Abstract
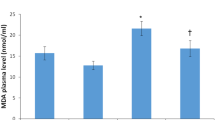
The aim of this study was to assess the effects of 2-weeks’ X-ray and/or nonylphenol (NP) exposure on male mice’s sperm count and quality. Pzh:SFIS mice were exposed to X-rays (0.05 Gy, 0.10 Gy, 0.20 Gy) or to nonylphenol (25 mg/kg bw, 50 mg/kg bw, 100 mg/kg bw) or to both agents (0.05 Gy + 25 mg/kg bw NP, 0.10 Gy + 50 mg/kg bw NP). At 24 h and 5 weeks after the end of exposure the sperm count, morphology and frequency of DNA damage in the male germ cells were estimated. Each agent alone diminished sperm count and morphology. The dose of 0.05 Gy of X-rays decreased the frequency of DNA damage. Combined exposure to lower doses of both agents significantly improved sperm morphology and decreased the level of DNA damage compared to one agent alone. Combined exposure to higher doses reduced the frequency of DNA damage compared to the effect of the appropriate dose of NP. Results of combined exposure to low doses of both agents suggest that 0.05 Gy of X-rays stimulate the DNA damagecontrol system and in consequence repair of DNA caused by X-rays and NP. It may be correlated with increased antioxidant capacity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonde J.P., Giwercman A., Occupational hazards to male fecundity, Reprod. Med. Rev., 1995, 4, 59–73
Carlsen E., Giwercman A., Keiding N., Skakkebaek N.E., Evidence for decreasing quality of semen during the past 50 years, Br. Med. J., 1992, 305, 609–612
Toppari J., Larsen J.C., Christiansen P., Giwercman A., Grandjean P., Guilette L.J. Jr., et al., Male reproductive health and environmental xenoestrogens, Environ. Health Perspect., 1996, 104, 741–803
Aitken R.J., Koopman P., Lewis S.E., Seeds of concern, Nature, 2004, 432, 48–52
Sharpe R.M., Toxicity of spermatogenesis and its detection, In: Korack K.S., (Ed.), Reproductive and developmental toxicology, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1998
Chitra K.C., Latchoumycandane C., Mathur P.P., Effect of nonylphenol on the antioxidant system in epididymal sperm of rats, Arch. Toxicol., 2002, 76, 545–551
Kimura N., Kimura T., Suzuki M., Totsukawa K., Effect of gestational exposure to nonylphenol on the development and fertility of mouse offspring, J. Reprod. Dev., 2006, 52, 789–795
Hale R.C., Smith C.L., de Fur P.O., Harvey E., Bush E.O., La Gaurdia L.J., et al., Nonylphenols in sediments and effluents associated with diverse wastewater outfalls, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2000, 19, 946–952
Lee P.C., Distribution of male reproductive tract development by administration of the xenoestrogen, nonylphenol to male newborn rats, Endocrine, 1998, 9, 105–111
Weber L.P., Kiparissis Y., Hwang G.S., Niimi A.J., Jantz D.M., Increased cellular apoptosis after chronic aqueous exposure to nonylphenol and quercetin in adult medaka (Oryzias latipes), Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 2002, 131, 51–59
Cardinalli M., Maradonna F, Olivotto I., Bartoluzzi G., Mosconi G., Polzonetti-Magni A.M., et al., Temporary impairment of reproduction in freshwater teleost exposed to nonylphenol, Reprod. Toxicol., 2004, 18, 597–604
Giger W., Brunner P.H., Schaffner C., 4-nonylphenol in sewage sludge: accumulation of toxic metabolites from nonionic surfacants, Science, 1984, 225, 623–625
Ahel M., McEvoy J., Giger W., Bioaccumulation of the lipophilic metabolites of nonionic surfacants in freshwater organisms, Environ. Pollut., 1993, 79, 243–248
Lee P.C., Disruption of male reproductive tract development by administration of the xenoestrogen, nonylphenol, to male newborn rats, Endocrine, 1998, 9, 105–111
De Jager C., Bornman M.S., Wandrag S., van der Horst D., Effect of p-nonylphenol, an environmental toxicant with oestrogenic properties, on fertility potential in adult male rats, Andrologia, 1999, 31, 99–106
