Abstract
Bariatric surgery is the most effective method to achieve weight loss in obese subjects.
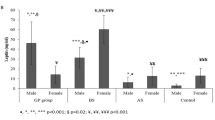
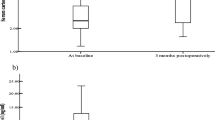
The aim of this study was to evaluate some adipocytokines and insulin, as well as parameters of metabolic syndrome of the obese patients, for three and six months after vertical banded gastroplasty, in the time of dynamic weight loss.
Seven males and two females aged 28 to 49 years, with long lasting simple obesity and the presence of metabolic syndrome, were studied. After surgical treatment the values of the body mass index, waist circumference, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood concentrations of leptin decreased significantly.
Before surgical operation of all obese patients no statistically significant correlations between studied parameters were noted. Three and six months later a lot of correlations between studied parameters appeared.
In conclusion, (a) vertical-banded gastroplasty is a valuable method in treatment of obese subjects, leading to a significant decrease in body weight and improvement in some parameters of metabolic syndrome in a few months after surgery, (b) adipocytokines, together with an unknown gastric factor, may be key factors in the control of some features of the metabolic syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.E. Cummings and M.W. Schwartz: “Genetics and pathophysiology of human obesity”, Ann. Rev. Med., Vol. 54, (2003), pp. 453–471.
B.E. Wisse and M.W. Schwartz: “The skinny of neurotrophins”, Nature Neurosci., Vol. 6, (2003), pp. 655–656.
S.M. Grundy: “Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease”, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol., Vol. 89, (2004), pp. 2595–2600.
C.C. Carr and J.D. Brunzell: “Abdominal obesity and dyslipidemia in the metabolic syndrome: Importance of type 2 diabetes and familial combined hyperlipidemia in coronary artery disease risk”, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol., Vol. 89, (2004), pp. 2601–2607.
M. Lafontan and M. Berlan: “Do regional differences in adipocyte biology provide new pathopysiological insights?”, Trends Pharmacol. Sci., Vol. 24, (2003), pp. 276–283.
K.G. Alberti and P.Z. Zimmet: “Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. I. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation, Diabetes Med., Vol. 15, (1998), pp. 539–553.
National Cholesterol Educational Program Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive summary of the third report on the National Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III)”, JAMA, Vol. 285 (2001), pp. 2486–2497.
W. Fujimoto, S. Abbate, S. Kahn, J. Hokanson and J. Brunzell: “The visceral adiposity syndrome in Japanese-American men”, Obes. Res., Vol. 2, (1994), pp. 364–371.
N. Ruderman, D. Chisholm, X. Pi-Sunyer and S. Schneider: “The metabolically obese, normal-weight individuals revisited”, Diabetes, Vol. 47, (1998), pp. 699–713.
N. Barzilai, L. She, B.Q. Liu, P. Vuguin, P. Cohen, J. Wang and L. Rosetti,:, “Surgical removal of visceral fat reverses hepatic insulin resistance”, Diabetes, Vol. 48, (1999), pp. 94–98.
J. Harvey and M.L.J. Ashford: “Leptin in CNS: Much for than a satiety signal”, Neuropharmacology, Vol. 44, (2003), pp. 845–854.
J. Komorowski, J. Jankiewicz-Wika and H. Stępień: “Effects of Gn-RH, TRH, and CRF administration on plasma leptin levels ln lean and obese women”, Neuropeptides, Vol. 34, (2000), pp. 89–97.
S. Ten and N. MacLaren: “Insulin resistance in children”, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol., Vol. 89, (2004), pp. 2526–2539.
G.K. Shetty, P.A. Economides, E.S. Horton, Ch.S. Mantzoros and A. Veves: “Circulating adiponectin and resistin levels in relation to metabolic factors, inflammatory markers, and vascular reactivity in diabetic patients and subjects at risk for diabetes”, Diabetes Care, Vol. 27, (2004), pp. 2450–2457.
Y. Arita, S. Kihara, N. Ouchi, M. Takahashi, K. Maeda, J. Miyagawa, K. Hotta, I. Shimomura, T. Nakamura, K. Miyaoka, H. Kuriyama, M. Nishida, S. Yamashita, K. Okubo, K. Matsubara, M. Muraguchi, Y. Ohmoto, T. Funahashi and Y. Matsuzawa: “Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity”, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., Vol. 257, (1999), pp. 79–83.
