Abstract
Background and Objectives: St John’s wort (SJW; Hypericum perforatum) has been one of the most commonly used herbal remedies for mood disorders. This study aimed to investigate the effect of SJW, a pregnane X receptor (PXR) agonist, on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repaglinide, a widely consumed glucose-lowering drug.
Methods: In a two-phase, randomized, crossover study with a 4-week washout period between phases, 15 healthy subjects with specific solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 (SLCO1B1) genotypes were given pretreatment with SJW 325 mg or placebo three times daily for 14 days, and a single dose of repaglinide 1mg was administered followed by 75 g glucose at 15 minutes after repaglinide administration.
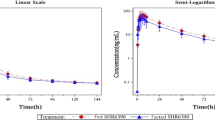
Results: In all subjects, SJW had no effect on the total area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time zero to infinity (AUC∞), the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) or the elimination half-life (t½) of repaglinide. In addition, SJW had no significant effect on the blood glucose-lowering and insulin-elevating effects of repaglinide.
Conclusion: Consumption of SJW for 14 days had no clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repaglinide.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambavane V, Patil R, Ainapure SS. Repaglinide: a short acting insulin secretagogue for postprandial hyperglycaemia. Postgrad Med 2002 Jul–Sep; 48(3): 246–8
Hatorp V. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repaglinide. Clin Pharmacokinet 2002; 41(7): 471–83
Kirchheiner J, Roots I, Goldammer M, et al. Effect of genetic polymorphisms in cytochrome p450 (CYP) 2C9 and CYP2C8 on the pharmacokinetics of oral antidiabetic drugs: clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacokinet 2005; 44(12): 1209–25
Kalliokoski A, Backman JT, Neuvonen PJ, et al. Effects of the SLCO1B1*1B haplotype on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repaglinide and nateglinide. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2008 Nov; 18(11): 937–42
Niemi M, Backman JT, Kajosaari LI, et al. Polymorphic organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 is a major determinant of repaglinide pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005 Jun; 77(6): 468–78
Kajosaari LI, Laitila J, Neuvonen PJ, et al. Metabolism of repaglinide by CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 in vitro: effect of fibrates and rifampicin. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2005 Oct; 97(4): 249–56
Niemi M, Backman JT, Neuvonen M, et al. Rifampin decreases the plasma concentrations and effects of repaglinide. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2000 Nov; 68(5): 495–500
Kalliokoski A, Backman JT, Kurkinen KJ, et al. Effects of gemfibrozil and atorvastatin on the pharmacokinetics of repaglinide in relation to SLCO1B1 polymorphism. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2008 Oct; 84(4): 488–96
Kajosaari LI, Niemi M, Neuvonen M, et al. Cyclosporine markedly raises the plasma concentrations of repaglinide. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005 Oct; 78(4): 388–99
Borrelli F, Izzo AA. Herb-drug interactions with St John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum): an update on clinical observations. AAPS J 2009 Dec; 11(4): 710–27
Zhou S, Chan E, Pan SQ, et al. Pharmacokinetic interactions of drugs with St John’s wort. J Psychopharmacol 2004 Jun; 18(2): 262–76
Henderson L, Yue QY, Bergquist C, et al. St John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum): drug interactions and clinical outcomes. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2002 Oct; 54(4): 349–56
Moore LB, Goodwin B, Jones SA, et al. St John’s wort induces hepatic drug metabolism through activation of the pregnane X receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000 Jun 20; 97(13): 7500–2
Watkins RE, Maglich JM, Moore LB, et al. 2.1 A crystal structure of human PXR in complex with the St John’s wort compound hyperforin. Biochemistry 2003 Feb 18; 42(6): 1430–8
Tirona RG, Leake BF, Merino G, et al. Polymorphisms in OATP-C: identification of multiple allelic variants associated with altered transport activity among European- and African-Americans. J Biol Chem 2001 Sep 21; 276(38): 35669–75
Dai D, Zeldin DC, Blaisdell JA, et al. Polymorphisms in human CYP2C8 decrease metabolism of the anticancer drug paclitaxel and arachidonic acid. Pharmacogenetics 2001 Oct; 11(7): 597–607