Committee on the Biological Effects on Ionizing Radiations, Board on Radiation Effects, Research Commission on Life Sciences, National Research Council, Biological Effects on Ionizing Radiation (BEIR), Health effects of exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation, National Academy Press, Washington, 1990
Collins B., Howard D., Allen J., Kinetochorestaining of spermatid micronulei: studies of mice treated with X-radiation or acrylamide, Mutat. Res., 1992, 281, 287–294
Dobrzyńska M.M., Gajewski A.K., Induction of micronuclei in bone marrow and sperm head abnormalities after combined exposure of mice to low doses of X-rays and acrylamide, Teratogen. Carcinogen. Mutagen., 2000, 20, 133–140
Rowley M.J., Leach D.R., Warner G.A., Heller C.G., Effect of graded doses of ionizing radiation on human testis, Radiat. Res., 1974, 58, 665–678
Bonde J.P., Giwercman A., Occupational hazards to male fecundity, Reprod. Med. Rev., 1995, 4, 59–73
Dobrzyńska M.M., The changes in the quantity and quality of semen following subchronic exposure of mice to irradiation, In: Cebulska-Wasilewska A., Au W.W., Sram R.J., (Eds.), Human Monitoring for Genetic Effects, IOS Press, Amsterdam, 2003
Searle A.G., Beechey C.V., Sperm count, eggfertilization and dominant lethality after X-irradiation of mice, Mutat. Res., 1974, 22, 69–74
Singh N.P., Mc Coy M., Tice R.R., Schneider E.L., A simple technique for quantization of low level of DNA damage in individual cells, Exp. Cell Res., 1988, 175, 184–191
Anderson D., Yu T.W., Phillips B.J., Schmezer P., The effects of various antioxidants and other modifying agents on oxygen-radical-generated damage in human lymphocytes in Comet assay, Mutat. Res., 1994, 307, 261–271
Kumaravel T.S., Jha A.N., Reliable comet assay measurements for detecting DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation and chemicals, Mutat. Res., 2006, 605, 7–16
Wyrobek A.J., Bruce W.R. Chemical induction of sperm abnormalities in mice, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1975, 72, 4425–4429
Destinger H., Jung H., Molecular Biology, Springer, Heidelberg, 1970
Sharpe R.M., Irvine D.S., How strong is the evidence of a link between environmental chemicals and adverse effects on human reproductive health?, Br. Med. J., 2004, 328, 447–451
Oberley L.W., Lindgren L.A., Baker S.A., Stevens R.H., Superoxide ion as the cause of the oxygen effect, Radiat. Res., 1976, 68, 320–328
Biaglow J.E., Mitchell J.B., Heid K., The importance of peroxide and superoxide in the X-rays response, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys., 1992, 22, 665–669
Malekirad A.A., Ranjbar A., Rahzani K., Pilehvarian A.A., Rezaie A., Zamani M.J., et al., Oxidative stress in radiology staff, Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2005, 20, 215–218
Tobin D.J., Swanson N.N., Pittelkow M.R., Peters E.M., Schallreuter K.V., Melanocytes are not absent in lesional skin of long duration vitiligo, J. Pathol., 2000, 191, 407–416
Anderson D., Cemeli E., Schmidt T.E., Baumgartner A., Brinkworth M.H., Wood J.M., Oestrogenic compounds and oxidative stress, In: Anderson D., Brinkworth M.H., (Eds.), Male mediated Developmental Toxicity, RSC Publishing, Cambridge, 2007
Ochsendorf F.R., Buhl R., Bastlein A., Beschmann H., Glutathione in spermatozoa and seminal plasma of infertile men, Hum. Reprod., 1998, 13, 353–359
Gong Y., Han X.D., Nonylphenol-induced oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in testicular Sertoli cells, Reprod. Toxiciol., 2006, 22, 623–630
Chitra K.C., Latchoumycandane C., Mathur P.P., Effect of nonylphenol on the antioxidant system in epididymal sperm of rats, Arch. Toxicol., 2002, 76, 545–551
De Jager C., Bornman M.S., van der Horst G., The effect of p-nonylphenol, an environmental toxicant with oestrogenic properties, on fertility potential in adult male rats, Andrologia, 1999, 31, 99–106
