Abstract
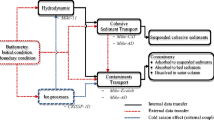
The water column concentration and bioaccumulation of the polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) congener CB052 was modeled in New Bedford Harbor, Massachusetts, using site-specific hydrodynamics and loading information. Equilibrium partitioning theory was used to estimate interstitial water CB052 concentrations from sediment concentrations in New Bedford Harbor and Buzzards Bay, Massachusetts. The rate of CB052 vertical flux from the interstitial water to the overlying water column was calculated by multiplying the vertical concentration gradient at the sedimentwater interface by a flux coefficient. The vertical flux coefficient and the flux rate from model-generated water-column concentrations were calculated using an interative procedure. Movement of CB052 within New Bedford Harbor was simulated using calibrated two-dimensional, vertically-integrated, finite element hydrodynamic and transport models. Quasi-steady-state water column concentrations and a field-derived bioconcentration factor were used to predict the expected concentration of CB052 in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) at two stations in New Bedford Harbor. The model was used to predict the effects of two remedial scenarios (i.e., reducing average sediment total PCB concentrations to 50 ppm or 10 ppm) on concentrations of CB052 in water and blue mussel tissue. Based on the model results, the CB052 concentration in blue mussels would be reduced by 33–53% for the 50 ppm option and by 67–84% for the 10 ppm option.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Abdelrhman, M. A. andE. H. Dettmann. 1997. Modeling of current circulation, residence time, and salinity distribution in New Bedford Harbor, Massachusetts. Final United States Environmental Protection Agency Report, National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory, Atlantic Ecology Division, Narraganssett, Rhode Island.
Applied Science Associates, Inc. 1987. Selected studies of PCB transport in New Bedford Harbor. Technical Report (ASA, 86-18), Submitted to Ropes and Gray, Inc., by Applied Science Associates, Inc., 70 Dean Knauss Drive, Narragansett, Rhode Island.
Battelle Memorial Institute. 1990. Modeling of the transport, distribution, and fate of PCBs and heavy metals in the Acushnet River/New Bedford Harbor/Buzzards Bay system. Final Report, submitted to EBASCO Services, Inc., by Battelle Memorial Institute, Duxbury, Massachusetts.
Bergen, B. J., W. G. Nelson, andR. J. Pruell. 1993a. Bioaccumulation of PCB congeners by blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) deployed in New Bedford Harbor, Massachusetts,Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 12:1671–1681.
Bergen, B. J., W. G. Nelson, andR. J. Pruell. 1993b. Partitioning of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in the seawater of New Bedford Harbor, Massachusetts.Environmental Science and Technology 27:938–942.
BOSS International. 1993. BOSS SMS, Hydrodynamic Modeling Reference Manual. BOSS Corporation, Madison, Wisconsin.
DiToro, D. M., C. S. Zarba, D. J. Hansen, W. J. Berry, R. C. Swartz, C. E. Cowan, S. P. Pavlou, H. E. Allen, N. A. Thomas, andP. R. Paquin. 1991. Technical basis for establishing sediment quality criteria for nonionic organic chemicals using equilibrium partitioning.Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 10:1541–1583.
Garton, L. S., J. S. Bonner, A. N. Ernest, andR. L. Autenrieth. 1996. Fate and transport of PCBS at the New Bedford Harbor superfund site.Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 15:736–745.
Lerman, A. 1988. Geochemical Processes Water and Sediment Environments. Robert E. Krieger Publishing Company, Malabar, Florida.
King, I. P. 1988. RMA2-A Two-dimensional Finite Element Model for Flow in Estuaries and Streams, Version 4.2. Resource Management Associates, Lafayette, California.
King, I. P. andR. R. Rachiele. 1989. RMA4-A Two-dimensional Finite Element Water Quality Model, Version 3.0. Resource Management Associates, Lafayette, California.
Nelson, W. G. andD. J. Hansen. 1991. Development and use of site-specific chemical and biological criteria for assessing New Bedford Harbor pilot dredging project.Environmental Management 15:105–112.
Nelson, W. G., B. J. Bergen, S. J. Benyi, G. Morrison, R. A. Voyer, C. J. Strobel, S. Rego, G. Thursby, andC. E. Pesch. 1996. New Bedford Harbor long-term monitoring assessment report: Baseline sampling. United States Environmental Protection Agency, National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory, Atlantic Ecology Division, Narragansett, Rhode Island. EPA/600/R-96/097.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 1986. Map No. 13230, 7th Edition United States East Coast, Massachusetts, Buzzards Bay, United States Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Ocean Service, Washington, D.C.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 1992. Tide tables 1993, high and low water predictions, east and west coast of North America, including Greenland. United States Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Ocean Service, Washington, D.C.
Norton, W. R., I. P. King, andG. T. Orlob. 1973. A Finite Element Model for Lower Granite Reservoir. Water Resources Engineering, Inc., Walnut Creek, California.
Richmond, M. C., L. F. Hibler, T. E. Michener, M. L. Kemner, D. S. Trent, andY. Onishi. 1989. Long-term fate of PCB contamination in the New Bedford Harbor, Massachusetts, system, p. 72–81.In Malcom Spaulding (ed.) Proceedings of the First International Conference-Estuarine and Coastal Modeling. The Americal Society of Civil Engineers. Newport, Rhode Island.
Schwarzenbach, R. P., P. M. Gschwend, andD. M. Imboden. 1993. Environmental Organic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Publication, New York.
Teeter, A. M. 1988. New Bedford Harbor superfund project, Acushnet River estuary engineering feasibility study of dredging and dredged material disposal alternatives, Report 2: Sediment and contaminant hydraulic transport investigation. Technical Report EL-88-15, Hydraulics Laboratory, United States Army Corps of Engineers, Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg, Mississippi.
Teeter, A. M. 1989. Modeling and data uses in hydraulic transport investigations, New Bedford Estuary, Massachusetts, p. 50–59.In Malcom Spaulding (ed.), Proceedings of the First International Conference-Estuarine and Coastal Modeling. The Americal Society of Civil Engineers. Newport, Rhode Island.
Thibodeaux, L. J. 1996. Environmental Chemodynamics, Movement of Chemicals in Air, Water, and Soil, Second ed. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Tracey, G. A., J. Charles, G. Hatcher, and W. G. Nelson. 1991. Development and validation of methods for real-time measurement of pollutant transport from an urbanized estuary. Proceedings of Oceans ’91, October 1–3, Honolulu, HA, Sponsored by Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc., 501–508.
Yabusaki, S., Y. Onishi, M. Richmond, and D. Trent. 1989. Circulation and transport modeling in New Bedford Harbor, p. 72–81.In Malcom Spaulding (ed.), Proceedings of the First International Conference-Estuarine and Coastal Modeling. Newport, Rhode Island.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelrhman, M.A., Bergen, B.J. & Nelson, W.G. Modeling of PCB concentrations in water and biota (Mytilus edulis) in New Bedford Harbor, Massachusetts. Estuaries 21, 435–448 (1998). https://doi.org/10.2307/1352842
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/1352842