Abstract
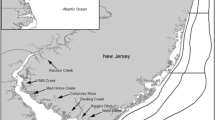
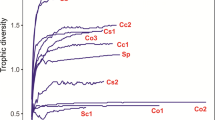
Food habits of the dominant fishes collected from 1974 to 1980 at eight locations in Elkhorn Slough, California, and the adjacent ocean were investigated. Epifaunal crustacea was the major prey group identified from stomach contents of more than 2,000 fishes, followed by epifaunal and infaunal worms, and molluscs. Overall, 18 fish species consumed 263 different prey taxa, ranging from 10 taxa to 125 taxa per fish species and including 99 crustacean, 56 polychaete, and 39 molluscan taxa. Mean prey richness was greatest at stations near the ocean and lowest at inshore stations. Detailed dietary data for all prey taxa were summarized as trophic spectra for each fish species. Trophic spectra represented functional groups of prey and were used for comparisons of dietary similarity. Cluster analyses, based on trophic spectra, resulted in four feeding guilds of fishes. Of 18 fish species, seven (Amphistichus argenteus, Leptocottus armatus, Embiotoca jacksoni, Clevelandia ios, Gillichthys mirabilis, Cymatogaster aggregata, andCitharichthys stimaeus) fed principally on epifaunal crustacea. Four species (Pleuronectes vetulus, Platichthys stellatus, Phanerodon furcatus, andMyliobatus californica) consumed mostly molluscs and infaunal worms. Two species (Psettichthys melanostictus andTriakis semifasciata) fed on mobile crustacea, and five species (Hyperprosopon anale, Engraulis mordax, Clupea pallasi, Atherinopsis californiensis, andAtherinops affinis) fed largely on zooplankton and plant material. Our results suggest that high food availability enhances the nursery function of imshore habitats, and emphasize the importance of invertebrate prey populations and the indirect linkage of plant production to the ichthyofaunal assemblarly marine immigrant species that are likely ‘estuarine dependent’.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Allen, L. G. 1982. Seasonal abundance, composition, and productivity of the littoral fish assemblage in upper Newport Bay, California.Fishery Bulletin United States 80:769–790.
Allen, L. G. andM. H. Horn. 1975. Abundance, diversity and seasonality of fishes in Colorado Lagoon, Alamitos Bay, California.Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 3:371–380.
Ambrose, D. A. 1976. The distribution, abundance, and feeding ecology of four species of flatfish in the vicinity of Elkhorn Slough, California. M.A. Thesis, San jose State University, San Jose, California.
Antrim, B. S. 1981. Habitat and food resource utilization of three species of embiotocids in Elkhorn Slough, Monterey Bay, California. M.A. Thesis, Calfornia State University. Fresno, California.
Barry, J. P. 1983. Utilization of shallow marsh habitats by fishes in Elkhorn Slough, California. M.A. Thesis, San Jose State University, San Jose, California.
Barry, J. P. andG. M. Cailliet. 1981. The utilization of shallow marsh habitats by commercially important fishes in Elkhorn Slough, California.Cal-Neva Wildlife Transactions 1981:38–47.
Barry, J. P. andM. J. Ehret. 1993. Diet, food preference, and algal availability for fishes and crabs on intertidal reef communities in southern California.Environmental Biology of Fishes 37:75–95.
Boesch, D. F. 1977. A new look at the zonation of benthos along the estuarine gradient, p. 245–266.In B. C. Coull (ed.), Ecology of Marine Benthos. University South Carolina Press, Columbia, South Carolina.
Boesch, D. F. andR. E. Turner. 1984. Dependence of fishery species on salt marshes: The role of food and refuge.Estuaries 7:460–468.
Bozeman, E. L., Jr. andJ. M. Dean 1980. The abundance of estuarine larval and juvenile fish in a South Carolina intertidal creek.Estuaries 3:89–97.
Bregnballe, F. 1961. Plaice and flounder as consumers of the microscopic bottom fauna.Meddelelser fra Danmarks Fiskeri-org Havundersogelser. 3:133–182.
Broenkow, W. 1977. Water chemistry of Elkhorn Slough and Moss Landing Harbor, p. 387–465.In J. Nybakken, G. Cailliet, and W. Broenkow (eds.), Ecologic and Hydrographic Studies of Elkhorn Slough Moss Landing Harbor and Nearshore Coastal Waters. Moss Landing Marine Laboratories Technical Publication, Moss Landing, California.
Browning, B. M. 1972. The natural resources of Elkhorn Slough: Their present and future use.California Department of Fish and Game, Coastal Wetlands Series 4.
