Abstract
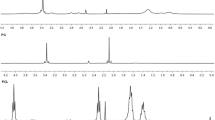
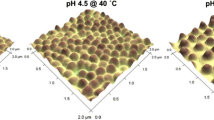
Influence of the initiator and additional hydrophobic copolymer on the morphology of thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (pNIPAM) microspheres, and their presumed application for the stabilization of biologically active molecules were evaluated in this study. Three different types of pNIPAM were synthesized, applying various components: PN1 is a polymer with terminal anionic groups resulting from potassium persulfate initiator; PN2 was synthesized with a 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride initiator introducing cationic amidine terminal groups; in the PN3 polymer, anionic terminals were implemented, however, increased hydrophobicity was maintained using N-tert-butyl functional groups. Turbidity measurements of the obtained dispersions confirmed specific thermosensitivity of synthesized microspheres in the range of 32–33°C. The polymerization course was proved by infrared spectroscopy and 1H NMR assessments, whereas the size of the synthesized microspheres, expressed as planar area, was evaluated by dynamic light scattering (DLS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and optical microscopy (OM). The respective surface patterns of the freeze-dried microspheres were evaluated by SEM. Planar area of the synthesized macromolecules was in the range between 0.41–3.22 μm, depending on the substrates composition and the method applied for the measurements. The assessments performed in the dry stage gave higher values of the diameter and planar area of the observed microspheres. The measured diameter and planar area increased in the following order for the PN3 microspheres: DLS, OM, SEM. In the case of PN1 and PN2, the observed diameters were positioned as: DLS, SEM, OM. These differences were assigned both to varied intramolecular hydrophobic-hydrophilic interactions of the polymer chains and to the environment, i.e. low pressure in the SEM conditions and aqueous solvent in the DLS measurements. The observed gaps in the freeze-dried PN2 polymer resulted in an attempt to evaluate the application of this polymer for mechanical stabilization of certain macromolecules or nanocrystals in the size range between 10 nm and 20 nm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, B. N., Barnes, C. A., Kasick, R. T., Michel, R., Gilbert, T. W., Beer-Stolz, D., Castner, D. G., Ratner, B. D., & Badylak, S. F. (2009). Surface characterization of extracellular matrix scaffolds. Biomaterials, 3, 428–437. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.09.061.
Castanheira, E.M. S., Martinho, J. M. G., Duracher, D., Charreyre, M. T., Elaïssari, A., & Pichot, C. (1999). Study of cationic N-isopropylacrylamide-styrene copolymer latex particles using fluorescent probes. Langmuir, 15, 6712–6717. DOI: 10.1021/la990130p.
Chen, G., McCarley, R. L., Soper, S. A., Situma, C., & Bolivar, J. G. (2007). Functional template-derived poly(methyl methacrylate) nanopillars for solid-phase biological reactions. Chemistry of Materials, 19, 3855–3857. DOI: 10.1021/cm0702870.
Chen, J.-P., & Chiu, S.-H. (2000). A poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-acryloxysuccinimide-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) composite hydrogel membrane for urease immobilization to enhance urea hydrolysis rate by temperature swing. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 265, 359–367. DOI: 10.1016/S0141-0229(99)00181-7.
Chung, J. E., Yokoyama, M., Aoyagi, T., Sakurai, Y., & Okano, T. (1998). Effect of molecular architecture of hydrophobically modified poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) on the formation of thermoresponsive core-shell micellar drug carriers. Journal of Controlled Release, 53, 119–130. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-3659(97)00244-7.
Coates, J. (2000). Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. In R. A. Meyers (Ed.), Encyclopedia of analytical chemistry (pp. 10815–10837). Chichester, UK: Wiley.
Coughlan, D. C., & Corrigan, O. I. (2006). Drug-polymer interactions and their effect on thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) drug delivery systems. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 313, 163–174. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.02.005.
Delair, T., Meunier, F., Elaïssari, A., Charles, M.-H., & Pichot, C. (1999). Amino-containing cationic latex-oligodeoxyribonucleotide conjugates: application to diagnostic test sensitivity enhancement. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 153, 341–353. DOI: 10.1016/S0927-7757(98)00456-7.
