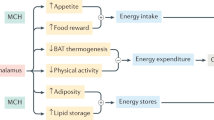
Abstract
There is compelling genetic and pharmacologic evidence to indicate that melanin-concentrating hormone receptor-1 (MCHR1) signaling is involved in the regulation of food intake and energy expenditure. The medical need for novel therapies to treat obesity and related metabolic disorders has led to a great deal of interest by pharmaceutical companies in the discovery of MCHR1 antagonists. Recent publications describing preclinical studies have demonstrated that small-molecule MCHR1 antagonists decrease food intake, bodyweight, and adiposity in rodent models of obesity. Results from ongoing early-stage clinical trials with MCHR1 antagonists are eagerly awaited, as is the movement of other MCHR1 antagonists into the clinic.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, et al. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003; 289 (1): 76–9
Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 2000; 404 (6778): 635–43
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, et al. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA 2002; 288 (14): 1723–7
The Surgeon General’s call to action to prevent and decrease overweight and obesity 2001. Rockville (MD): Public Health Service, Office of the Surgeon General, 2001
Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, et al. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA 1999; 282 (16): 1523–9
Ford ES, Giles WH, Mokdad AH. Increasing prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults. Diabetes Care 2004; 27 (10): 2444–9
Wilson PW, Kannel WB, Silbershatz H, et al. Clustering of metabolic factors and coronary heart disease. Arch Intern Med 1999; 159 (10): 1104–9
Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, et al. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 2001; 344 (18): 1343–50
Wadden TA, Butryn ML, Byrne KJ. Efficacy of lifestyle modification for long-term weight control. Obes Res 2004; 12 Suppl.: 151S–62S
National prescription audit monthly data. Plymouth Meeting (PA): IMS Health, 2006 Mar
Erondu N, Gantz I, Musser B, et al. Neuropeptide Y5 receptor antagonism does not induce clinically meaningful weight loss in overweight and obese adults. Cell Metab 2006; 4 (4): 275–82
Ettinger MP, Littlejohn TW, Schwartz SL, et al. Recombinant variant of ciliary neurotrophic factor for weight loss in obese adults: a randomized, dose-ranging study. JAMA 2003; 289 (14): 1826–32
Collins T. IDDB Reference 766650. Drug development for obesity: key strategies for effective drug discovery. London: Thompson Scientific, 2007
Kim D, Macconell L, Zhuang D, et al. Effects of once-weekly dosing of a long-acting release formulation of exenatide on glucose control and body weight in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007; 12: 1487–93
Jandacek RJ. APD-356 (Arena). Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2005; 6 (10): 1051–6
Griffond B, Baker BI. Cell and molecular cell biology of melanin-concentrating hormone. Int Rev Cytol 2002; 213: 233–77
Kawauchi H, Kawazoe I, Tsubokawa M, et al. Characterization of melanin-concentrating hormone in chum salmon pituitaries. Nature 1983; 305 (5932): 321–3
Presse F, Nahon JL, Fischer WH, et al. Structure of the human melanin concentrating hormone mRNA. Mol Endocrinol 1990; 4 (4): 632–7
Vaughan JM, Fischer WH, Hoeger C, et al. Characterization of melanin-concentrating hormone from rat hypothalamus. Endocrinology 1989; 125 (3): 1660–5
Nahon JL, Presse F, Bittencourt JC, et al. The rat melanin-concentrating hormone messenger ribonucleic acid encodes multiple putative neuropeptides coexpressed in the dorsolateral hypothalamus. Endocrinology 1989; 125 (4): 2056–65
Viale A, Zhixing Y, Breton C, et al. The melanin-concentrating hormone gene in human: flanking region analysis, fine chromosome mapping, and tissue-specific expression. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1997; 46 (1–2): 243–55
Hervieu G, Nahon JL. Pro-melanin concentrating hormone messenger ribonucleic acid and peptides expression in peripheral tissues of the rat. Neuroendocrinology 1995; 61 (4): 348–64
Bittencourt JC, Presse F, Arias C, et al. The melanin-concentrating hormone system of the rat brain: an immuno- and hybridization histochemical characterization. J Comp Neurol 1992; 319 (2): 218–45
Elias CF, Lee CE, Kelly JF, et al. Characterization of CART neurons in the rat and human hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol 2001; 432 (1): 1–19
Vrang N, Larsen PJ, Clausen JT, et al. Neurochemical characterization of hypothalamic cocaine-amphetamine-regulated transcript neurons. J Neurosci 1999; 19 (10): RC5
