Abstract
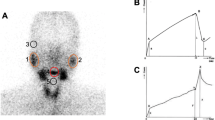
The purpose of this study was to compare the quantitative parameters of salivary gland functions in patients with allergic rhinitis and healthy volunteers using [99mTc] pertechnetate salivary gland scintigraphy. Thirty-six patients with allergic rhinitis (14 males and 22 females, mean age 30.6 ± 5.2 years) and thirty-nine healthy controls (18 males and 21 females, mean age 32.2 ± 5.6 years) were evaluated. Dynamic salivary gland scintigraphy was performed after intravenous administration of 185 MBq (5 mCi) of [99mTc] pertechnetate for 25 minutes. Lemon juice was used to stimulate the salivary glands. On the basis of the time-activity curves, the following glandular function parameters were calculated for the parotid and submandibular salivary glands: uptake ratio, maximum accumulation, and ejection fraction. Statistically, all the functional parameters of the parotid and submandibular glands obtained for the allergic rhinitis patients were significantly lower than those of the healthy controls group (p < 0.05). This study demonstrated that there was a significant difference in salivary gland function between patients with allergic rhinitis and healthy controls, which can easily be evaluated by [99mTc] pertechnetate salivary gland scintigraphy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daniels T.E., Evaluation, differential diagnosis, and treatment of xerostomia, J. Rheumatol. Suppl., 2000, 61, 6–10
Booker J., Howarth D., Taylor L., Voutnis D., Sutherland D., Appropriate utilization of semi-quantitative analysis in salivary scintigraphy, Nucl. Med. Commun., 2004, 25, 1203–1210
Anjos D.A., Etchebehere E.C., Santos A.O., Lima M.C., Ramos C.D., Paula R.B., et al., Normal values of [99mTc]pertechnetate uptake and excretion fraction by major salivary glands, Nucl. Med. Commun., 2006, 27, 395–403
Skoner D.P., Allergic rhinitis: definition, epidemiology, pathophysiology, detection, and diagnosis, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 2001, 108, 2–8
Bousquet J., Van Cauwenberge P., Khaltaev N.; Aria Workshop Group; World Health Organization, Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 2001, 108, 147–334
International Consensus Report on the diagnosis and management of rhinitis, International Rhinitis Management Working Group, Allergy, 1994, 49, 1–34
Ng M.L., Warlow R.S., Chrishanthan N., Ellis C., Walls R., Preliminary criteria for the definition of allergic rhinitis: a systematic evaluation of clinical parameters in a disease cohort (I and II), Clin. Exp. Allergy, 2000, 30, 1314–1331, 1417–1422
Elad S., Heisler S., Shalit M., Saliva secretion in patients with allergic rhinitis, Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol., 2006, 141, 276–280
Kaya M., Cermik T.F., Ustün F., Sen S., Berkarda S., Salivary function in patients with chronic renal failure undergoing hemodialysis, Ann. Nucl. Med., 2002, 16, 117–120
Mishkin F.S., Radionuclide salivary gland imaging, Semin. Nucl. Med., 1981, 11, 258–265
Kohn W.G., Ship J.A., Atkinson J.C., Patton L.L., Fox P.C., Salivary gland 99mTc-scintigraphy: a grading scale and correlation with major salivary gland flow rates, J. Oral Pathol. Med., 1992, 21, 70–74
Firat F., Cermik T.F., Sarikaya A., Berkarda S., Effects of gender and age on the quantitative parameters of [99mTc]pertechnetate salivary gland scintigraphy in normal subjects, Nucl. Med. Commun., 2006, 27, 447–453
De Rossi G., Focacci C., A computer-assisted method for semi-quantitative assessment of salivary gland diseases, Eur. J. Nucl. Med., 1980, 5, 499–503
Klutmann S., Bohuslavizki K.H., Kröger S., Bleckmann C., Brenner W., Mester J., et al., Quantitative salivary gland scintigraphy, J. Nucl. Med. Technol., 1999, 27, 20–26
Mygind N., Essential Allergy, An Illustrated Text for Students and Specialists, Oxford, Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1986
Sreebny L.M., Valdini A., Yu A., Xerostomia. Part II: Relationship to nonoral symptoms, drugs, and diseases, Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol., 1989, 68, 419–427
Streckfus C.F., Baur U., Brown L.J., Bacal C., Metter J., Nick T., Effects of estrogen status and aging on salivary flow rates in healthy Caucasian women, Gerontology, 1998, 44, 32–39
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yoruk, O., Seven, B., Varoglu, E. et al. Evaluation of salivary gland function in allergic rhinitis patients by [99mTc] pertechnetate salivary gland scintigraphy. cent.eur.j.med 5, 246–250 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-009-0041-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-009-0041-6