Y. Yamamoto, Y. Hirose, I. Saito, M. Tomita, M. Taniyama, K. Matsubara, Y. Okazaki, T. Ishi, K. Nishikai and T. Saruta: “Correlation of the adipocyte-derived protein adiponectin with insulin resistance index and serum high-density lipoprotein-choesterol, independent of body mass index, in the Japanese population”, Clin. Sci. (Lond.), Vol. 103, (2002), pp. 132–147.
M. Matsubara, S. Maruka and S. Katayose: “Inverse relationship between plasma adiponectin and leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese women”, Eur. J. Endocrinol., Vol. 147, (2002), pp. 173–180.
C.M. Steppan, S.T. Bailey, S. Bhat, E.J. Brown, R.R. Banerjee, C.M. Wright, H.M. Patel, R.S. Ahima and M.A. Lazar: “The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes”, Nature, Vol. 409, (2001), pp. 307–312.
C.M. Steppan and M.A. Lazar: “Resistin and obesity-associated insulin resistance”, Trends Endocrinol. Metab., Vol. 13, (2002), pp. 18–23.
R. Ohmori, Y. Momiyama, R. Kato, H. Toniguchi, M. Ogura, M. Ayori, H. Nakamura and F. Ohsuzu: “Associations between serum resistin levels and insulin resistance, inflammation, and coronary artery disease”, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., Vol. 45, (2005), pp. 379–380.
R.E. Brolin: “Bariatric surgery and long-term control of morbid obesity”, JAMA, Vol. 288, (2002), pp. 2793–2796.
E.C. Mun, G.L Blackburn and J.B. Matthews: “Current status of medical and surgical therapy for obesity”, Gastroenterology, Vol. 120, (2001), pp. 669–681.
D.E. Cummings, J. Overduin and K.E. Foster-Schubert: “Gastric bypass for obesity: mechanisms of weight loss and diabetes resolution”, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol, Vol. 89, (2002), pp. 2608–2615.
G.A. Bray and L.A. Tartaglia: “Medicinal strategies in the treatment of obesity”, Nature, Vol. 404, (2000), pp. 672–677.
K.M. Mc Tigue, R. Harris, B. Hemphill, L. Lux, S. Sutton, A.J. Bunton and K.N. Lohr: “Screening and interventions for obesity in adults: summary of the evidence for the US Prevention Task Force”, Ann. Intern. Med., Vol. 139, (2003), pp. 933–949.
W.J. Pories, M.S. Swanson, K.G. Mac Donald, S.B. Long, P.G. Morris, B.M. Brown, H.A. Barakat, R.A. de Ramon, D. Israel and J.M. Dolezal: “Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult onset diabetes mellitus”, Ann. Surg., Vol. 222, (1995), pp. 339–352.
L. Sjostrom, A-K. Lindroos, M. Peltonen, J. Torgrson, C. Bouchard, B. Carlsoon, S. Dahlgren, B. Larsen, K. Narbro, C.D. Siostrom, M. Sullivan and H. Wedel: “Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery”. N. Engl. J. Med., Vol. 351, (2004), pp. 2683–2693.
H. Buchwald, Y. Avidor, E. Braunwald, M.D. Jensen, W. Pories, K. Fahrbach and K. Schoelles: “Bariatric surgery”, JAMA, Vol. 292, (2004), pp. 1724–1737.
N. Kubota, Y. Terauchi, T. Yamauchi, T. Kubota, M. Moroi, J. Matsui, K. Eto, T. Yamashita, J. Kamon, H. Satoh, W. Yano, P. Frogeul, R. Nagai, S. Kimura, T. Kadowaki and T. Noda: “Disruption of adiponectin causes insulin resistance and neointimal formation”, J. Biol. Chem., Vol. 277, (2002), pp. 25863–25866.
T. Yamauchi, J. Kamon, H. Waki, Y. Terauchi, N. Kubota, K. Hara, Y. Mori, T. Ide, K. Murakami, N. Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, O. Ezaki, Y. Akanuma, O. Gavrilova, C. Vinson, M.L. Reitman, K. Kagechika, Y. Shudo, M. Yoda, Y. Nakano, K. Tobe, R. Nagai, S. Kimura, M. Tomita, P. Froguel and T. Kadowaki: “The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity”, Nat. Med, Vol. 7, (2001), pp. 941–946.
