Abstract
-
▲ Aripiprazole is a novel atypical antipsychotic that is approved in the US for use in adolescents with schizophrenia.
-
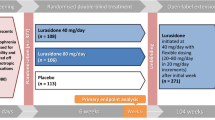
▲ In adolescents with schizophrenia, oral aripiprazole 10 or 30 mg/day lead to significantly greater reductions than placebo in the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score from baseline to 6 weeks, according to findings from a randomized, double-blind, multicenter trial (n = 302).
-
▲ In addition, aripiprazole 10 or 30 mg/day recipients had significantly greater improvements in the PANSS positive subscale and Clinical Global Impression-Severity and -Improvement scale scores than placebo recipients, and a significantly greater improvement in the PANSS negative subscale score was seen with aripiprazole 10 mg/day than with placebo.
-
▲ Aripiprazole was generally well tolerated in adolescents with schizophrenia, with most adverse events being of mild to moderate severity. Clinically significant weight gain (≥7% as defined by the US FDA) occurred in 4.0% of aripiprazole 10 mg/day recipients, 5.2% of aripiprazole 30 mg/day recipients, and 1% of placebo recipients. The mean weight change was significantly different in aripiprazole and placebo recipients (0, +0.2, and −0.8kg in aripiprazole 10 mg/day, aripiprazole 30 mg/day, and placebo recipients, respectively).

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The use of trade names is for product identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Gillberg C, Wahlstrom J, Forsman A, et al. Teenage psychoses: epidemiology, classification and reduced optimality in the pre-, peri-, and neonatal periods. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 1986 Jan; 27(1): 87–98
Masi G, Mucci M, Pari C. Children with schizophrenia: clinical picture and pharmacological treatment. CNS Drugs 2006; 20(10): 841–66
Lenior ME, Dingemans PMAJ, Schene AH, et al. Predictors of the early 5-year course of schizophrenia: a path analysis. Schizophr Bull 2005; 31(3): 781–91
McClellan J, Werry J. Summary of the practice parameters for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with schizophrenia. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2000 Dec; 39(12): 1580–2
Horacek J, Bubenikova-Valesova V, Kopecek M, et al. Mechanism of action of atypical antipsychotic drugs and the neurobiology of schizophrenia. CNS Drugs 2006; 20(5): 389–409
Kumra S, Oberstar JV, Sikich L, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of second-generation antipsychotics in children and adolescents with schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. Epub 2007 Oct 8
Toren P, Ratner S, Laor N, et al. Benefit-risk assessment of atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia and comorbid disorders in children and adolescents. Drug Saf 2004; 27(14): 1135–56
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company and Otsuka America Pharmaceutical Inc. Abilify® (aripiprazole) tablets prescribing information [online]. Available from URL: http://www.abilify.com [Accessed 2007 Nov 19]
Swainston Harrison T, Perry CM. Aripiprazole: a review of its use in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Drugs 2004; 64(15): 1715–36
Grunder G, Kungel M, Ebrecht M, et al. Aripiprazole: pharmacodynamics of a dopamine partial agonist for the treatment of schizophrenia. Pharmacopsychiatry 2006 Feb; 39Suppl. 1: S21–5
Findling RL, Nyilas M, Auby P, et al. Tolerability of aripiprazole in the treatment of adolescents with schizophrenia [abstract no. NR741 plus poster]. 160th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2007 May 19–24; San Diego (CA)
Correll CU, Mughal T, Parikh U, et al. Insulin resistance in treatment-naive youngsters treated with novel antipsychotics [abstract no. NR654 plus poster]. American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting; 2005 May 21–26; Atlanta (GA)
Blumer JL, Findling R, Kauffman R, et al. Pharmacokinetics, tolerability and safety of aripiprazole in children and adolescents with conduct disorder [abstract no. MPI-3]. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2002 Feb; 71: 5A
Findling RL, Auby P, Nyilas M, et al. Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of aripiprazole in children and adolescents with major psychiatric diagnoses [abstract no. NR654 plus poster]. 159th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2006 May 20–25; Toronto (ON)
Mallikaarjun S, Salazar DE, Bramer SL. Pharmacokinetics, tolerability, and safety of aripiprazole following multiple oral dosing in normal healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 2004 Feb; 44(2): 179–87
Robb AS, Auby P, Nyilas M, et al. Efficacy of aripiprazole in the treatment of adolescents with schizophrenia [abstract no. NR742 plus poster]. 160th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2007 May 19–24; San Diego (CA)
Acknowledgments and Disclosures
The manuscript was reviewed by: A. Robb, Department of Child Psychiatry and Pediatrics, Children’s National Medical Center, Washington, DC, USA; P. Toren, Department of Child Psychiatry, Tel-Aviv Community Health Centre, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel.
During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article; changes based on any comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanford, M., Keating, G.M. Aripiprazole. Pediatr Drugs 9, 419–423 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2165/00148581-200709060-00009
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00148581-200709060-00009