Dudek, M. J., & Ponder, J. W. (1995). Accurate modeling of the intramolecular electrostatic energy of proteins. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 16, 791–816. DOI: 10.1002/jcc.540160702.
Eke, I., Elmas, B., Tuncel, M., & Tuncel, A. (2006). A new, highly stable cationic-thermosensitive microgel: Uniform isopropylacrylamide-dimethylaminopropylmethacrylamide copolymer particles. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 279, 247–253. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.01.011.
Elaïssari, A., & Bourrel, V. (2001). Thermosensitive magnetic latex particles for controlling protein adsorption and desorption. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 225, 151–155. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-8853(00)01244-0.
Elaïssari, A., Rodrigue, M, Meunier, F., & Herve, C. (2001). Hydrophilic magnetic latex for nucleic acid extraction, purification and concentration. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 225, 127–133. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-8853(00)01240-3.
Elmas, B., Onur, M. A., Şenel, S., & Tuncel, A. (2004). Thermosensitive N-isopropylacrylamide-vinylphenyl boronic acid copolymer latex particles for nucleotide isolation. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 232, 253–259. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2003.11.007.
Fu, G., & Soboyejo, W. O. (2010). Swelling and diffusion characteristics of modified poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 30, 8–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2009.07.017.
Gilányi, T., Varga, I., Mészáros, R., Filipcsei, G., & Zrínyi, M. (2000). Characterisation of monodisperse poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel particles. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2, 1973–1977. DOI: 10.1039/b000571l.
Hellweg, T., Kratz, K., Pouget, S., & Eimer, W. (2002). Internal dynamics in colloidal PNIPAM microgel particles immobilised in mesoscopic crystals. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 202, 223–232. DOI: 10.1016/S0927-7757(01)01077-9.
Hirashima, Y., Sato, H., & Suzuki, A. (2005). ATR-FTIR spectroscopic study on hydrogen bonding of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) gel. Macromolecules, 38, 9280–9286. DOI: 10.1021/ma051081s.
Huo, D., Li, Y., Qian, Q., & Kobayashi, T. (2006). Temperature -pH sensitivity of bovine serum albumin protein-microgels based on cross-linked poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid). Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 50, 36–42. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2006.03.020.
Ichikawa, H., & Fukumori, Y. (2000). A novel positively thermosensitive controlled-release microcapsule with membrane of nano-sized poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel dispersed in ethylcellulose matrix. Journal of Controlled Release, 63, 107–119. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-3659(99)00181-9.
Ignatyev, I. S., Lazarev, A. N., Smirnov, M. B., Alpert, M. L., & Trofimov, B. A. (1981). Vibrational spectra and molecular structure of methyl vinyl ether. Journal of Molecular Structure, 72, 25–39. DOI: 10.1016/0022-2860(81)85005-3.
Imaz, A., & Forcada, J. (2009). Optimized buffered polymerizations to produce N-vinylcaprolactam-based microgels. European Polymer Journal, 45, 3164–3175. DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2009.08.003.
Kato, N., Sakai, Y., & Shibata, S. (2003). Wide-range control of deswelling time for thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel treated by freeze-drying. Macromolecules, 36, 961–963. DOI: 10.1021/ma0214198.
Katsumoto, Y., Tanaka, T., & Ozaki, Y. (2005). Molecular interpretation for the solvation of poly(acrylamide)s. I. Solventdependent changes in the C=O stretching band region of poly(N, N-dialkylacrylamide)s. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 109, 20690–20696. DOI: 10.1021/jp052263r.
Kondo, A., Imura, K., Nakama, K., & Higashitani, K. (1994). Preparation of immobilized papain using thermosensitive latex particles. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 78, 241–245. DOI: 10.1016/0922-338X(94)90297-6.
Kratz, K., Hellweg, T., & Eimer, W. (2001). Structural changes in PNIPAM microgel particles as seen by SANS, DLS, and EM techniques. Polymer, 42, 6631–6639. DOI: 10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00099-4.