Cailliet, G. M., B. S. Antrim, andD. A. Ambrose. 1978. Trophic spectrum analysis of fishes in Elkhorn Slough and near-by waters, p. 118–128.In S. J. Lipovsky and C. A. Simenstad (eds.), Fish Food Habits Studies, Proceedings of the Second Pacific Northwest Technical Workshop. University of Washington, Washington Sea Grant WSG-WO-77-2. Seattle, Washington.
Gailliet, G. M., B. Antrim, D. Ambrose, S. Pace, andM. Stevenson. 1977. Species composition, abundance and ecological studies of fishes, larval fishes, and zooplankton in Elkhorn Slough, p. 216–386.In J. Nybakken, G. Cailliet, and W. Broenkow (eds.), Ecologic and Hydrographic Studies of Elkhorn Slough Moss Landing Harbor and Nearshore Coastal Waters. Moss Landing Harine Laboratories Technical Publication, Moss Landing, California.
Cailliet, G. M. andJ. P. Barry. 1978. Comparison of food array overlap measures useful in fish feeding habit analysis, p. 67–79.In S. J. Lipovsky and C. A. Simenstad (eds.), Fish Food Habits Studies, Proceedings of the Second Pacific Northwest Technical Workshop. University of Washington, Washington Sea Grant WSG-WO-77-2, Seattle, Washington.
Carpenter, S. R. andJ. P. Kitchell. 1992. Trophic cascade and biomanipulation: Interface of research and management—A reply to the comment by DeMelo et al.,Limnology and Oceanography 37:208–213.
Carr, W. E. S. andJ. T. Geisel. 1975. Impact of thermal effluent a steam-electric station on a marshland nursery area during the hot season.Fishery Bulletin United States 73:67–80.
Crampton, T. A. 1994. Long-term effects of Moss Landing Harbor on the wetlands of Elkhorn Slough. M.S. Thesis, University of California, Santa Cruz, California.
Dahlberg, M. D. 1972. An ecological study of Georgia coastal fishes.Fishery Bulletin United States 70:323–353.
Dando, P. R. 1984. Reproduction in estuarine fish, p. 155–170.In G. W. Potts and R. J. Wootton (eds.), Fish Reproduction Strategies and Tactics. Academic Press, London.
Darnell, R. M. 1958. Food habits of fishes and larger invertebrates of Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana, an estuarine community.Publications of the Institute of Marine Science, University of Texas 5:353–416.
Darnell, R. M. 1961. Trophic spectrum of an estuarine community, based on studies of Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana.Ecology 42:553–568.
Darnell, R. M. andT. M. Soniat. 1979. The Estuary/Continental Shelf as an Interactive System.In R. J. Livingston (ed.), Ecological Processes in Coastal and Marine Systems. Plenum Press, New York.
Day, J. W., Jr. andA. Yanez-Arancibia. 1985. Coastal lagoons and estuaries as an environment for nekton, Chaper 3, p. 17–34.In A. Yanez-Arancibia (ed.), Fish Community Ecology in Estuaries and Coastal Lagoons: Toward and Ecosystem Integration. DR(R) UNAM Press Mexico, Mexico City.
Gainey, L. F., Jr. andM. J. Greenberg. 1977. Physiological basis of the species abundance-salinity relationship in molluscs: A speculation.Marine Biology (Berl.) 40:41–49.
Gobalet, K. W. 1990. Prehistoric status of freshwater fishes of the Pajaro-Salinas River system of California.Copeia 1990:680–685.
Gobalet, K. W. 1992. Inland utilization of marine fishes by Native Americans along the central California coast.Journal of California and Great Basin Anthropology 14:72–84.
Gunderson, D. R., D. A. Armstrong, Y.-B. Shi, andR. A. McConnauchey. 1990. Patterns of estuarine use by juvenile English sole (Parophrys vetulus) and Dungeness crab (Cancer magister).Estuaries 13:59–71.
Gunter, G. 1938. Seasonal variations in abundance of certain estuarine and marine fishes in Louisiana, with particular reference to life histories.Ecological Monographs 8:313–345.
Hackney, C. T. andE. B. Haines. 1980. Stable carbon isotope composition of fauna and organic matter collected in a Mississippi estuary.Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 10:703–708.
Haertel, L. andC. Osterberg. 1967. Ecology of zooplankton, benthos and fishes in the Columbia River estuary.Ecology 48: 459–472.
Haines, E. B. 1979. Interactions between Georgia salt marshes and coastal waters: A changing paradigm, p. 35–46.In R. J. Livingston (ed.), Ecological Processes in Coastal and Marine systems. Plenum Press, New York.
Haines, E. B. andC. L. Montague. 1979. Food sources of estuarine invertebrates analyzed using15C/12C ratios.Ecology 60: 48–56.
Harvey, J. T., R. Helm, and G. V. Morejohn. In press. Food habits of harbor seals inhabiting Elkhorn Slough, California.California Department of Fish and Game Fish Bulletin
Hay, M. E. 1994. Species as ‘noise’ in community ecology: Do seaweeds block our view of the kelp forest?Trends In Ecology and Evolution 9:414–416.
