Abstract
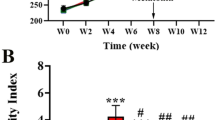
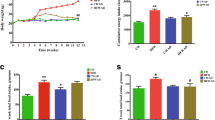
Emerging evidence support an important role of reactive oxygen species in various forms of insulin resistance. It is identified that melatonin has antioxidant properties and prevents toxic effects of reactive oxygen species. In this study, we sought to assess the involvement of melatonin in the progression of insulin resistance in response to a high-fat diet (HFD) and to investigate the underlying mechanisms. Male rats were fed with a control diet, a high-fat diet, or a high-fat diet supplemented with melatonin (5 mg kg−1, i.p.) for 10 weeks. Glucose homeostasis, insulin sensitivity, antioxidative potency, and metabolic profiles in the rats were evaluated. Our results showed that a HFD led to increasing body mass, adipose tissue weight, plasma insulin, total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), free fatty acids (FFA), and decreased HDL-cholesterol (HDL-C) in rats. There was also a significant increase in the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) and decrease in superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, oxidative stress markers both in the plasma and liver. An enhanced hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxy-kinase (PEPCK) activity and RNA expression were observed. Impaired insulin signaling was evidenced by reducing insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2) tyrosine phosphorylation and protein kinase B (PKB) serine phosphorylation in response to insulin. Overactivation of stress-activated protein kinases JNK was also observed in the liver of HFD rats. However, simultaneous administration of melatonin to HFD rats significantly reduced oxidative stress in the system and liver, markedly improved impaired glucose homeostasis, insulin sensitivity, antioxidative potency, metabolic profiles and all the aforesaid adverse changes in HFD rats. Our results demonstrated that anti-oxidative property of melatonin is sufficient to ameliorate the insulin resistance condition, leading to the improvement of glucose homeostasis and the restoration of hepatic insulin signaling in a rat model of HFD-induced insulin resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahn C.R., Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes, Diabetes, 1994, 43, 1066–1084
DeFronzo R.A., Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes: metabolic and molecular implications for identifying diabetes genes, Diabetes, 1997, 5, 177–269
Kahn B.B., Flier J.S., Obesity and insulin resistance, J Clin Invest, 2000, 106, 473–481
Maritim A.C., Sanders R.A., Watkins J.B., Diabetes, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: a review, J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2003, 17, 24–38
Pablos M.I., Guerrero J.M., Ortiz G.G., Agapito M.T., ReiterBoth R.J., Melatonin and a putative nuclear melatonin receptor agonist CGP 52608 stimulate glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase activities in mouse brain in vivo, Neuroendocrinol Lett, 1997, 18, 49–58
Barlow-Walden L.R., Reiter R.J., Abe M., Pablos M., Menendez-Pelaez A., Chen L.D., et al., Melatonin stimulates brain glutathione peroxidase activity, Neurochem Int, 1995, 26, 497–502
Antolin I., Rodriquez C., Sainz R.M., Mayo J.C., Aria H., Kotler M., et al., Neurohormone melatonin prevent damage: effect on gene expression for antioxidative enzymes, FASEB J, 1996, 10, 882–890
Okatani Y., Wakatsuki A., Kaneda C., Melatonin increases activities of glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase in fetal rat brain, J Pineal Res, 2000, 28, 89–96
Forrest C.M., Mackay G.M., Stoy N., Stone T.W., Darlington L.G., Inflammatory status and kynurenine metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis treated with melatonin, Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2007, 64, 517–526
