Abstract
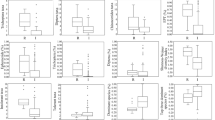
A multimetric benthic index of biotic integrity (B-IBI) was developed using data from five Chesapeake Bay sampling programs conducted between 1972 and 1991. Attributes of the index were selected by comparing the response of 17 candidate measures of benthic condition (metrics) between a set of minimally affected reference sites and at all other sites for which data were available. This procedure was conducted independently for each of seven habitats defined by salinity and substrate. Fifteen of the 17 candidate metrics differed significantly between reference sites and other sites for at least one habitat. No metric differed significantly in all seven habitats; however, four metrics, species diversity, abundance, biomass, and percent of abundance as pollution-indicative taxa, differed in six habitats. The index was calculated by scoring each selected metric as 5, 3, or 1 depending on whether its value at a site approximated, deviated slightly from, or deviated greatly from conditions at the best reference sites. Validation based on independent data collected between 1992 and 1994 indicated that the index correctly distinguished stressed sites from reference sites 93% of the time, with the highest validation rates occurring in high salinity habitats.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Bilyard, G. R. 1987. The value of benthic infauna in marine pollution monitoring studies.Marine Pollution Bulletin 18:581–585.
Boesch, D. F. 1973. Classification and community structure of macrobenthos in the Hampton Roads area, Virginia.Marine Biology 21:226–244.
Boesch, D. F. 1977. A new look at the zonation of benthos along the estuarine gradient, p. 245–266.In B. C. Coull (ed.), Ecology of Marine Benthos. University of South Carolina Press, Columbia, South Carolina.
Boesch, D. F. andR. Rosenberg. 1981. Response to stress in marine benthic communities, p. 179–200.In G. W. Barret and R. Rosenberg (eds.), Stress Effects on Natural Ecosystems. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Bousfield, E. L. 1973. Shallow-water Gammaridean Amphipoda of New England. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York.
Cooper, S. R. andG. S. Brush. 1993. A 2500-year history of anoxia and eutrophication in Chesapeake Bay.Estuaries 16: 617–626.
Dauer, D. M. 1993. Biological criteria, environmental health and estuarine macrobenthic community structure.Marine Pollution Bulletin 26:249–257.
Dauer, D. M. andR. W. Alden. 1995. Long-term trends in the macrobenthos and water quality of the lower Chesapeake Bay (1985–1991).Marine Pollution Bulletin 30:840–850.
Dauer, D. M. andW. G. Conner. 1980. Effects of moderate sewage on benthic polychaete populations.Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 10:335–346.
Dauer, D. M., R. M. Ewing, andA. J. Rodi, Jr. 1987. Macrobenthic distribution within the sediment along an estuarine salinity gradient.Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie 72:529–538.
Dauer, D. M., C. A. Maybury, andR. M. Ewing. 1981. Feeding behavior and general ecology of several spionid polychaetes from Chesapeake Bay.Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 54:21–38.
Dauer, D. M., T. L. Stokes, Jr.,H. R. Barker, Jr.,R. M. Ewing, andJ. W. Sourbeer. 1984. Macrobenthic communities of the lower Chesapeake Bay. IV. Baywide transects and the inner continental shelf.Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie 69:1–22.
DeShon, J. E. 1995. Development and application of the invertebrate community index, p. 217–243.In W. P. Davis and T. P. Simon (eds.), Biological Assessment and Criteria. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida.
Diaz, R. J. 1989. Pollution and tidal benthic communities of the James River Estuary, Virginia.Hydrobiologia 180:195–211.
Elliott, M. 1994. The analysis of macrobenthic community data.Marine Pollution Bulletin 28:62–64.
Ewing, R. M., J. A. Ranasinghe, and D. M. Dauer. 1988. Comparison of five benthic sampling devices. Prepared for the Virginia Water Control Board, Richmond, Virginia.
Fauchald, K. andP. A. Jumars. 1979. The diet of worms. A study of polychaete feeding guilds.Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review 17:193–284.
Ferraro, S. P., R. C. Swartz, F. A. Cole, andD. W. Schults. 1991. Temporal changes in the benthos along a pollution gradient: Discriminating the effects of natural phenomena from sewage-industrial wastewater effects.Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 33:383–407.
Grassle, J. F. andJ. P. Grassle. 1974. Opportunistic life histories and Genetic systems in marine benthic polychaetes.Journal of Marine Research 32:253–284.
Grassle, J. P. andJ. F. Grassle. 1984. The utility of studying the effects of pollutants on single species populations in benthos of mesocosms and coastal ecosystems, p. 621–642.In H. H. White (ed.), Concepts in Marine Pollution Measurements, Maryland Sea Grant College, College Park, Maryland.
Gray, J. S. 1979. Pollution-induced changes in populations.Transaction of the Royal Philosophical Society of London (B) 286: 545–561.
Gray, J. S., K. R. Clarke, R. M. Warwick, andG. Hobbs. 1990. Detection of initial effects of pollution on marine benthos: An example from the Ekofisk and Eldfisk oilfields, North Sea.Marine Ecology Progress Series 66:285–299.
Heip, C. andJ. A. Craeymeersch. 1995. Benthic community structures in the North Sea.Helgolander Meeresuntersuchungen 49:313–328.
Holland, A. F., A. Shaughnessey, andM. H. Heigel. 1987. Long-term variation in mesohaline Chesapeake Bay benthos: Spatial and temporal patterns.Estuaries 10:227–245.
Jorgensen, C. B. 1966. Biology of Suspension Feeding. Pergamon Press, Oxford, England.
