Abstract
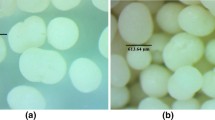
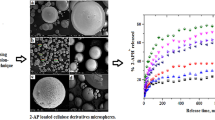
The present paper provides details of the preparation of polymeric tablets and microspheres based on piroxicam as a therapeutic active agent and the drug release study from these formulations. Tablets composed of ethylcellulose, Eudragit® or mixtures of Eudragit® and synthesised poly(oxepan-2-one) were prepared and tested. The effect of the matrix on the drug release at 37°C was studied. The drug-loaded microparticles were prepared using solvent evaporation microencapsulation. These systems were characterised by SEM and FTIR spectroscopy and the size and size distribution were also determined. The results demonstrated that the drug release could be modified by means of these formulations. Finally, piroxicam dissolution rate constants were calculated from Higuchi’s release model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arshady, R. (1993). Microcapsules for food. Journal of Microencapsulation, 10, 413–435. DOI: 10.3109/0265dy2049309015320.
Belarbi, L., Boudouaia, N., & Mesli, A. (2009). Synthese et caracterisation de poly(ɛ-caprolactone) a partir d’ɛ-caprolactone et differents diacides. Physical and Chemical News, 46, 104–110.
Casas, M., Ferrero, C., & Jiménez-Castellanos, M. R. (2010). Graft tapioca starch copolymers as novel excipients for controlled-release matrix tablets. Carbohydrate Polymers, 80, 71–77. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.10.065.
Chung, T. W., Huang, Y. Y., & Liu, Y. Z. (2001). Effects of the rate of solvent evaporation on the characteristics of drug loaded PLLA and PDLLA microspheres. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 212, 161–169. DOI: 10.1016/s0378-5173(00)00574-3.
De Brabander, C., Vervaet, C., & Remon, J. P. (2003). Development and evaluation of sustained release mini-matrices prepared via hot melt extrusion. Journal of Controlled Release, 89, 235–247. DOI: 10.1016/s0168-3659(03)00075-0.
Duarte, A. R. C., Costa, M. S., Simplício, A. L., Cardoso, M. M., & Duarte, C. M. M. (2006). Preparation of controlled release microspheres using supercritical fluid technology for delivery of anti-inflammatory drugs. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 308, 168–174. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.11.012.
El Bahri, Z., & Taverdet, J. L. (2007). Preparation and optimization of 2,4-D loaded cellulose derivatives microspheres by solvent evaporation technique. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 103, 2742–2751. DOI: 10.1002/app.25488.
Freiberg, S., & Zhu, X. X. (2004). Polymer microspheres for controlled drug release. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 282, 1–18. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.04.013.
Fujimori, J., Yonemochi, E., Fukuoka, E., & Terada, K. (2002). Application of Eudragit RS to thermo-sensitive drug delivery systems. I. Thermo-sensitive drug release from acetaminophen matrix tablets consisting of Eudragit RS/PEG 400 blend polymers. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 50, 408–412. DOI: 10.1248/cpb.50.408.
Higuchi, T. (1963). Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. Journal Pharmaceutical Sciences, 52, 1145–1149. DOI: 10.1002/jps.2600521210.
Jain, V., Jain, D., & Singh, R. (2011). Factors affecting the morphology of eudragit S-100 based microsponges bearing dicyclomine for colonic delivery. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 100, 1545–1552. DOI: 10.1002/jps.22360.
Khan, M. A., & Reddy, I. K. (1997). Development of solid oral dosage forms with acrylate polymers. S.T.P Pharma Sciences, 7, 483–490.
Kibbe, A. H. (2000). Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients. Washington, DC, USA: American Pharmaceutical Association.
Korsmeyer, R. W., Gurny, R., Doelker, E., Buri, P., & Peppas, N. A. (1983). Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 15, 25–35. DOI: 10.1016/0378-5173(83)90064-9.
Lai, M. K., & Tsiang, R. C. C. (2004). Encapsulating acetaminophen into poly(l-lactide) microcapsules by solvent evaporation technique in an O/W emulsion. Journal of Microencapsulation, 21, 307–316. DOI: 10.1080/02652040410001673928.
Le Corre, P. Le Guevello, P., Gajan, V., Chevanne, F., & Le Verge, R. (1994). Preparation and characterization of bupivacaine-loaded polylactide and polylactide-co-glycolide microspheres. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 107, 41–49, DOI: 10.1016/0378-5173(94)90300-X.
Mao, Z., Wang, B., Ma, L., Gao, C., & Shen, J. (2007). The influence of polycaprolactone coating on the internalization and cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine, 3, 215–223. DOI: 10.1016/j.nano.2007.04.001.