Kedziora-Kornatowska K., Szewczyk-Golec K., Czuczejko J., Pawluk H., van Marke de Lumen K., Kozakiewicz M., et al., Antioxidative effects of melatonin administration in elderly primary essential hypertension patients, J Pineal Res, 2008, 45, 312–317
Tamura H., Takasaki A., Miwa I., Taniguchi K., Maekawa R., Asada H., et al., Oxidative stress impairs oocyte quality and melatonin protects oocytes from free radical damage and improves fertilization rate, J Pineal Res, 2008, 44, 280–287
Jang J.W., Lee J.K., Lee M.C., Piao M.S., Kim S.H., Kim H.S., Melatonin reduced the elevated matrix metalloproteinase-9 level in a rat photothrombotic stroke model, J Neurol Sci, 2012, 323, 221–227
Hirai N., Kawano H., Hirashima O., Motoyama T., Moriyama Y., Sakamoto T., et al., Insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction in smokers: effects of vitamin C, Am J Physiol, 2000, 279, H1172–H1178
Jacob S., Ruus P., Hermann R., Tritschler H.J., Maerker E., Renn W., et al., Oral administration of RAC-α-lipoic acid modulates insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a placebo-controlled pilot trial, Free Radic Biol Med, 1999, 27, 309–314
Caballero B., Vitamin E improves the action of insulin, Nutr Rev, 1993, 51, 339–340
Paolisso G., Di Maro G., Pizza G., D’Amore A., Sgambato S., Tesauro P., et al., Plasma GSH/GSSG affects glucose homeostasis in healthy subjects and non-insulin-dependent diabetics, Am J Physiol, 1992, 263, E435–E440
Montilla P.L., Vargas J.F., Túnez I.F., Muñoz de Agueda M.C., Valdelvira M.E., Cabrera E.S., Oxidative stress in diabetes rats induced by streptozotocin: protective effects of melatonin, J Pineal Res, 1998, 25, 94–100
Nishida S., Segawa T., Murai I., Nakagawa S., Long-term melatonin administration reduces hyperinsulinemia and improves the altered fatty-acid compositions in type 2 diabetic rats via the restoration of Delta-5 desaturase activity, J Pineal Res, 2002, 32, 26–33
Jomain-Baum M., Schramm V.L., Kinetic mechanism of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) from rat liver cytosol. Product inhibition, isotope exchange at equilibrium, and partial reactions, J Biol Chem, 1978, 253, 3648–3659
Nakatani Y., Kaneto H., Kawamori D., Hatazaki M., Miyatsuka T., Matsuoka T.A., Modulation of the JNK pathway in liver affects insulin resistance status, J Biol Chem, 2004, 279, 45803–45809
Hariri N., Thibault L., High-fat diet-induced obesity in animal models, Nutr Res, 2010, 23, 270–299
Golay A., Bobbioni E., The role of dietary fat in obesity, Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord, 1997, 3, S2–11
Boden G., Role of fatty acids in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and NIDDM, Diabetes, 1997, 46, 3–10
Henry R.R., Impaired muscle fat metabolism: a cause or effect of visceral obesity? J Clin Invest, 1995, 95, 1427–1428
Lewis G.F., Carpentier A., Adeli K., Giacca A., Disordered fat storage and mobilization in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, Endocr Rev, 2002, 23, 201–229
McGarry J.D., Glucose-fatty acid interactions in health and disease, Am J Clin Nutr, 1998, 67, 500S–504S
Thamer C., Machann J., Stefan N., Haap M., Schäfer S., Brenner S., High visceral fat mass and high liver fat are associated with resistance to lifestyle intervention, Obesity (Silver Spring), 2007, 15, 531–538
Lin C.Y., Chen P.C., Kuo H.K., Lin L.Y., Lin J.W., Hwang J.J., Effects of obesity, physical activity, and cardiorespiratory fitness on blood pressure, inflammation, and insulin resistance in the National Health and Nutrition Survey, Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 2010, 20, 713–719
Wolden-Hanson T., Mitton D.R., McCants R.L., Yellon S.M., Wilkinson C.W., Matsumoto A.M., et al., Daily melatonin administration to middle-aged male rats suppresses body weight, intraabdominal adiposity, and plasma leptin and insulin independent of food intake and total body fat, Endocrinology, 2000, 141, 487–497