Hoff, J. G. andR. M. Ibara. 1977. Factors affecting the seasonal abundance, composition and diversity of fishes in a southeastern New England estuary.Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 5:665–678.
Hornberger, M. I. 1991. Paleoenvironment of Elkhorn Slough and surrounding wetland habitats: A geological study using an ecological approach. M.S. Thesis, Moss Landing Marine Laboratories and San Jose State University, California.
Krebs, C. J. 1989. Ecological Methodology. Harper and Row, Publishers, New York.
Krygier, E. E. andW. G. Pearcy. 1986. The role of estuarine and offshore nursery areas for young English sole,Parophrys vetulus Girard, off Oregon.Fishery Bulletin United States 84:119–132.
Langton, R. W. andL. Watling. 1990. The fish-benthos connection: A definition of prey groups in the Gulf of Maine. p. 424–438.In M. Barnes and R. N. Gibson (eds.), Trophic Relationships in the Marine Environment, Proceedings 24th European Marine Biology Symposium, Aberdeen University Press, Scotland.
Levings, C. D. 1974. Seasonal changes in feeding and particle selection by winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus).Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 103:828–832.
Marinucci, A. C. 1982. Trophic importance ofSpartina alterniflora production and decomposition to the marsh-estuarine ecosystem.Biological Conservation 22:35–58.
McErlean, A. J., S. G. O'Connor, J. A. Mihursky, andC. I. Gibson. 1973. Abundance, diversity and seasonal patterns of estuarine fish populations.Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 1:19–36.
McGowan, M. F. 1986. Northern anchovy,Engraulis mordax, spawning in San Francisco Bay, California, 1978–79, relative to hydrography and zooplankton prey of adults and larvae.Fishery Bulletin United States 84:879–894.
Miller, B. S. 1967. Stomach contents of adult starry flounder and sand sole in East Sound, Orcas Island, Washington.Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada 24:2515–2526.
Naiman, R. J. andJ. R. Sibert. 1979. Detritus and juvenile salmon production in the Nanaimo Estuary: III. Importance of detrital carbon to the estuarine ecosystem.Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada 36:504–520.
Nixon, S. W. 1980. Between coastal marshes and coastal waters—A review of twenty years of speculation and research on the role of salt marshes in estuarine productivity and water chemistry, p. 437–525In P. Hamilton and K. B. MacDonald (eds.), Estuarine and Wetland Processes. Plenum Press, New York.
Nybakken, J. W. 1987. Marine Biology: An Ecological Approach, second ed. Harper and Row, New York.
Nybakken, J. andC. Jong. 1977. Benthic invertebrate baseline studies of the Moss Landing-Elkhorn Slough environment, p. 1–215.In J. Nybakken, G. Cailliet, and W. Broenkow (eds.), Ecologic and Hydrographic Studies of Elkhorn Slough Moss Landing Harbor and Nearshore Coastal Waters. Moss Landing Marine Laboratories Technical Publication, Moss Landing, California.
Odum, E. P. 1971. Fundamentals of Ecology, third ed. W. B. Saunders, Co., Philadelphia.
Odum, E. P. andE. J. Heald. 1975. The detritus-based food web of an estuarine mangrove community, p. 265–286.In L. E. Cronin (ed.), Estuarine Research, Vol. 1. Academic Press, New York.
Onuf, C. P. andM. L. Quammen. 1983. Fishes in a California coastal lagoon: Effects of major storms on distribution and abundance.Marine Ecology Progress Series 12:1–14.
Orcutt, H. G. 1950. The life history of the starry flounder,Platichthys stellatus (Pallas).California Department of Fish and Game Fish Bulletin 78:1–64.
Oxman, D. S. 1995. Seasonal abundance, movements, and food habits of harbor seals (Phoca vitulina richardsi) in Elkhorn Slough, California. M.S. Thesis, California State University, Stanislaus, California.
Pearcy, W. G. andS. S. Myers. 1974. Larval fishes of Yaquina Bay, Oregon: A nursery ground for marine fishes?Fishery Bulletin United States 72:201–213.
Pinkas, L., M. S. Oliphant, and I. L. K. Iverson. 1971. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters.California Department of Fish and Game Fish Bulletin 152.
Quammen, M. L. 1984. Predation by shorebirds, fish, and crabs on invertebrates in intertidal mudflats: An experimental test.Ecology 65:529–537.
Raffaelli, D. andS. J. Hall, 1992. Compartments and predation in an estuarine food web.Journal of Animal Ecology 61: 551–560.
Ramer, B. A., G. W. Page, andM. M. Yoklavich, 1991. Seasonal abundance, habitat use, and diet of shorebirds in Elkhorn Slough, California.Western Birds 22:157–174.
