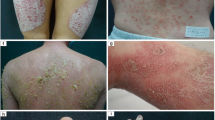
Abstract
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the skin and joints that typically follows a relapsing/remitting disease course. Whereas psoriasis is primarily a T-cell-mediated disease, intrinsic alterations in epidermal keratinocytes also play an important role. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) has been identified as an important cytokine in the inflammatory cascade of psoriasis. The importance of TNFα is further underlined by the therapeutic efficacy of compounds that interfere with TNFα function, such as biological agents

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Section 1. Overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol 2008; 58: 826–50
Tschachler E. Psoriasis: the epidermal component. Clin Dermatol 2007; 25: 589–95
Langley RG, Krueger GG, Griffiths CE. Psoriasis: epidemiology, clinical features, and quality of life. Ann Rheum Dis 2005; 64 (Suppl. 2): ii18–23; discussion ii4-5
De Rosa G, Mignogna C. The histopathology of psoriasis. Rheumatismo 2007; 59 (Suppl. 1): 46–8
Nickoloff BJ, Xin H, Nestle FO, et al. The cytokine and chemokine network in psoriasis. Clin Dermatol 2007; 25: 568–73
Di Cesare A, Di Meglio P, Nestle FO. The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 2009; 129: 1339–50
Fitch E, Harper E, Skorcheva I, et al. Pathophysiology of psoriasis: recent advances on IL-23 and Th17 cytokines. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2007; 9: 461–7
Iwakura Y, Ishigame H. The IL-23/IL-17 axis in inflammation. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 1218–22
Ma HL, Liang S, Li J, et al. IL-22 is required for Th17 cell-mediated pathology in a mouse model of psoriasis-like skin inflammation. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 597–607
Piskin G, Sylva-Steenland RM, Bos JD, et al. In vitro and in situ expression of IL-23 by keratinocytes in healthy skin and psoriasis lesions: enhanced expression in psoriatic skin. J Immunol 2006; 176: 1908–15
Kauffman CL, Aria N, Toichi E, et al. A phase I study evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics, and clinical response of a human IL-12 p40 antibody in subjects with plaque psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 2004; 123: 1037–44
Albanesi C, De Pita O, Girolomoni G. Resident skin cells in psoriasis: a special look at the pathogenetic functions of keratinocytes. Clin Dermatol 2007; 25: 581–8
Mossner R, Schon MP, Reich K. Tumor necrosis factor antagonists in the therapy of psoriasis. Clin Dermatol 2008; 26: 486–502
Wong M, Ziring D, Korin Y, et al. TNF alpha blockade in human diseases: mechanisms and future directions. Clin Immunol 2008; 126: 121–36
Gottlieb AB, Chamain F, Masus S, et al. TNF inhibition rapidly downregulates multiple proinflammatory pathways in psoriasis plaques. J Immunol 2005; 175: 2721–9
Acknowledgments
Editorial assistance for the preparation of this manuscript was provided by Anna Battershill and Stephanie Blick of inScience Communications. This assistance was funded by Pfizer. Dr Miteva received an education fostering grant from the Department of Dermatology, University of Maiami, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miteva, M. Psoriasis: Targeting Therapy Towards the Inflammatory Cascade. AM J Clin Dermatol 11 (Suppl 1), 11–13 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2165/1153414-S0-000000000-00000
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/1153414-S0-000000000-00000