Abstract
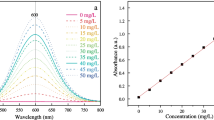
In the effort to improve the performance of hydroxylapatite (HA) in removing lead ions from aqueous solutions, millimeter-sized granules with 50 % porosity were synthesized. Such HA particles, after drying at 100°C, or heating at 800°C or 1100°C, exhibited the specific surface areas of 50 m2 g−1, 25 m2 g−1, and 5 m2 g−1, respectively. It was found that heavy metal sorption capacity of HAs can be related to their surface area. Non-calcined granules were difficult to handle and easy to crush. Hardened granules showed heavy metal absorption on their outer surfaces. Absorption capacity of sintered HA particles towards lead was lower but adsorbed lead ions were spread inside the porous structure of HA granules more evenly. Under flow conditions, lead ions were captured by HA at a rate of 0.5 mg g−1 min−1. Small lead phosphate aggregates were released from the HA sorbent together with calcium ions. Size of the aggregates depended on the lead concentration and ranged from 1–50 μm in diameter; the aggregates could be removed by ultrafiltration. Results show that porous hardened HA granules can be used as an efficient phosphate source for the immobilization of lead ions from aqueous media. Organic ligands tend to interfere with the water purification procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Admassu, W., & Breese, T. (1999). Feasibility of using natural fishbone apatite as a substitute for hydroxyapatite in remediating aqueous heavy metals. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B69, 187–196. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3894(99)00102-8.
Baillez, S., Nzihou, A., Benache-Assolant, D., Champion, E., & Sharrock, P. (2007). Removal of aqueous lead ions by hydroxyapatites: equilibria and kinetic processes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, A139, 443–446. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.039.
Baker, W. E. (1964). Mineral equilibrium studies of the pseudomorphism of pyromorphite by hinsdalite, American Mineralogist, 49, 607–613.
Boisson, J., Ruttens, A., Mench, M., & Vangronsveld, J. (1999). Evaluation of hydroxyapatite as a metal immobilizing soil additive for the remediation of polluted soils. Part 1. Influence of hydroxyapatite on metal exchangeability in soil, plant growth, and plant metal accumulation. Environmental Pollution, 104, 225–233. DOI: 10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00184-5.
Chander, S., & Fuerstenau, D. W. (1979). Interfacial properties and equilibria in the apatite-aqueous solution system. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 70, 506–516. DOI: 10.1016/0021-9797(79)90058-4.
Da Rocha, N. C. C., Decampos, R. C., Rossi, A. M., Moreira, E. L., Barbosa, A. F., & Moure, G. T. (2002). Cadmium uptake by hydroxyapatite synthesized in different conditions and submitted to thermal treatment. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 1630–1635. DOI: 10.1021/es0155940.
Fedoroff, M., Jeanjean, J., Rouchaud, J. C., Mazerolles, L., Trocellier, P., Maireles-Torres, P., & Jones, D. J. (1999). Sorption kinetics and diffusion of cadmium in calcium hydroxyapatites. Solid State Science, 1, 71–84. DOI: 10.1016/S1293-2558(00)80066-7.
Hayek, E., & Newesely, H. (1963). Pentacalcium monohydroxyorthophosphate. Inorganic Synthesis, 7, 63–65.
Hodson, M. E., Valsami-Jones, E., Cotter-Howells, J. D., Dubbin, W. E., Kemp, A. J. Thornton, I., & Warren, A. (2001). Effect of bone meal (calcium phosphate) amendments on metal release from contaminated soils — a leaching column study. Environmental Pollution, 112, 233–243. DOI: 10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00116-0.
Jeanjean, J., McGrellis, S., Rouchaud, J. C., Fedoroff, M., Rondeau, A., Perocheau, S., & Dubis, A. (1996). A crystallographic study of the sorption of cadmium on calcium hydroxyapatites: incidence of cationic vacancies. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 126, 195–201. DOI: 10.1006/jssc.1996.0329.
Jowett, M., & Price, H. I. (1932). Solubilities of the phosphates of lead. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 28, 668–681. DOI: 10.1039/TF9322800668.
Knox, A. S., Kaplan, D. I., & Paller M. H. (2006). Phosphate sources and their suitability for remediation of contaminated soils. Science of the Total Environment, 357, 271–279. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.07.014.
Lang, F., & Kaupenjohann, M. (2003). Effect of dissolved organic matter on the precipitation and mobility of the lead compound chloropyromorphite in solution. European Journal of Soil Science, 54, 139–147. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2389.2003.00505.x.