Broberger C. Hypothalamic cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) neurons: histochemical relationship to thyrotropin-releasing hormone, melanin-concentrating hormone, orexin/hypocretin and neuropeptide Y. Brain Res 1999; 848 (1–2): 101–13
Chambers J, Ames RS, Bergsma D, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone is the cognate ligand for the orphan G-protein-coupled receptor SLC-1. Nature 1999; 400 (6741): 261–5
Lembo PM, Grazzini E, Cao J, et al. The receptor for the orexigenic peptide melanin-concentrating hormone is a G-protein-coupled receptor. Nat Cell Biol 1999; 1 (5): 267–71
Saito Y, Nothacker HP, Wang Z, et al. Molecular characterization of the melanin-concentrating-hormone receptor. Nature 1999; 400 (6741): 265–9
Bachner D, Kreienkamp H, Weise C, et al. Identification of melanin concentrating hormone (MCH) as the natural ligand for the orphan somatostatin-like receptor 1 (SLC-1). FEBS Lett 1999; 457 (3): 522–4
Shimomura Y, Mori M, Sugo T, et al. Isolation and identification of melanin-concentrating hormone as the endogenous ligand of the SLC-1 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 261 (3): 622–6
Hawes BE, Kil E, Green B, et al. The melanin-concentrating hormone receptor couples to multiple G proteins to activate diverse intracellular signaling pathways. Endocrinology 2000; 141 (12): 4524–32
Tan CP, Sano H, Iwaasa H, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone receptor subtypes 1 and 2: species-specific gene expression. Genomics 2002; 79 (6): 785–92
Saito Y, Cheng M, Leslie FM, et al. Expression of the melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) receptor mRNA in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 2001; 435 (1): 26–40
Wang S, Behan J, O’Neill K, et al. Identification and pharmacological characterization of a novel human melanin-concentrating hormone receptor, mch-r2. J Biol Chem 2001; 276 (37): 34664–70
An S, Cutler G, Zhao JJ, et al. Identification and characterization of a melanin-concentrating hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001; 98 (13): 7576–81
Sailer AW, Sano H, Zeng Z, et al. Identification and characterization of a second melanin-concentrating hormone receptor, MCH-2R. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001; 98 (13): 7564–9
Rodriguez M, Beauverger P, Naime I, et al. Cloning and molecular characterization of the novel human melanin-concentrating hormone receptor MCH2. Mol Pharmacol 2001; 60 (4): 632–9
Mori M, Harada M, Terao Y, et al. Cloning of a novel G protein-coupled receptor, SLT, a subtype of the melanin-concentrating hormone receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 283 (5): 1013–8
Hill J, Duckworth M, Murdock P, et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of MCH2, a novel human MCH receptor. J Biol Chem 2001; 276 (23): 20125–29
Fried S, O’Neill K, Hawes BE. Cloning and characterization of rhesus monkey MCH-R1 and MCH-R2. Peptides 2002; 23 (8): 1401–8
Chiocchio SR, Gallardo MG, Louzan P, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone stimulates the release of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and gonado-tropins in the female rat acting at both median eminence and pituitary levels. Biol Reprod 2001; 64 (5): 1466–72
Tsukamura H, Thompson RC, Tsukahara S, et al. Intracerebroventricular administration of melanin-concentrating hormone suppresses pulsatile luteinizing hormone release in the female rat. J Neuroendocrinol 2000; 12 (6): 529–34
Murray JF, Adan RA, Walker R, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone, mela-nocortin receptors and regulation of luteinizing hormone release. J Neuroendocrinol 2000; 12 (3): 217–23
Gonzalez MI, Baker BI, Wilson CA. Stimulatory effect of melanin-concentrating hormone on luteinising hormone release. Neuroendocrinology 1997; 66 (4): 254–62
Kennedy AR, Todd JF, Dhillo WS, et al. Effect of direct injection of melanin-concentrating hormone into the paraventricular nucleus: further evidence for a stimulatory role in the adrenal axis via SLC-1. J Neuroendocrinol 2003; 15 (3): 268–72
Bluet-Pajot MT, Presse F, Voko Z, et al. Neuropeptide-E-I antagonizes the action of melanin-concentrating hormone on stress-induced release of adrenocortico-tropin in the rat. J Neuroendocrinol 1995; 7 (4): 297–303
Jezova D, Bartanusz V, Westergren I, et al. Rat melanin-concentrating hormone stimulates adrenocorticotropin secretion: evidence for a site of action in brain regions protected by the blood-brain barrier. Endocrinology 1992; 130 (2): 1024–9
