Abstract
Roflumilast is an orally administered, selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor that is a novel treatment for patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Across four randomized, double-blind, multinational trials in patients with moderate to severe or severe COPD, roflumilast 500 μg/day produced significantly greater improvements from baseline than placebo in pre- and post-bronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1). While mean increases in FEV1 in roflumilast groups were small, they were in marked contrast to the decreases or negligible increase in FEV1 in the placebo groups. In three of four trials, roflumilast significantly reduced the COPD exacerbation rate; in a pooled analysis of two 52-week trials, roflumilast was associated with a 17% reduction over placebo.
Further randomized, double-blind, multinational trials compared roflumilast 500 μg plus salmeterol with placebo plus salmeterol and roflumilast 500 μg plus tiotropium bromide with placebo plus tiotropium bromide. In both trials, roflumilast plus long-acting bronchodilator produced significantly greater increases in pre- and post-bronchodilator FEV1 than placebo plus long-acting bronchodilator.
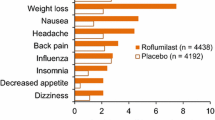
Roflumilast had an acceptable tolerability profile. In a pooled analysis of two trials, 19% and 22% of roflumilast and placebo recipients had serious adverse events; in the corresponding groups, 14% and 11% discontinued medications because of adverse events.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao H, de Boer W, Rahman I. Targeting lung inflammation: novel therapies for the treatment of COPD. Curr Respir Med Rev 2008; 4(1): 57–68
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). At-a-glance outpatient reference guide for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [online]. Available from URL: http://www.goldcopd.com [Accessed 2010 May 20]
Wedzicha JA, Seemungal TA. COPD exacerbations: defining their cause and prevention. Lancet 2007 Sep 1; 370(9589): 786–96
Hansel TT, Barnes JJ. New drugs for exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2009 Aug 29; 374(9691): 744–55
Burgel P-R, Nesme-Meyer P, Chanez P, et al. Cough and sputum production are associated with frequent exacerbations and hospitalizations in COPD subjects. Chest 2009 Apr; 135(4): 975–82
Barnes PJ, Celli BR. Systemic manifestations and comorbidities of COPD. Eur Respir J 2009; 33(5): 1165–85
Halpin D. Mortality in COPD: inevitable or preventable? Insights from the cardiovascular arena. COPD 2008 Jun; 5(3): 187–200
O’Donnell DE. Assessment of bronchodilator efficacy in symptomatic COPD: is spirometry useful? Chest 2000 Feb; 117 (2 Suppl.): 42s–7s
Celli BR, MacNee W. Standards for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD: a summary of the ATS/ERS position paper. ATS/ERS Task Force. Eur Respir J 2004; 23: 932–46
Hatzelmann A, Schudt C. Anti-inflammatory and immuno-modulatory potential of the novel PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001; 297(1): 267–79
European Medicines Agency. Daxas 500 micograms film-coated tablets: summary of product characteristics [online]. Available from URL: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/001179/WC500095209.pdf [Accessed 2010 Aug 2]
Nycomed. Nycomed and Forest Laboratories receive complete FDA response letter for roflumilast — no additional patient trials were requested [media release]. 2010 May 17 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.nycomed.com/News/NewsReleases/2010/Nycomed%20and%20Forest%20Laboratories%20receive%20complete%20FDA%20response%20letter%20for%20Roflumilast.aspx
Hatzelmann A, Morcillo EJ, Lungarella G, et al. The preclinical pharmacology of roflumilast: a selective, oral phosphodies-terase inhibitor in development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2010 Aug; 23(4): 235–56
Wohlsen A, Hirrle A, Tenor H, et al. Effect of cyclic AMP-elevating agents on airway ciliary beat frequency in central and lateral airways in rat precision-cut lung slices. Eur J Pharmacol 2010 Jun 10; 635(1-3): 177–83
Martorana PA, Beume R, Lucattelli M, et al. Roflumilast fully prevents emphysema in mice chronically exposed to cigarette smoke. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2005 Oct; 172(7): 848–53
Hohlfeld JM, Schoenfeld K, Lavae-Mokhtari M, et al. Roflumilast attenuates pulmonary inflammation upon segmental endotoxin challenge in healthy subjects: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2008 Aug; 21(4): 616–23
Grootendorst DC, Gauw SA, Verhoosel RM, et al. Reduction in sputum neutrophil and eosinophil numbers by the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in patients with COPD. Thorax 2007 Dec; 62(12): 1081–7
Calverley PM, Rabe KF, Goehring UM, et al. Roflumilast in symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2009 Aug 29; 374(9691): 685–94
Bethke TD, Böhmer GM, Hermann R, et al. Dose-proportional intraindividual single-and repeated-dose pharmacokinetics of roflumilast, an oral, once-daily phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor. J Clin Pharmacol 2007 Jan; 47(1): 26–36
Hauns B, Hermann R, Hünnemeyer A, et al. Investigation of a potential food effect on the pharmacokinetics of roflumilast, an oral, once-daily phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 2006 Oct; 46(10): 1146–53
Lahu G, Hünnemeyer A, Diletti E, et al. Population phar-macokinetic modelling of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide by total phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitory activity and development of a population pharmacodynamic-adverse event model. Clin Pharmacokinet 2010; 49(9): 589–606
Rabe KF, Bateman ED, O’Donnell D, et al. Roflumilast — an oral anti-inflammatory treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005 Aug 13–2005; 366(9485): 563–71
Calverley PM, Sanchez-Toril F, McIvor A, et al. Effect of 1-year treatment with roflumilast in severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2007 Jul 15; 176(2): 154–61
Fabbri LM, Calverley PM, Izquierdo-Alonso JL, et al. Roflumilast in moderate-to-severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with longacting bronchodilators: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2009 Aug 29; 374(9691): 695–703
Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM. The St Georges Respiratory Questionnnaire. Respir Med 1991 Sep; 85 Suppl. B: 25–31
Mahler DA, Weinberg DH, Wells CK, et al. The measurement of dyspnea: contents, interobserver agreement, and physiologic correlates of two clinical indices. Chest 1984 Jun; 85(6): 751–8
Eakin EG, Resnikoff PM, Prewitt LM, et al. Validation of a new dyspnea measure: the UCSD Shortness of Breath Questionnaire. Chest 1998 Mar; 113(3): 619–24
Rutten-van Mölken MP, van Nooten FE, Lindemann M, et al. A 1-year prospective cost-effectiveness analysis of roflumilast for the treatment of patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacoeconomics 2007; 25(8): 695–711
Martinez FJ, Rabe KF, Wouters EFM, et al. Time course and reversibility of weight decrease with roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor [abstract no. A4441]. 2010 American Thoracic Society (ATS) International Conference; 2010 May 14–19; New Orleans (LA)
Wouters EFM, Teichmann P, Brose M, et al. Effects of roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, on body composition in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [abstract no. A4473]. 2010 American Thoracic Society (ATS) International Conference; 2010 May 14–19; New Orleans (LA)
Acknowledgements and Disclosures
The manuscript was reviewed by: A.D. D’Urzo, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada; O.E. Della Pasqua, Leiden/Amsterdam Centre for Drug Research, Leiden, the Netherlands, and GlaxoSmithKline Research and Development, Stockley Park, Uxbridge, UK; J.A. Falk, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, USA; A.F. Gelb, Pulmonary Division, Department of Medicine, Lakewood Regional Medical Center, Lakewood, California, USA; J. Walters, Menzies Research Institute, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia.
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from any comments were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanford, M. Roflumilast. Drugs 70, 1615–1627 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2165/11205930-000000000-00000
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/11205930-000000000-00000