Zhang W, He YJ, Han CT, et al. Effect of SLCO1B1 genetic polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of nateglinide. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2006 Nov; 62(5): 567–72
Moore LB, Goodwin B, Jones SA, et al. St John’s wort induces hepatic drug metabolism through activation of the pregnane X receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000; 97: 7500–2
Lehmann JM, McKee DD, Watson MA, et al. The human orphan nuclear receptor PXR is activated by compounds that regulate CYP3A4 gene expression and cause drug interactions. J Clin Invest 1998; 102: 1016–23
Bertilsson G, Heidrich J, Svensson K, et al. Identification of a human nuclear receptor defines a new signaling pathway for CYP3A induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998; 95: 12208–13
Bidstrup TB, Stilling N, Damkier P, et al. Rifampicin seems to act as both an inducer and an inhibitor of the metabolism of repaglinide. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2004 Apr; 60(2): 109–14
Hatorp V, Hansen KT, Thomsen MK. Influence of drugs interacting with CYP3A4 on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of the prandial glucose regulator repaglinide. J Clin Pharmacol 2003; 43: 649–60
Rae JM, Johnson MD, Lippman ME, et al. Rifampin is a selective, pleiotropic inducer of drug metabolism genes in human hepatocytes: studies with cDNA and oligonucleotide expression arrays. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001 Dec; 299(3): 849–57
Skerjanec A, Wang J, Maren K, et al. Investigation of the pharmacokinetic interactions of deferasirox, a once-daily oral iron chelator, with midazolam, rifampin, and repaglinide in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 2010 Feb; 50(2): 205–13
Madan A, Graham RA, Carroll KM, et al. Effects of prototypical microsomal enzyme inducers on cytochrome P450 expression in cultured human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos 2003 Apr; 31(4): 421–31
Kalliokoski A, Neuvonen M, Neuvonen PJ, et al. Different effects of SLCO1B1 polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repaglinide and nateglinide. J Clin Pharmacol 2008 Mar; 48(3): 311–21
Kalliokoski A, Neuvonen M, Neuvonen PJ, et al. The effect of SLCO1B1 polymorphism on repaglinide pharmacokinetics persists over a wide dose range. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2008 Dec; 66(6): 818–25
Meyer zu Schwabedissen HE, Kim RB. Hepatic OATP1B transporters and nuclear receptors PXR and CAR: interplay, regulation of drug disposition genes, and single nucleotide polymorphisms. Mol Pharm 2009 Nov–Dec; 6(6): 1644–61
Kamiyama Y, Matsubara T, Yoshinari K, et al. Role of human hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha in the expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in human hepatocytes assessed by use of small interfering RNA. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 2007 Aug; 22(4): 287–98
Meyer zu Schwabedissen HE, Böttcher K, Chaudhry A, et al. Liver X receptor α and farnesoid X receptor are major transcriptional regulators of OATP1B1. Hepatology 2010 Nov; 52(5): 1797–807
Mai I, Bauer S, Perloff ES, et al. Hyperforin content determines the magnitude of the St John’s wort-cyclosporine drug interaction. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2004; 76: 330–40
Mueller SC, Majcher-Peszynska J, Mundkowski RG, et al. No clinically relevant CYP3A induction after St John’s wort with low hyperforin content in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2009; 65: 81–7
Will-Shahab L, Bauer S, Kunter U, et al. St John’s wort extract (Ze 117) does not alter the pharmacokinetics of a low-dose oral contraceptive. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2009; 65: 287–94
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research grants from the National Scientific Foundation of China (grant nos. 30801421, 30901834 and 30873089), Huge Project to Boost Chinese Drug Development (grant nos. 2009ZX09501-032 and 2009ZX09304-003), 863 Project (grant nos. 2009AA022710, 2009AA022703 and 2009AA022704), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant nos. 2010QZZD010 and 201023100001), Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (grant no. IRT0946) and State Key Laboratory of Drug Research (grant no. SIMM0812KF-01). The authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, L., Zhou, G., Guo, D. et al. The Pregnane X Receptor Agonist St John’s Wort Has No Effects on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Repaglinide. Clin Pharmacokinet 50, 605–611 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2165/11587310-000000000-00000
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/11587310-000000000-00000