Laperche, V., Treina, S. J., Gaddam, P., & Logan, J. T. (1996). Chemical and mineralogical characterizations of Pb in a contaminated soil: reactions with synthetic apatite. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 3321–3326. DOI: 10.1021/es960141u.
Ma, Q. Y., Traina, S. J., Logan, T. J., & Ryan J. A. (1993). In situ lead immobilization by apatite. Environmental Science and Technology, 27, 1803–1810. DOI: 10.1021/es00046a007.
Middleburgh, J. J., & Commans, R. N. J. (1991). Sorption of cadmium on hydroxyapatite. Chemical Geology, 90, 45–53. DOI: 10.1016/0009-2541(91)90032-M.
Millet, H., & Jowett, M. (1929). The solubilities of lead phosphates. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 51, 997–1004. DOI: 10.1021/ja01379a004.
Monteil-Rivera, F., & Fedoroff, M. (2002). Sorption of inorganic species on apatites from aqueous solutions. In A. T. Hubbard (Ed.), Encyclopedia of surface and colloid science (pp. 1–26). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Nriagu, J. O. (1973a). Lead orthophosphates-II. Stability of chloropyromorphite at 25 °C. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 37, 367–377. DOI: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90206-8.
Nriagu, J. O. (1973b). Lead orthophosphates-III. Stabilities of fluoropyromorphite and Bromopyromorphite at 25 °C. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 37, 1735–1743. DOI: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90159-2.
Ryan, J. A., Scheckel, K. G., Berti, W. R., Brown, S. L., Casteel, S. W., Chaney, R. L., Hallfrisch, J., Doolan, M., Grevatt, P., Maddaloni, M., & Mosby, D. (2004). Reducing children’s risk from lead in soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 18A–24A.
Sauvé, S., McBride, M., & Hendershot, W. (1998). Lead phosphate solubility in water and soil suspensions. Environ. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 388–393. DOI: 10.1021/es970245k.
Scheckel, K. G., & Ryan, J. A. (2002). Effects of aging and pH on dissolution kinetics and stability of chloropyromorphite. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 2198–2204. DOI: 10.1021/es015803g.
Srinivasan, M., Ferraris, C., & White, T. (2006). Cadmium and lead ion capture with three dimensionally ordered macroporous hydroxyapatite. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 7054–7059. DOI: 10.1021/es060972s.
Suzuki, T. (1990). Modified apatites and their feasibility of removing toxic ions in polluted water. Bulletin of the Society for Sea Water Science of Japan, 44, 159–166.
Suzuki, T., Ishigaki, K., & Miyake, M. (1984). Synthetic hydroxyapatites as inorganic cation exchangers: Part 3. Exchange characteristics of lead ions (Pb2+). Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions, 80, 3157–3165. DOI: 10.1039/F19817701059.
Suzuki, Y., & Takeuchi, Y. (1994). Uptake of a few divalent heavy metal ionic species by a fixed bed of hydroxyapatite particles. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 27, 571–576.
Takeuchi, Y., & Arai, H. (1990). Removal of coexisting Pb2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+ ions from water by addition of hydroxyapatite powder. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 23, 75–80.
Takeuchi, Y., Suzuki, T., & Arai, H. (1998). A study of equilibrium and mass transfer in processes for removal of heavy-metal ions by hydroxyapatite. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 21, 98–100.
Xu, Y., & Schwartz, F. W. (1994). Sorption of Zn2+ and Cd2+ on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Environmental Science and Technology, 28, 1472–1480. DOI: 10.1021/es00057a015.
Zhang, P., & Ryan, J. A. (1998). Formation of pyromorphite in anglesite-hydroxyapatite suspensions under varying pH conditions. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 3318–3324. DOI: 10.1021/es980232m.
Zhang, P., & Ryan, J. A. (1999). Transformation of Pb(II) from cerussite to chloropyromorphite in the presence of hydroxyapatite under varying conditions of pH. Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 625–630. DOI: 10.1021/es980268e.
Zhang, P., & Ryan, J. A. (1997). Formation of pyromorphite in apatite and lead mineral suspensions: Effects of reaction kinetics. Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society, 213, 109-GEOC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadioui, M., Sharrock, P., Mecherri, MO. et al. Reaction of lead ions with hydroxylapatite granules. Chem. Pap. 62, 516–521 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-008-0062-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-008-0062-7