Abstract
Objectives
The effectiveness of pharmacologic support with orlistat is shown on a group of the obese patients.
Methods
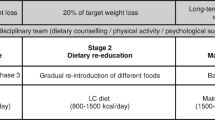
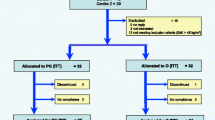
In ambulatory patients, basic anthropometric parameters as body weight, BMI, waist circumference and the total amount of adipose tissue were compared before substitution with 120 mg orlistat three times a day and after a four-month therapy. This group included 52 patients who were administered the same dose of orlistat for the whole period of time. The control group consisted of 49 patients. These patients were not administered orlistat.
Results
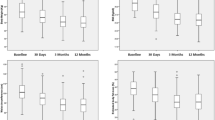
After a four-month therapy with orlistat there was a mean reduction in weight by 6.7 ± 2.6 kg in the monitored group of patients. Their BMI was reduced by 2.0 ± 0.9 kg/m2 and the waist circumference by 3.7 ± 3.3 cm. The decrease in the percentage of the total body lipid was 2.5 %. There was a statistically significant reduction in all of the monitored parameters. In the control group, there was no statistically significant decrease in the majority of the monitored parameters.
Conclusion
We can state that in our patients we have proven a positive effect of orlistat substitution on their weight reduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reaven P., Metabolic syndrome, J. Insur. Med., 2004, 36, 132–142
Ginter E, Simko V., Adult obesity at the beginning od the 21st century: epidemiology, pathophysiology and health risk, Bratisl. Lek. Listy, 2008, 109, 224–230
Waden T.A, Berkowitz R.I, Womble L.G., Randomized trial of lifestyle modification and pharmacotherapy for obesity, N. Engl. J. Med., 2005, 353, 2111–2116
Svendsen M, Tonstad S., Orlistat after initial dietary/behavioural treatment: changes in body weight and dietary maintenance in subjects with sleep related breathing disorders, Nutr. J., 2011, 8, 10–21
Torp-Pedersen C, Caterson I, Coutinho W., Cardiovascular responses to weight management and sibutramine in high-risk subjects: an analysis from the SCOUT trial, Eur. Heart. J., 2007, 28(23), 2915–2923
James W.P, Caterson I.D, Coutinho W., Effect of sibutramine on cardiovascular outcomes in overweight and obese subjects, N. Engl. J. Med., 2010, 363(10), 905–917
Hainer V., Comparative efficiency and safety of pharmacological approaches to the management of obesity. Diabetes Care, 2011, 34, 349–354
Bray G.A., Medical therapy for obesity, Mt. Sinai J. Med., 2010, 77(5), 407–417
Li Z, Maglione M, Tu W., Pharmacologic treatment of obesity, Ann. Intern. Med., 2005, 142, 532–538
Hainer V., Orlistat a perspektivy farmakoterapie obezity, JAMA, 1999, 7, 371–373
Li M.F, Cheung B.M., Rise and fall of anti-obesity drugs, World J. Diabetes, 2011, 15(2), 19–23
Jain S.S, Ramajane S.J, Akat P.B., Evaluation of efficacy and safety of orlistat in obese patients, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab., 2011, 15(2), 99–104
Derosa G, Maffioli P, Salvadeo S.A., Comparison of orlistat treatment and placebo in obese type 2 diabetic patients, Expert Opin. Pharmacother., 2010, 11(12), 1971–1982
Minarčíková I., Farmakoekonomické aspekty ve farmakoterapii obezity, Česká a Slov. Farm., 2003, 52, 258–261
Hainer V., Comment to the article: Assessment of morbid obesity treatment cost efficiency in the Czech Republic, Diab. Metab. Endokr., 2012, 15(3), 199–200
Russell-Jones D., Gough S. Recent advances in incretin-based therapies, Clin. Endocrinol. 2012, 77(4), 489–499
Hayes M.R., De Jonghe B.C., Kanoski S.E., Role of the glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor in the control of energy balance, Physiology and Behavior, 2010, 100(5), 503–510
Allison D.B., Gadde K.M., Garvey W.T., Controlledrelease phentermine/topiramate in severely obese adults: a randomized controlled trial, Obesity, 2012, 20(2), 330–42
Gadde K.M., Day W.W., Low-dose, controlledrelease phentermin/topiramate for reduction of weight, Obesity reviews from 11th International Congress on Obesity, 11–15 July 2010 Stockholm, 2010, 11(1), 42–43
Ornellas T., Chavez B., A New Approach to Weight Loss in Obese Adults, Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 2011, 36(5), 255–256, 261–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlík, V., Fajfrová, J. & Drahokoupilová, E. The effect of orlistat on body weight in obese Czech adults. cent.eur.j.med 8, 553–557 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-013-0194-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-013-0194-1