Lee, C.-F., Lin, C.-C., Chien, C.-A., & Chiu, W.-Y. (2008). Thermosensitive and control release behavior of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid)/nano-Fe3O4 magnetic composite latex particle that is synthesized by a novel method. European Polymer Journal, 44, 2768–2776. DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2008.07.001.
Liapis, A. I., & Bruttini, R. (2009). A mathematical model for the spray freeze drying process: The drying of frozen particles in trays and in vials on trays. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 52, 100–111. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2008.06.026.
Lima, K. M., & Rodrigues, J. M., Jr. (1999). Poly-DL-lactide-co-glycolide microspheres as a controlled release antigen delivery system. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 32, 171–180. DOI: 10.1590/S0100-879X1999000200005.
Lin, C.-L., Chiu, W.-Y., & Lee, C.-F. (2005). Thermal/pHsensitive core-shell copolymer latex and its potential for targeting drug carrier application. Polymer, 46, 10092–10101. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2005.07.098.
Lindman, S., Lynch, I., Thulin, E., Nilsson, H., Dawson, K. A., & Linse, S. (2007). Systematic investigation of the thermodynamics of HSA adsorption to N-iso-propylacrylamide/N-tert-butylacrylamide copolymer nanoparticles. Effects of particle size and hydrophobicity. Nano Letters, 7, 914–920. DOI: 10.1021/nl062743.
López-León, T., Ortega-Vinuesa, J. L., Bastos-González, D., & Elaïssari, A. (2006). Cationic and anionic poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) based submicron gel particles: Electrokinetic properties and colloidal stability. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 110, 4629–4636. DOI: 10.1021/jp0540508.
Lynch, I., Miller, I., Gallagher, W. M., & Dawson, K. A. (2006). Novel method to prepare morphologically rich polymeric surfaces for biomedical applications via phase separation and arrest of microgel particles. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 110, 14581–14589. DOI: 10.1021/jp061166a.
MacAdam, A. B., Shafi, Z. B., James, S. L., Marriott, C., & Martin, G. P. (1997). Preparation of hydrophobic and hydrophilic albumin microspheres and determination of surface carboxylic acid and amino residues. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 151, 47–55. DOI: 10.1016/S0378-5173(97)04886-2.
Meersman, F., Wang, J., Wu, Y., & Heremans, K. (2005). Pressure effect on the hydration properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in aqueous solution studied by FTIR spectroscopy. Macromolecules, 38, 8923–8928. DOI: 10.1021/ma051582d.
Michailova, V., Berlinova, I., Iliev, P, Ivanov, L., Titeva, S., Momekov, G., & Dimitrov, I. (2010). Nanoparticles formed from PNIPAM-g-PEO copolymers in the presence of indomethacin. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 384, 154–164. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.09.034.
Murugan, R., Mohan, S., & Bigotto, A. (1998). FTIR and polarised Raman spectra of acrylamide and polyacrylamide. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 32, 505–512.
Ono, Y., & Shikata, T. (2007). Contrary hydration behavior of N-isopropylacrylamide to its polymer, P(NIPAm), with a lower critical solution temperature. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 111, 1511–1513. DOI: 10.1021/jp068954k.
Pelton, R. (2000). Temperature-sensitive aqueous microgels. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 85, 1–33. DOI: 10.1016/S0001-8686(99)00023-8.
Pelton, R. H., & Chibante, P. (1986). Preparation of aqueous latices with N-isopropylacrylamide. Colloids and Surfaces, 20, 247–256. DOI: 10.1016/0166-6622(86)80274-8.
Principi, T., Goh, C. C. E., Liu, R. C. W., & Winnik, F. M. (2000). Solution properties of hydrophobically modified copolymers of N-isopropylacrylamide and N-glycine acrylamide: A study by microcalorimetry and fluorescence spectroscopy. Macromolecules, 33, 2958–2966. DOI: 10.1021/ma9919054.