Karr, J. R. 1991. Biological integrity: A long-neglected aspect of water resource management.Ecological Applications 1:66–84.
Karr, J. R., K. D. Fausch, P. L. Angermeier, P. R. Yant, andI. J. Schlosser. 1986. Assessing biological integrity in running waters: A method and its rationale. Special Publication 5. Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, Illinois.
Kerans, B. L. andJ. R. Karr. 1994. A benthic index of biotic integrity (B-IBI) for rivers of the Tennessee Valley.Ecological Applications 4:768–785.
Lenat, D. R. andM. T. Barbour. 1994. Using benthic macro-invertebrate community structure for rapid, cost-effective, water-quality monitoring: Rapid bioassessment, p. 187–216.In S. L. Loeb and A. Spacie (eds.), Biological Monitoring of Aquatic Systems. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida.
Long, E. R., D. D. McDonald, S. L. Smith, andF. D. Calder. 1995. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments.Environmental Management 19:81–95.
Magnien, R., D. Boward, and S. Bieber. 1995. The state of the Chesapeak Bay 1995. Report by the United States Environmental Protection Agency Chesapeake Bay Program, Annapolis, Maryland.
McCall, P. L. 1977. Community patterns and adaptive strategies of the infaunal benthos of Long Island Sound.Journal of Marine Research 35:221–266.
McManus, J. W. andD. Pauly. 1990. Measuring ecological stress: Variations on a theme by R. M. Warwick.Marine Biology 106:305–308.
Norris, R. H. 1995. Biological monitoring: The dilemna of data analysis.Journal of the North American Biological Society 14: 440–450.
Officer, C. B., R. B. Biggs, J. L. Taft, L. E. Cronin, M. A. Tyler, andW. R. Boynton. 1984. Chesapeake Bay anoxia: Origin, development and significance.Science 223:22–27.
Paul, J. F., K. J. Scott, A. F. Holland, S. B. Weisberg, J. K. Summers, andA. Robertson. 1992. The estuarine component of the U.S. EPA's Environmental Monitoring and Assessment Program.Chemistry and Ecology 7:93–116.
Pearson, T. H. andR. Rosenberg. 1978. Macrobenthic succession in relation to organic enrichment and pollution of the marine environment.Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review 16:229–311.
Ranasinghe, J. A., L. C. Scott, R. Newport, and S. B. Weisberg. 1994a. Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Monitoring Program, Long-term Benthic Monitoring and Assessment Component. Level I Comprehensive Report, July 1984–December 1993. Prepared for the Maryland Department of the Environment, Baltimore, Maryland.
Ranasinghe, J. A., S. B. Weisberg, J. B. Frithsen, D. M. Dauer, L. C. Schaffner, andR. J. Diaz. 1994b. Chesapeake Bay Benthic Community Restoration Goals. Report CBP/TRS 107/94. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Chesapeake Bay Program. Annapolis, Maryland.
Rhoads, D. C. andL. F. Boyer. 1982. The effects of marine benthos on physical properties of sediments: A successional perspective, p. 3–52.In P. L. McCall and M. S. Tevesz (eds.), Animal-Sediment Relations. Plenum Press, New York.
Rhoads, D. C., P. L. McCall, andJ. Y. Yingst. 1978. Disturbance and production on the estuarine sea floor.American Scientist 66:577–586.
Schaffner, L. C. 1990. Small-scale organism distributions and patterns of species diversity: Evidence for positive interactions in an estuarine benthic community.Marine Ecology Progress Series 61:107–117.
Schaffner, L. C., R. J. Diaz, C. R. Olson, andI. L. Larsen. 1987. Faunal characteristics and sediment accumulation processes in the James River Estuary, Virginia.Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 25:211–226.
Seitz, R. D. andL. C. Schaffner. 1995. Population ecology and secondary production of the polychaeteLoimia medusa (Terebellidae).Marine Biology 121:701–711.
Snelgrove, P. V. andC. A. Butman. 1994. Animal-sediment relationships revisited: Cause vs. effect.Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review 32:111–177.
Stewart, A. J. andJ. M. Loar. 1994. Spatial and temporal variation in biological monitoring data, p. 91–124.In S. L. Loeb and A. Spacie (eds.), Biological Monitoring of Aquatic Systems. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida.
Tapp, J. F., N. Shillabeer andC. M. Ashman. 1993. Continued observation of the benthic fauna of the industrialised Tees estuary, 1979–1990.Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 172:67–80.
Warwick, R. M. 1986. A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities.Marine Biology 92:557–562.
Warwick, R. M. 1988. The level of taxonomic discrimination required to detect pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities.Marine Pollution Bulletin 19:259–268.
Warwick, R. M. andK. R. Clarke. 1991. A comparison of some methods for analysing changes in benthic community structure.Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 71:225–244.
Wass, M. L. 1967. Indicators of pollution, p. 271–183.In T. A. Olsen and F. Burgess (eds.), Pollution and Marine Ecology. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Wilson, J. G. andD. W. Jeffrey. 1994. Benthic biological pollution indices in estuaries, p. 311–327.In J. M. Kramer (ed.), Biomonitoring of Coastal Waters and Estuaries. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Word, J. Q. 1978. The infaunal trophic index, p. 19–39.In W. Bascom (ed.), Coastal Water Research Project, Annual Report for the Year 1978. Southern California Coastal Water Research Project, El Segunda, California.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weisberg, S.B., Ranasinghe, J.A., Dauer, D.M. et al. An estuarine benthic index of biotic integrity (B-IBI) for Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries 20, 149–158 (1997). https://doi.org/10.2307/1352728
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/1352728