M. Blucher, M.D. Michael, O.D. Peroni, K. Ueki, N. Carter, B.B. Kahn and C.R. Kahn: “Adipose tissue selective insulin receptor knockout protects against obesity and obesity-related glucose intolerance”, Dev. Cell., Vol. 3, (2002), pp. 25–38.
N. Stefan, B. Vozarova, T. Funahashi, Y. Matsuzawa, C. Weyer, S. Lindsay, J.F. Yongren, P.J. Havel, R.E. Pratley, C. Bogardus and P.A. Tataranni: “Plasma adiponectin concentrations in association with skeletal muscle insulin receptor tyrosine phosphorylation, and low plasma concentration precedes a decrease in whole-body insulin sensitivity in humans”, Diabetes, Vol. 51, (2002), pp. 1884–1888.
R.S. Lindsay, T. Funahashi, L.R. Hanson, Y. Matsuzawa, S. Tanaka, P.A. Tataranni, W.C. Knowler and J. Krakoff: “Adiponectin and development of type 2 diabetes in the Pima Indian population”, Lancet, Vol. 360, (2002), pp. 57–58.
T. Yokota, K. Oritani, I. Takahashi, J. Ishikawa, A. Matsuyama, N. Ouchi, S. Kichara, T. Funahashi, A.J. Tenner, Y. Tomiyama and Y. Matsuzawa: “Adiponectin, a new member of the family of soluble defense collagens, negatively regulates the growth of myelomonocytic progenitors and the functions of macrophages”, Blood, Vol. 96, (2000), pp. 1723–1732.
N. Ouchi, S. Kichara, Y. Arilsa, K. Maeda, H. Kuriyama, Y. Okamoto, K. Hotta, M. Nishida, M. Takahashi, T. Nakamura, S. Yamashita, T. Funahashi and Y. Matsuzawa: “Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin”, Circulation, Vol. 100, (1999), pp. 2473–2476.
N. Ouchi, S. Kihara, Y. Ariata, M. Nishida, A. Matsuyama and Y Okamoto: “Adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, suppresses lipid accumulation and class A scavenger receptor expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages”, Circulation, Vol. 103, (2001), pp. 1057–1063.
M. Matsubara, S. Maruka and S. Katayose: “Inverse relationship between plasma adiponectin and leptin concentrations in normal weight and obese women. Eur. J. Endocrinol., Vol. 147, (2002), pp. 173–180.
C. Weyer, T. Funahashi, S. Tanaka, K. Hotta, Y. Matsuzawa, R.E. Pratley and P.A. Tataranni: “Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia”, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol., Vol. 86, (2001), pp. 1930–1935.
J.G. Yu, A.L. Javorschi Havener, Y.T. Kruszynska, R.A. Norman, M. Sinha and J.M. Olefsky: “The effect of thiazolidinediones on plasma adiponectin levels in normal, obese, and type 2 diabetes subjects”, Diabetes, Vol. 51, (2002), pp. 2968–2974.
N. Satoh, Y. Ogawa, T. Usui, T. Tagami, S. Kono, H. Uesugi, H. Sugiyama, A. Sugawara, K. Yamada, A. Shimatsu, H. Kuzuya and K. Nakao: “Antiatherogenic effect of pioglitazone in type 2 diabetic patients irrespective of the responsiveness to its antidiabetic effect”, Diabetes Care, Vol. 26, (2003), pp. 2493–2499.
I.A. Harsch, C. Koebnick, H. Wallaschofski, S.P. Schahin, E.G. Hahn, J.H. Ficker, T. Lohmann and P.C. Konturek: “Resistin levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome-the link to subclinical inflammation?”, Med. Sci. Monitor, Vol. 10, (2004), pp. CR510–515.
N. Siswal, A.K Singh, B. Aruna, S. Mukhopadhyay, S. Ghosh and N.Z. Ehtesham: “Human resistin stimulates the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-12 in macrophages by NF-kappaB-dependent pathway”, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., Vol. 334, (2005), pp. 1092–1101.
G.H. Ballantyne, A. Gumbs and I.M. Modlin: “Changes in insulin resistance following bariatric surgery and the adipoinsular axis: role of the adipocytokines, leptin, adiponectin and resistin”, Obes Surg, Vol. 15, (2005), pp. 692–699.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Jankiewicz-Wika, J., Kołomecki, K., Cywiński, J. et al. The relationship between features of metabolic syndrome and blood adipocytokine concentrations in the morbid obese patients during dynamic weight loss. cent.eur.j.med 1, 136–147 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-006-0015-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-006-0015-x