Abstract
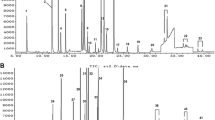
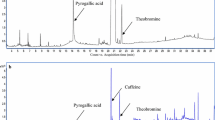
An efficient and sensitive method for simultaneous determination of 118 pesticide residues in teas has been established and validated. A multi-residue analysis of pesticides in tea involved extraction with ethyl acetate-hexane, clean-up using gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and solidphase extraction (SPE), and subsequent identification and quantification of the selected pesticides by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). For most of the target analytes, optimized pretreatment processes led to no significant interference with analysis of sample matrix, and the determination of 118 compounds was achieved in about 60 min. In the linear range of each pesticide, the correlation coefficient was R 2 ≥ 0.99. At the low, medium and high three fortification levels of 0.05–2.5 mg kg−1, 118 pesticides average recoveries range from 61 % to 121 % and relative standard deviations (RSD) were in the range of 0.6–9.2 % for all analytes. The limits of detection for the method were 0.00030-0.36 mg kg−1, depending on each pesticide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bordet, F., Inthavong, D., & Fremy, J.-M. (2002). Interlaboratory study of a multiresidue gas chromatographic method for determination of organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticides and polychlorobiphenyls in milk, fish, eggs, and beef fat. Journal of AOAC International, 85, 1398–1409.
Cai, L. S., Xing, J., Dong, L., & Wu, C. (2003). Application of polyphenylmethylsiloxane coated fiber for solid-phase microextraction combined with microwave-assisted extraction for the determination of organochlorine pesticides in Chinese teas. Journal of Chromatography A, 1015, 11–21. DOI: 10.1016/S0021-9673(03)01328-1.
Cserháti, T., Forgács, E., Deyl, Z., Miksik, I., & Eckhardt, A. (2004). Chromatographic determination of herbicide residues in various matrices. Biomedical Chromatography, 18, 350–359. DOI: 10.1002/bmc.378.
Dejonckheere, W., Steurbaut, W., Drieghe, S., Verstraeten, R., & Braeckman, H. (1996). Monitoring of pesticide residues in fresh vegetables, fruits, and other selected food items in Belgium, 1991–1993. Journal of AOAC International, 79, 97–110.
European Commission Directive 2002/657/EC (2002) Official Journal of the European Communities, L 221, 8–36.
Fillion, J., Sauvč, F., & Selwyn, J. (2000). Multiresidue method for the determination of residues of 251 pesticides in fruits and vegetables by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Journal of AOAC International, 83, 698–713.
Huang, Z., Li, Y., Chen, B., & Yao, S. (2007). Simultaneous determination of 102 pesticide residues in Chinese teas by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B, 853, 154–162. DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.03.013.
Naithani, V., & Kakkar, P. (2004). An evaluation of residual organochlorine pesticides in popular Indian herbal teas. Archives of Environmental Health, 59, 426–430. DOI: 10.3200/AEOH.59.8.426-430.
Pang, G.-F., Cao, Y.-Z., Zhang, J.-J., Fan, C.-L., Liu, Y.-M., Li, X.-M., Jia, G.-Q., Li, Z.-Y., Shi, Y.-Q., Wu, Y.-P., & Guo, T.-T. (2006). Validation study on 660 pesticide residues in animal tissues by gel permeation chromatography cleanup/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1125, 1–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.05.023.
Sood, C., Jaggi, S., Kumar, V., Ravindranath, S. D., & Shanker, A. (2004). How manufacturing processes affect the level of pesticide residues in tea. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 84, 2123–2127. DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.1774.
Tekel, J., & Hatrík, Š. (1996). Pesticide residue analyses in plant material by chromatographic methods:clean-up procedures and selective detectors. Journal of Chromatography A, 754, 397–410. DOI: 10.1016/S0021-9673(96)00489-X.
Yang, C. S., & Landau, J. M. (2000). Effects of tea consumption on nutrition and Health. Journal of Nutrition, 130, 2409–2412.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Xu, D.C., Qiu, J.W. et al. Simultaneous determination of 118 pesticide residues in Chinese teas by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chem. Pap. 63, 39–46 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-008-0090-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-008-0090-3