Messina MM, Overton JM. Cardiovascular effects of melanin-concentrating hormone. Regul Pept 2006; 10: 10
Kela J, Salmi P, Rimondini-Giorgini R, et al. Behavioural analysis of melanin-concentrating hormone in rats: evidence for orexigenic and anxiolytic properties. Regul Pept 2003; 114 (2–3): 109–14
Monzon ME, De Barioglio SR. Response to novelty after i.c.v. injection of melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) in rats. Physiol Behav 1999; 67 (5): 813–7
Qu D, Ludwig DS, Gammeltoft S, et al. A role for melanin-concentrating hormone in the central regulation of feeding behaviour. Nature 1996; 380 (6571): 243–7
Della-Zuana O, Presse F, Ortola C, et al. Acute and chronic administration of melanin-concentrating hormone enhances food intake and body weight in Wistar and Sprague-Dawley rats. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26 (10): 1289–95
Rossi M, Choi SJ, O’Shea D, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone acutely stimulates feeding, but chronic administration has no effect on body weight. Endocrinology 1997; 138 (1): 351–5
Ludwig DS, Mountjoy KG, Tatro JB, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone: a functional melanocortin antagonist in the hypothalamus. Am J Physiol 1998; 274 (4 Pt 1): E627–33
Tritos NA, Vicent D, Gillette J, et al. Functional interactions between melanin-concentrating hormone, neuropeptide Y, and anorectic neuropeptides in the rat hypothalamus. Diabetes 1998; 47 (11): 1687–92
Hanada R, Nakazato M, Matsukura S, et al. Differential regulation of melanin-concentrating hormone and orexin genes in the agouti-related protein/mela-nocortin-4 receptor system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 268: 88–91
Stricker-Krongrad A, Dimitrov T, Beck B. Central and peripheral dysregulation of melanin-concentrating hormone in obese Zucker rats. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2001; 92 (1–2): 43–8
Sergeyev V, Broberger C, Gorbatyuk O, et al. Effect of 2-mercaptoacetate and 2-deoxy-D-glucose administration on the expression of NPY, AGRP, POMC, MCH and hypocretin/orexin in the rat hypothalamus. Neuroreport 2000; 11 (1): 117–21
Ito M, Gomori A, Ishihara A, et al. Characterization of MCH-mediated obesity in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 284 (5): E940–5
Gomori A, Ishihara A, Ito M, et al. Chronic intracerebroventricular infusion of MCH causes obesity in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 284 (3): E583–8
Shearman LP, Camacho RE, Stribling D, et al. Chronic MCH-1 receptor modulation alters appetite, body weight and adiposity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2003; 475 (1–3): 37–47
Ludwig DS, Tritos NA, Mastaitis JW, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone overexpression in transgenic mice leads to obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2001; 107 (3): 379–86
Elias CF, Saper CB, Maratos-Flier E, et al. Chemically defined projections linking the mediobasal hypothalamus and the lateral hypothalamic area. J Comp Neurol 1998; 402 (4): 442–59
Jo YH, Chen YJ, Chua Jr SC, et al. Integration of endocannabinoid and leptin signaling in an appetite-related neural circuit. Neuron 2005; 48 (6): 1055–66
Tadayyon M, Welters HJ, Haynes AC, et al. Expression of melanin-concentrating hormone receptors in insulin-producing cells: MCH stimulates insulin release in RINm5F and CRI-G1 cell-lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 275 (2): 709–12
Bradley RL, Kokkotou EG, Maratos-Flier E, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone regulates leptin synthesis and secretion in rat adipocytes. Diabetes 2000; 49 (7): 1073–7
Hervieu G, Volant K, Grishina O, et al. Similarities in cellular expression and functions of melanin-concentrating hormone and atrial natriuretic factor in the rat digestive tract. Endocrinology 1996; 137 (2): 561–71
Shimada M, Tritos NA, Lowell BB, et al. Mice lacking melanin-concentrating hormone are hypophagic and lean. Nature 1998; 396 (6712): 670–4
Kokkotou E, Jeon JY, Wang X, et al. Mice with MCH ablation resist diet-induced obesity through strain-specific mechanisms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2005; 289 (1): R117–24
Segal-Lieberman G, Bradley RL, Kokkotou E, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone is a critical mediator of the leptin-deficient phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003; 100 (17): 10085–90
Marsh DJ, Weingarth DT, Novi DE, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone 1 receptor-deficient mice are lean, hyperactive, and hyperphagic and have altered metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002; 99 (5): 3240–5