Prunet-Marcassus B., Desbazeille M., Bros A., Louche K., Delagrange P., Renard P., et al., Melatonin reduces body weight gain in Sprague Dawley rats with diet-induced obesity, Endocrinology, 2003, 44, 5347–5352
Cardinali D.P., Bernasconi P.A., Reynoso R., Toso C.F., Scacchi P., Melatonin may curtail the metabolic syndrome: studies on initial and fully established fructose-induced metabolic syndrome in rats, Int J Mol Sci, 2013, 14, 2502–2514
Faria J.A., Kinote A., Ignacio-Souza L.M., de Araújo T.M., Razolli D.S., Doneda D.L., et al., Melatonin acts through MT1/MT2 receptors to activate hypothalamic AKT and suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis in rats, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2013, doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00094.2013
Zanuto R., Siqueira-Filho M.A., Caperuto L.C., Bacurau R.F., Hirata E., Peliciari-Garcia R.A., et al., Melatonin improves insulin sensitivity independently of weight loss in old obese rats, J Pineal Res, 2013, doi: 10.1111/jpi.12056
Korkmaz A., Ma S., Topal T., Rosales-Corral S., Tan D.X., Reiter R.J., Glucose: a vital toxin and potential utility of melatonin in protecting against the diabetic state, Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2012, 349, 128–137
Agil A., Rosado I., Ruiz R., Figueroa A., Zen N., Fernández-Vázquez G., Melatonin improves glucose homeostasis in young Zucker diabetic fatty rats, J Pineal Res, 2012, 52, 203–210
Blair A.S., Hajduch E., Litherland G.J., Hundal H.S., Regulation of glucose transport and glycogen synthesis in L6 muscle cells during oxidative stress. Evidence for cross-talk between the insulin and SAPK2/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways, J Biol Chem, 1999, 274, 36293–36299
Tirosh A., Potashnik R., Bashan N., Rudich A., Oxidative stress disrupts insulin-induced cellular redistribution of insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. A putative cellular mechanism for impaired protein kinase B activation and GLUT4 translocation, J Biol Chem, 1999, 274, 10595–10602
Tirosh A., Rudich A., Potashnik R., Bashan N., Oxidative stress impairs insulin but not plateletderived growth factor signalling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, Biochem J, 2001, 355, 757–763
Evans J.L., Goldfine I.D., Maddux B.A., Grodsky G.M., Oxidative stress and stress-activated signaling pathways: a unifying hypothesis of type 2 diabetes, Endocr Rev, 2002, 23, 599–622
Barthel A., Schmoll D., Novel concepts in insulin regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2003, 285, E685–692
Wan X.D., Yang W.B., Xia Y.Z., Wang J.F., Lu T., Wang X.M., Disruption of glucose homeostasis and induction of insulin resistance by elevated free fatty acids in human L02 hepatocytes, J Endocrinol Invest, 2009, 32, 454–459
Manning B.D., Cantley L.C., AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream, Cell, 2007, 129, 1261–1274
Liu H.Y., Wen G.B., Han J., Hong T., Zhuo D., Liu Z., et al., Inhibition of gluconeogenesis in primary hepatocytes by stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) through a c-Src/Akt-dependent signaling pathway, J Biol Chem, 2008, 283, 30642–30649
Altomonte J., Richter A., Harbaran S., Suriawinata J., Nakae J., Thung S.N., et al., Inhibition of Foxo1 function is associated with improved fasting glycemia in diabetic mice, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2003, 285, E718–728
Marzban L., Rahimian R., Brownsey R.W., McNeill J.H., Mechanisms by which bis(maltolato)oxovanadium(IV) normalizes phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glucose-6-phosphatase expression in streptozotocindiabetic rats in vivo, Endocrinology, 2002, 143, 4636–4645
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, XD., Li, SQ., Xi, SM. et al. Long-term melatonin administration improves glucose homeostasis and insulin resistance state in high-fat-diet fed rats. cent.eur.j.biol. 8, 958–967 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-013-0211-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-013-0211-z