Rasband, W. S. (1997–2008). Image J [computer software]. Retrieved March 2, 2008, from http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij
Scherer, J. R., & Potts, W. J. (1959). Normal coordinates for the out-of-plane deformations of vinyl bromide. Journal of Chemical Physics, 30, 1527–1529. DOI: 10.1063/1.1730231.
Shamim, N., Hong, L., Hidajat, K., & Uddin, M. S. (2006). Thermosensitive-polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticles: Adsorption and desorption of Bovine Serum Albumin. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 304, 1–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2006.08.047.
Shibayama, M., Mizutani, S., & Nomura, S. (1996). Thermal properties of copolymer gels containing N-isopropylacrylamide. Macromolecules, 29, 2019–2024. DOI: 10.1021/ma9513 90q.
Snowden, M. J., & Vincent, B. (1992). The temperaturecontrolled flocculation of crosslinked latex particles. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, 16, 1103–1105. DOI: 10.1039/C39920001103.
Tan, B. H., & Tam, K. C. (2008). Review on the dynamics and micro-structure of pH-responsive nano-colloidal systems. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 136, 25–44. DOI: 10.1016/j.cis.2007.07.002.
Taniguchi, T., Duracher, D., Delair, T., Elaïssari, A., & Pichot, C. (2003). Adsorption/desorption behavior and covalent grafting of an antibody onto cationic amino-functionalized poly(styrene-N-isopropylacrylamide) core-shell latex particles. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 29, 53–65. DOI: 10.1016/S0927-7765(02)00176-5.
Taşddelen, B., Kayaman-Apohan, N., Güven, O., & Baysal, B. M. (2005). Anticancer drug release from poly(N-isopropylacrylamide/itaconic acid) copolymeric hydrogels. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 73, 340–345. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2004.09.028.
Tokuyama, H., & Kato, Y. (2008). Preparation of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) emulsion gels and their drug release behaviors. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 67, 92–98. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2008.08.003.
Varshosaz, J. (2007). The promise of chitosan microspheres in drug delivery systems. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 4, 263–273. DOI: 10.1517/17425247.4.3.263.
Wang, F., Bronich, T. K., Kabanov, A. V., Rauh, R. D., & Roovers, J. (2008). Synthesis and characterization of star poly(ɛ-caprolactone)-b-poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(l-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers: Evaluation as drug delivery carriers. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 19, 1423–1429. DOI: 10.1021/bc7004285.
Wang, G., Pelton, R., & Zhang, J. (1999). Sodium dodecyl sulfate binding to poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel latex studied by isothermal titration calorimetry. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 153, 335–340. DOI: 10.1016/S0927-7757(98)00455-5.
Wei, H., Cheng, S.-X., Zhang, X.-Z., & Zhuo, R.-X. (2009). Thermo-sensitive polymeric micelles based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) as drug carriers. Progress in Polymer Science, 34, 893–910. DOI: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.05.002.
Wei, H., Zhang, X.-Z., Cheng, H., Chen, W.-Q., Cheng, S.-X., & Zhuo, R.-X. (2006). Self-assembled thermo- and pH responsive micelles of poly(10-undecenoic acid-b-N-isopropylacrylamide) for drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 116, 266–274. DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.08.018.
Yashida, H., Furukawa, Y., & Tasumi, M. (1989). Structural studies and vibrational analyses of stable and less stable conformers of 1,3,5-hexatriene based on ab initio MO calculations. Journal of Molecular Structure, 194, 279–299. DOI: 10.1016/0022-2860(89)80086-9.
Zhang, X.-Z., Yang, Y.-Y., Chung, T.-S., & Ma, K.-X. (2001). Preparation and characterization of fast response macroporous poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. Langmuir, 17, 6094–6099. DOI: 10.1021/la010105v.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Musial, W., Vincent, B., Szumny, A. et al. Morphological characteristics of modified freeze-dried poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microspheres studied by optical microscopy, SEM, and DLS. Chem. Pap. 64, 602–612 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-010-0041-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-010-0041-7