Abstract
Background
In our part of the world, the majority of the patients with breast cancer present with locally advanced disease and require neo-adjuvant chemotherapy as the primary treatment modality. It is essential to monitor the response to chemotherapy in these patients. Clinical examination as the sole criterion of response assessment is entirely subjective and fallacious. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) are expensive. The role of Doppler ultrasonography as an imaging modality for this purpose is therefore being evaluated.
Methods
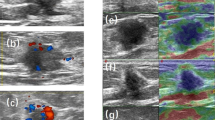
A prospective study was undertaken of 25 cases of locally advanced breast carcinoma (LABC) and Color Doppler sonography was used for the sequential assessment of chemotherapeutic response. The response assessed on the basis of clinical examination and Color Doppler was compared with the histological response. The parameters assessed on color Doppler were a change in the number of flow signals, maximum flow velocity (Vmax), pulsatility index (PI) and resistivity index (RI). Responses were analysed statistically using the Pearson correlation coefficient and Kappa statistics (κ). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive & negative predictive values for predicting complete histological response were calculated.
Results
Color Doppler showed a sensitivity of 88.88% for predicting complete histological response. The negative predictive value of color Doppler was 92.3%. A significant correlation was obtained between color Doppler & histopathological response.
Conclusions
Color Doppler was found to be an objective and effective tool or modality compared with clinical evaluation in sequential response assessment, especially for predicting complete histological response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Whelon SL, Ferlay J,et al: Cancer incidence in five continents. No 143. Vol VII. Lyons, France; International Agency for Research on Cancer Scientific Publications, 1997.
Newman LA: Management of patients with locally advanced breast cancer.Curr Oncol Rep 6:53–61, 2004.
Dixon JM, Senbanjo RO, Anderson TJ, Forrest AP, Elton RA: Clinical assessment of tumour size in primary breast carcinoma.Clin Oncol 10:117–121, 1984.
Forouhi P, Walsh JS, Anderson TJ, Chetty U: Ultrasonography as a method of measuring breast tumour size and monitoring response to primary systemic treatment.Br J Surg 81:223–225, 1994.
Fornage BD, Toubas O, Morel M: Clinical, mammographic, and sonographic determination of preoperative breast cancer size.Cancer 60:765–771, 1987.
Hayward JL, Carbone PP, Heuson JC, Kumaoka S, Segaloff A, Rubens RD: Assessment of response to therapy in advanced breast cancer. A project of the programme on clinical oncology of the UICC.Eur J Cancer 14:1291–1292, 1978.
Warr D, McKinney S, Tannock I: Influence of measurement error on assessment of response to anticancer chemotherapy: proposal for new criteria of tumor response.J Clin Oncol 2:1040–1046, 1984.
Fiorentino C, Berruti A, Bottini A, Bodini M, Brizzi MP,et al: Accuracy of mammography and echography versus clinical palpation in the assessment of response to primary chemotherapy in breast cancer patients with operable disease.Breast Cancer Res Treat 69:143–151, 2001.
Huber S, Medl M, Helbich T, Taucher S, Wagner T,et al: Locally advanced breast carcinoma: Computer assisted semi quantitative analysis of Color Doppler ultrasonography in the evaluation of tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy.J Ultrasound Med 19:601–607, 2000.
Landis JR, Koch GG: The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data.Biometrics 33:159–174, 1977.
Mansi JL, Smith JE, Walsh G, A’Hem RP, Hammer CL,et al: Primary medical therapy for operable breast cancer.Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 25:1623–1627, 1989.
Feldman LD, Hortobagyi GN, Buzdar AV, Ames FC, Blumenschein GR: Pathological assessment of response to induction chemotherapy in breast cancer.Cancer Res 46:2578–2581, 1986.
Cocconi G, Di Blasio B, Alberti G, Bisagni G, Botti E, Peracchia G: Problems in evaluating response of primary breast cancer to systemic therapy.Breast Cancer Res Treat 4:309–313, 1984.
Knopp MV, Brix G, Junkermann HJ, Sinn HP: MR mammography with pharmacokinetic mapping for monitoring breast cancer treatment during neoadjuvant therapy.MRI Clin North Am 2:633–658, 1994.
Lagalla R, Caruso G, Finazzo M: Monitoring treatment response with Color and power Doppler.Eur J Radiol 27 (Suppl 2):S149–156, 1998.
Kedar RP, Cosgrove DO, Bamber JC, Bell DS: Automated quantification of Color Doppler signals. A preliminary study in breast tumors.Radiology 197:39–43, 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Pradhan, S., Shukla, R.C. et al. Color doppler ultrasound as an objective assessment tool for chemotherapeutic response in advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer 12, 45–51 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2325/jbcs.12.45
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2325/jbcs.12.45