Moldenhauer, M. G., & Nairn, J. G. (1990). Formulation parameters affecting the preparation and properties of microencapsulated ion-exchanged resins containing theophylline. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 79, 659–666. DOI: 10.1002/jps.2600790802.
Mourão, S. C., da Silva, C., Bresolin, T. M. B., Serra, C. H. R., & Porta, V. (2010). Dissolution parameters for sodium diclofenac-containing hypromellose matrix tablet. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 386, 201–207. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.11.022.
Musial, W., Kokol, V., & Voncina, B. (2010a). Deposition and release of chlorhexidine from non-ionic and anionic polymer matrices. Chemical Papers, 64, 346–353. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-010-0013-y.
Musial, W., Kokol, V., & Voncina, B. (2010b). Lidocaine hydrochloride preparations with ionic and non-ionic polymers assessed at standard and increased skin surface temperatures. Chemical Papers, 64, 84–90. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-009-0089-4.
Natarajan, V., Krithica, N., Madhan, B., & Sehgal, P. K. (2011). Formulation and evaluation of quercetin polycaprolactone microspheres for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 100, 195–205. DOI: 10.1002/jps.22266.
Patel, S. N., Prajapati, P. H., Patel, C. N., Patel, C. M., & Patel, T. D. (2010). Formulation and development of enteric coated tablets of prednisolone as colon targeted drug delivery. Journal of Global Pharma Technology, 2, 128–132.
Phutane, P., Shidhaye, S., Lotlikar, V., Ghule, A., Sutar, S., & Kadam, V. (2010). In vitro evaluation of novel sustained release microspheres of glipizide prepared by the emulsion solvent diffusion-evaporation method. Pharmaceutics, 2, 35–41. DOI: 10.4103/0975-1483.62210.
Piao, M. G., Yang, C. W., Li, D. X., Kim, J. O., Jang, K. Y., Yoo, B. K., Kim, J. A., Woo, J. S., Lyoo, W. S., Han, S. S, Lee, Y. B., Kim, D. D., Yong, C. S., & Choi, H. G. (2008). Preparation and in vivo evaluation of piroxicam-loaded gelatin microcapsule by spray drying technique. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 31, 1284–1287. DOI: 10.1248/bpb.31.1284.
Prestwich, G. D., & Luo, Y. (2001). Novel biomaterials for drug delivery. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents, 11, 1395–1410. DOI: 10.1517/13543776.11.9.1395.
Puthli, S., & Vavia, P. R. (2009). Stability studies of microparticulate system with piroxicam as model drug. AAPS Pharm-SciTech, 10, 872–880. DOI: 10.1208/s12249-009-9280-8.
Rajesh, N., & Siddaramaiah (2010). Design and evaluation of controlled release of piroxicam from the pellets of microcrystalline cellulose and hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose blends. International Journal of PharmTech Research, 2, 1465–1473.
Rogalsky, V., & Todorov, I. N. (2012). Drug information portal. Retreived May 20, 2011, from http://www.druglib.com/druginfo/piroxicam/description_pharmacology/
Sahoo, S., Sasmal, A., Sahoo, D., & Nayak, P. (2010). Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-polycaprolactone blended with organoclay for control release of doxycycline. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 118, 3167–3175. DOI: 10.1002/app.32474.
Sastry, S. V., Nyshadham, J. R., & Fix, J. A. (2000). Recent technological advances in oral drug delivery — a review. Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Today, 3, 138–145. DOI: 10.1016/s1461-5347(00)00247-9.
Tsuji, K. (1998). Recent trends in pesticide formulations. In C. L. Foy, D. W. Pritchard, & G. B. Beestman (Eds.), Formulation Science: Proceedings from Formulation Forum’ 97 (pp. 53–83). Hattiesburg, MS, USA: The Association of Formulation Chemists.
Vlaia, L., Vlaia, V., Miclea, L. M., Olariu, I., & Coneac, G. (2009). Topical W/O/W double emulsions of piroxicam: In vitro drug release study. Farmacia, 57, 639–647.
Wade, A., & Weller, P. J. (1994) Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients (2nd ed.). Washington, DC, USA: Pharmaceutical Press.
Wang, S. H., Zhang, L. C., Lin, F., Sa, X. Y., Zuo, J. B., Shao, Q. X., Chen, G. S., & Zeng, S. (2005). Controlled release of levonorgestrel from biodegradable poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres: In vitro and in vivo studies. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 301, 217–225. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.05.038.
Wen, H., & Park, K. (2010). Oral controlled release formulation design and drug delivery. New Jersey, NJ, USA: Wiley.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diaf, K., Bahri, Z.E., Chafi, N. et al. Ethylcellulose, polycaprolactone, and eudragit matrices for controlled release of piroxicam from tablets and microspheres. Chem. Pap. 66, 779–786 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0191-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0191-x