Abstract
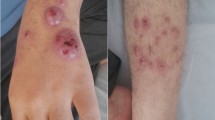
Painful granulomatous lesions appeared on the face of a 36-year-old man with myelodysplastic syndrome. Skin biopsy revealed chronic inflammatory granuloma. Bacterial cultures of the lesions and blood indicated the same unknown Gram-negative rod bacterium. The 16S ribosomal RNA sequence of the unknown bacterium yielded Phenylobacterium. Thus, we diagnosed cutaneous infectious granuloma caused by Phenylobacterium and myelodysplastic syndrome/refractory cytopenia with multi-lineage dysplasia. After treatment with combined antibacterials that were selected based on the tests for drug sensitivity, the lesions disappeared with only scars remaining and without any signs of relapse after 1 year. This is the first case report of cutaneous infectious granuloma caused by Phenylobacterium.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslam Z, Im WT, Ten LN, et al. Phenylobacterium koreense sp. nov., isolated from South Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2005; 55 (5): 2001–5
Kanso S, Patel BK. Phenylobacterium lituiforme sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic bacterium from a subsurface aquifer, and emended description of the genus Phenylobacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2004; 54 (6): 2141–6
Lingens F, Blecher R, Blecher H, et al. Phenylobacterium immobile gen. Nov., sp. Nov., a gram-negative bacterium that degrades the herbicide chloridazon. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1985; 35 (1): 26–39
Tiago I, Mendes V, Pires C, et al. Phenylobacterium falsum sp. nov., an alphaproteobacterium isolated from a nonsaline alkaline groundwater, and emended description of the genus Phenylobacterium. Syst Appl Microbiol 2005; 28 (4): 295–302
Zhang K, Han W, Zhang R, et al. Phenylobacterium zucineum sp. nov., a facultative intracellular bacterium isolated from a human erythroleukemia cell line K562. Syst Appl Microbiol 2007; 30 (3): 207–12
Tsukada H, Chou T, Ishizuka Y, et al. Disseminated Mycobacterium aviumintracellulare infection in a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome (refractory anemia). Am J Hematol 1994 Apr; 45 (4): 325–9
Komeno T, Itoh T, Ohtani K, et al. Disseminated nontuberculous mycobacteriosis caused by mycobacterium in a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome. Intern Med 1996; 35 (4): 323–6
Fry NK, Duncan J, Edwards MT, et al. A UK clinical isolate of Bordetella hinzii from a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome. J Med Microbiol 2007; 56 (Pt 12): 1700–3
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Ju Li-wen, Department of Epidemiology of School of Public Health Safety, Ministry of Education, Fudan University, Shanghai, China, for her assistance with the necessary research of bacterial cultures and organization of materials required to prepare this report. No sources of funding were used to assist in the preparation of this case report. The authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this case report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Xh., Li, F., Xu, Jh. et al. Cutaneous Infectious Granuloma Caused by Phenylobacterium in an Adult with Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Am J Clin Dermatol 11, 363–366 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2165/11533200-000000000-00000
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/11533200-000000000-00000