information from pharmaceutical dosage forms using near infrared microscopy. Vibrational Spectroscopy, 34, 25–35. DOI: 10.1016/j.vibspec.2003.08.005.
Gendrin, C., Roggo, Y., & Collet, C. (2007). Content uniformity of pharmaceutical solid dosage forms by near infrared hyperspectral imaging: A feasibility study. Talanta, 73, 733–741. DOI: 10.1016/j.talanta.2007.04.054.
Hoheisel, M. (2006). Review of medical imaging with emphasis on X-ray detectors. Nuclear Instrument and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 563, 215–224. DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2006.01.123.
Huang, Y., Wei, D., & Yang, C. (2008). Analysis of thiram, imidacloprid and diniconazole by RP-HPLC. Agrochemicals, 47, 114–115.
Kvalheim, O. M., & Liang, Y. Z. (1992). Heuristic evolving latent projections: resolving two-way multicomponent data. 1. Selectivity, latent-projective graph, datascope, local rank, and unique resolution. Analytical Chemistry, 64, 936–946. DOI: 10.1021/ac00032a019.
Lindberg, N. O., & Gabrielsson, J. (2004). Use of software to facilitate pharmaceutical formulation-experiences from a tablet formulation. Journal of Chemometrics, 18, 133–138. DOI: 10.1002/cem.853.
Lopes, M. B., & Wolff, J. C. (2009). Investigation into classification/sourcing of suspect counterfeit HeptodinTM tablets by near infrared chemical imaging. Analytica Chimica Acta, 633, 149–155. DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2008.11.036.
Ma, G., Wang, C., Fan, D., Xing, D., Qian, L., Wang, J., & Liu, S. (2006). Quantitative determination of imidacloprid by infrared absorption spectrometry. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 26, 434–437.
Rodionova, O. Y., Houmøller, L. P., Pomeranstev, A. L., Geladi, P., Burger, J., Dorofeyev, V. L., & Arzamastsev, A. P. (2005). NIR spectrometry for counterfeit drug detection: A feasibility study. Analytica Chimica Acta, 549, 151–158. DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2005.06.018.
Roggo, Y., Edmond, A., Chalus, P., & Ulmschneider, M. (2005). Infrared hyperspectral imaging for qualitative analysis of pharmaceutical solid forms. Analytica Chimica Acta, 535, 79–87. DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2004.12.037.
Sjöblom, J., Svensson, O., Josefson, M., Kullberg, H., & Wold, S. (1998). An evaluation of orthogonal signal correction applied to calibration transfer of near infrared spectra. Chemometric Intelligent Laboratory System, 44, 229–244. DOI: 10.1016/s0169-7439(98)00112-9.
Suutarinen, J., Änäkäi nen, L., & Autio, K. (1998). Comparison of light microscopy and spatially resolved Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) microscopy in the examination of cell wall components of strawberries. Lebensmittel Wissenschaft Technologie, 31, 595–601. DOI: 10.1006/fstl.1997.0331.
Wu, W., Walczak, B., Massart, D. L., Heuerding, S., Erni, F., Last, I. R., & Prebble, K. A. (1996). Artificial neural networks in classification of NIR spectral data: Design of the training set. Chemometric Intelligence Laboratory System, 33, 35–46. DOI: 10.1016/0169-7439(95)00077-1.
Zhang, L., Henson, M. J., & Sekulic, S. S. (2005). Multivariate data analysis for Raman imaging of a model pharmaceutical tablet. Analytica Chimica Acta, 545, 262–278. DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2005.04.080.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Min, SG., Cao, JL. et al. Near-infrared imaging for quantitative analysis of active component in counterfeit dimethomorph using partial least squares regression. Chem. Pap. 66, 1065–1072 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0212-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0212-9