Ribelin, B. W. andA. W. Collier, 1979. Ecological consideration of detrital aggregates in the salt marsh, p. 47–68.In R. J. Livingston (ed.), Ecological Processes in Coastal and Marine Systems. Plenum Press, New York.
Robinson, J. V. andG. A. Wellborn, 1988. Ecological resistance to the invasion of a freshwater clam,Corbicula fluminea: Fish predation effects.Oecologia 77:445–452.
Ruagh, A. A. 1976. Feeding habits of silversides (family Atherinidae) in Elkhorn Slough, Monterey Bay, California. M.A. Thesis, California State University, Fresno, California.
Schwartz, D. L. 1983. Geologic history of Elkhorn Slough, Monterey County, California. M.S. Thesis, Moss Landing Marine Laboratories and San Jose State University, San Jose, California.
Schwartz, D. L., H. T. Mullins, andD. F. Belknap. 1986. Holocene geologic history of a transform margin estuary: Elkhorn Slough, Central California.Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 22:285–302.
Shannon, C. E. andW. Weaver. 1963. The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, Illinois.
Shenker, J. M. andJ. M. Dean. 1979. The utilization of an intertidal salt marsh creek by larval and juvenile fishes; abundance, diversity, and temporal variation.Estuaries 2:154–163.
Simpson, E. H. 1949. Measurement of diversity.Nature 163:688.
Smith, R. E. 1973. The hydrography of Elkhorn Slough, a shallow California coastal embayment. Moss Landing Marine Laboratories Technical Publication 73-2, Moss Landing, California.
Smith, S. M., J. G. Hoff, S. P. O'Neil, andM. P. Weinstein. 1984. Community and trophic organization of nekton utilizing shallow marsh habitats, York River, Virginia.Fishery Bulletin United States 82:455–467.
Systat. 1992. SYSTAT for Windows: Statistics, Version 5 Edition. Systat, Inc. Evanston, Illinois.
Tenore, K. R. andD. L. Rice, 1980. A review of trophic factors affecting secondary production of deposit feeders, p. 325–340.In Marine Benthic Dynamics. University of South Carolina Press, Columbia, South Carolina.
Toole, C. L. 1980. Intertidal recruitment and feeding in relation to optimal utilization of nursery areas by juvenile English sole (Parophrys vetulus).Environmental Biology of Fishes 5:383–390.
Vanni, M. J., C. Luecke, J. F. Kitchell, Y. Allen, J. Temte, andJ. J. Magnuson. 1990. Effects on lower trophic levels of massive fish mortality.Nature 344:333–335.
Vetter, E. W. 1994. Hotspots of benthic production.Nature372:47.
Weins, J. A. 1977. On competition in variable environments.American Scientist 65:590–597.
Weinstein, M. P. 1979. Shallow marsh habitats as primary nurseries for fishes and shellfish, Cape Fear River, North Carolina.Fishery Bulletin United States 77:339–357.
Weinstein, M. P., S. L. Weiss, andM. F. Walters. 1980. Multiple determinants of community structure in shallow marsh habitats, Cape Fear River estuary, North Carolina.Marine Biology (Berl.) 58:227–243.
Werner, E. E. andJ. F. Gilliam. 1984. The ontogenetic niche and species interactions in size-structured populations.Annual Review Ecology and Systemmatics 15:393–425.
Williams, P. and Associates and Moffatt and Nichol Engineers. 1992. Elkhorn Slough tidal hydraulics erosion study. Prepared for United States Army Corps of Engineers, San Francisco District, San Francisco, California.
Yoklavich, M. M. 1982. Growth, food consumption, and conversion efficiency of juvenile English sole (Parophrys vetulus). p. 97–105.In G. M. Cailliet and C. A. Simenstad (eds.), Fish Food Habit Studies, Proceedings Third Pacific Workshop. University of Washington, Washington Sea Grant, Seattle, Washington.
Yoklavich, M. M., G. M. Cailliet, J. P. Barry, D. A. Ambrose, andB. S. Antrim. 1991. Temporal and spatial patterns in abundance and diversity of dish assemblages in Elkhorn Slough, California.Estuaries 14:465–480.
Yoklavich, M. M., M. Stevenson, andG. M. Cailliet. 1992. Seasonal and spatial patterns of ichthyoplankton abundance in Elkhorn Slough, California.Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 34:109–126.
Zedler, J., T. Winfield, andD. Mauriello. 1978. Primary productivity in a southern California estuary.Coastal Zone 3:649–662.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barry, J.P., Yoklavich, M.M., Cailliet, G.M. et al. Trophic ecology of the dominant fishes in Elkhorn Slough, California, 1974–1980. Estuaries 19, 115–138 (1996). https://doi.org/10.2307/1352657
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/1352657