Abstract
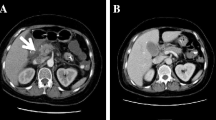
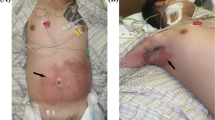
The incidence of drug-induced pancreatitis is rare. There have been several reports of acute pancreatitis as a complication in acute poisoning with drugs or toxins. We present a case of a young woman with acute pancreatitis secondary to an overdose of nifedipine and acetaminophen in a suicide attempt. We excluded other causes of acute pancreatitis by clinical history, serum toxicology, serology, and abdominal imaging. The most likely underlying pathophysiological mechanism was ischemic injury of the pancreas secondary to severe collapse induced by nifedipine and possible acetaminophen-induced direct pancreatotoxicity. The pancreatitis resolved with treatment that included continuous veno-venous haemofiltration in an intensive care unit. Emergency and intensive care units should be aware of this unusual complication of such poisoning. To our knowledge, this is the first reported association between massive nifedipine overdose and acute pancreatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaurich T. Drug-induced acute pancreatitis. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2008; 21(1): 77–81
Badalov N, Baradarian R, Iswara K, Li J, Steinberg W, Tenner S. Drug-induced acute pancreatitis: an evidence-based review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:648–661
Eltookhy A, Pearson NL. Drug-induced pancreatitis. Can Pharmacists J 2006; 139(6): 58–60
Trivedi CD, Pitchumoni CS. Drug-induced pancreatitis: an update. J Clin Gastroenterol 2005; 39:709–716
Schmidt LE, Dalhoff K. Hyperamylasaemia and acute pancreatitis in paracetamol poisoning. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004; 20: 173–179
Doyon S, Klein-Schwartz W. Hepatotoxicity despite early administration of intravenous N-acetylcysteine for acute acetaminophen overdose. Acad Emerg Med. 2009; 16(1): 34–39
Mallick S. Metformin induced acute pancreatitis precipitated by renal failure. Postgrad Med J 2004; 80: 239–240
Harris NS. Case 24-2006: A 40-Year-Old Woman with Hypotension after an Overdose of Amlodipine. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 602–611
Feierman DE. The effect of paracetamol (acetaminophen) on fentanyl metabolism in vitro. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2000; 44(5): 560–563
Dimova S, Koleva M, Rangelova D, Stoythchev T. Effect of nifedipine, verapamil, diltiazem and trifluoperazine on acetaminophen toxicity in mice. Arch Toxicol. 1995; 70(2): 112–118
Manjuck J, Zein J, Carpati C, Astiz M. Clinical significance of increased lipase levels on admission to the ICU. Chest 2005; 127: 246–250
Sakorafas GH, Tsiotos GG, Sarr MG. Ischemia/reperfusion-induced pancreatitis. Dig Surg 2000;17: 3–14
Pezzilli R, Morselli-Labate AM, Romboli E, Dibenedetti F, Massa M, Migliori M, et al. Pancreatic involvement during the early phase of shock. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2002; 3(4): 139–143
Schmidt LE, Dalhoff K. Hyperamylasaemia and acute pancreatitis in paracetamol poisoning. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004; 20: 173–179
Banks PA, Freeman ML, and the Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Practice Guidelines in Acute Pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2006; 101:2379–2400
Zhu AJ, Shi JS, Sun XJ. Organ failure associated with severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(11): 2570–2573
Beger HG, Rau BM. Severe acute pancreatitis: clinical course and management. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(38): 5043–5051
Pupelis G, Plaudis H, Grigane A, Zeiza K, Purmalis G. Continuous veno-venous haemofiltration in the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis: 6-year experience. HPB, 2007; 9: 295–301
Lionte C, Sorodoc L, Sorodoc V, Petris OR, Buga C, Ciuhodaru L, et al. Successful treatment of an acute poisoning with meprobamate, amobarbital, propranolol and nifedipin using continuous venovenous hemofiltration — case report. Timisoara Medical Journal 2006; 56(suppl.2): 475–478
Słomka M, Celiński K, Wargocki J, Kleinrok Z, Czerny K, Cichoz-Lach H. The influence of nifedipine (calcium channel blocker) and Bay-K-8644 (calcium channel agonist) on the development of experimental acute pancreatitis. Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska [Med]. 2001; 56:29–34
Prat F, Amaris J, Ducot B, Bocquentin M, Fritsch J, Choury AD, et al. Nifedipine for prevention of post-ERCP pancreatitis: a prospective, double-blind randomized study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56(2): 202–208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sorodoc, L., Lionte, C., Bologa, C. et al. Acute pancreatitis after nifedipine and acetaminophen poisoning — case report. cent.eur.j.med 4, 527–531 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-009-0057-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-009-0057-y