Lee P.C., Arnolt P., Nickels K.C., Testicular abnormalities in male rats after lactational exposure to nonylphenol, Endocrine, 1999, 11, 61–68
Zhang H., Zeng Y., Cheng W., Wu D., Adverse effects of nonylphenol on the reproductive function of adult male SD rats, Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 2003, 34, 292–297, (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Nagao T., Saito Y., Usumii K., Nakagomi M., Yoshimura S., Ono H., Disruption of the reproductive system and reproductive performance by administration of nonylphenol to newborn rats, Hum. Exp. Toxicol., 2000, 19, 284–296
Nagao T., Wada K., Marumo H., Yoshimura S., Ono H., Reproductive effects of nonylphenol in rats after gavage administration: A two generation study, Reprod. Toxicol., 2001, 15, 293–315
Tyl R.W., Myers C.B, Marr M.C., Castilo N.P., Seely J.C., Sloan C.S., et al., Three-generation evaluation of dietary para-nonylphenol in CD (Sprague-Dawley) rats, Toxicol. Sci., 2006, 92, 295–310
Liu G., Gong P., Zhao H., Wang Z., Gong S., Cai L., Effect of low-level radiation on the death of male germ cells, Radiat. Res, 2006, 165, 379–389
Hasegawa G., Wilson L.D., Russell L.D., Meistrich M.L., Radiation-induced cell death in the mouse testis: Relationship to apoptosis, Radiat. Res., 1997, 147, 457–467
Hasegawa G., Zhang Y., Niibe H., Tery N.H., Meistrich M.L., Resistance of diferentiating spermatogonia to radiation-induced apoptosis and loss in p53-deficient mice, Radiat. Res., 1998, 149, 263–270
Yin Y., Stahl B.C., DeWolf W.C., Morgentaler A., P53 mediated germ cell quality control in spermatogenesis, Dev. Biol., 1998, 204, 165–171
Kangasniemi M., Veromas T., Kulmala J., Kaipia A., Parvinen M., Toppari J., DNA-flow cutometry of defined stages of rat semiferous epithelium:effects of 3 Gy of high-energy X-irradiation, J. Androl., 1990, 11, 312–317
Otala M., Suomalainen L., Pentikainen M.O., Kovanen P., Tenhunen M., Erkkila K., et al., Protection from radiation-induced male germ cell loss by sphingosine-1-phosphate, Biol. Reprod., 2004, 70, 759–767
Beumer T.L., Roepers-Gajadien H.L., Gaderman I.S., Rutgers D.H., Rooi D.G., P2(Cp1/WAF1) expression in the mouse testis before and after X-irradiation, Mol. Reprod. Dev., 1997, 47, 240–247
Beumer T.L., Roepers-Gajadien H.L., Gaderman I.S., vav Buul P.P.W., Gil-Gomez G., Rutgers D.H., et al., The role of the tumor suppressor p53 in spermatogenesis, Cell Death Differ., 1998, 5, 669–677
Haines G.A., Hendry J.H., Daniel C.P., Morris I.D., Increased levels of comet-detected spermatozoa DNA damage following in vivo isotopic- or X-raysirradiation of spermatogonia, Mutat. Res., 2001, 495, 21–32
Haines G.A., Hendry J.H., Daniel C.P., Morris I.D., Germ cell and dose-dependent DNA damage measured by comet assay in murine spermatozoa after testicular X-irradiation, Biol. Reprod., 2002, 67, 854–861
Pollycove M., Nonlinearity of radiation health effects, Environ. Health Perspect., 1998, 106, 363–369
Pollycove M., Feinendegen L.E., Radiation reduced versus endogenous DNA damage possible effect of inducible protective responses in mitigating endogenous damage, Hum. Exp. Toxicol., 2003, 22, 290–306
Masaki H., Atsumi T., Sakurai H., Detection of hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals in murine skin fibroblasts under UVB irradiation, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1995, 206, 474–479
Goto R., Kubota T., Ibuki Y., Kaji K., Goto A., Degradation of nonylphenol polyethoxylates by ultraviolet B irradiation and effects of their products on mammalian cultured cells, Toxicology, 2004, 202, 237–247
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Dobrzyńska, M.M. Combined action of X-rays and nonylphenol on mouse sperm. cent.eur.j.biol. 6, 320–329 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-011-0021-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-011-0021-0