Chen Y, Hu C, Hsu CK, et al. Targeted disruption of the melanin-concentrating hormone receptor-1 results in hyperphagia and resistance to diet-induced obesity. Endocrinology 2002; 143 (7): 2469–77
Astrand A, Bohlooly YM, Larsdotter S, et al. Mice lacking melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 demonstrate increased heart rate associated with altered autonomie activity. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2004; 287 (4): R749–58
Bjursell M, Gerdin AK, Ploj K, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 deficiency increases insulin sensitivity in obese leptin-deficient mice without affecting body weight. Diabetes 2006; 55 (3): 725–33
Handlon AL, Zhou H. Melanin-concentrating hormone-1 receptor antagonists for the treatment of obesity. J Med Chem 2006; 49 (14): 4017–22
Kowalski TJ, McBriar MD. Therapeutic potential of melanin-concentrating hormone-1 receptor antagonists for the treatment of obesity. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2004; 13 (9): 1113–22
McBriar MD, Kowalski TJ. Melanin-concentrating hormone as a therapeutic target. Ann Rep Med Chem 2005; 40: 119–33
McBriar MD, Palani A, Shapiro SA, et al., inventors. Schering Corporation, assignee. MCH antagonists and their use in the treatment of obesity. WO 2002/ 057233 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.wipo.int/pctdb/en/search.jsp
Xu R, Li S, Paruchova J, et al. Bicyclic[4.1.0]heptanes as phenyl replacements for melanin concentrating hormone receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 2006; 14 (10): 3285–99
Sasikumar TK, Qiang L, Burnett DA, et al. Novel aminobenzimidazoles as selective MCH-R1 antagonists for the treatment of metabolic diseases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (20): 5427–31
Wu WL, Burnett DA, Spring R, et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of piperidine-based melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (14): 3668–73
Sasikumar TK, Qiang L, Wu WL, et al. Tetrahydroisoquinolines as MCH-R1 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (18): 4917–21
Wu WL, Burnett DA, Caplen MA, et al. Design and synthesis of orally efficacious benzimidazoles as melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (14): 3674–8
Witty DR, Bateson JH, Hervieu GJ, et al. SAR of biphenyl carboxamide ligands of the human melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 (MCH Rl): discovery of antagonist SB-568849. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (18): 4865–71
Witty DR, Bateson J, Hervieu GJ, et al. Discovery of potent and stable conformationally constrained analogues of the MCH Rl antagonist SB-568849. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (18): 4872–8
Hertzog DL, Al-Barazanji KA, Bigham EC, et al. The discovery and optimization of pyrimidinone-containing MCH Rl antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (18): 4723–7
Carpenter AJ, Al-Barazanji KA, Barvian KK, et al. Novel benzimidazole-based MCH Rl antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (19): 4994–5000
Warshakoon NC, Sheville J, Bhatt RT, et al. Design and synthesis of substituted quinolines as novel and selective melanin concentrating hormone antagonists as anti-obesity agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (19): 5207–11
Kim N, Meyers KM, Mendez-Andino JL, et al. Identification of substituted 4-aminopiperidines and 3-aminopyrrolidines as potent MCH-R1 antagonists for the treatment of obesity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (20): 5445–50
Dyck B, Zhao L, Tamiya J, et al. Substituted chromones and quinolones as potent melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (16): 4237–42
Rowbottom MW, Vickers TD, Dyck B, et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of retro bis-aminopyrrolidine urea (rAPU) derived small-molecule antagonists of the melanin-concentrating hormone receptor-1 (MCH-R1): part 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (17): 4450–7
Hudson S, Kiankarimi M, Rowbottom MW, et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of retro bis-aminopyrrolidine urea (rAPU) derived small-molecule antagonists of the melanin-concentrating hormone receptor-1 (MCH-R1): part 2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (18): 4922–30
Jiang J, Hoang M, Young JR, et al. 2-Aminoquinoline melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH)1R antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (20): 5270–4
Kym PR, Iyengar R, Souers AJ, et al. Discovery and characterization of aminopiperidinecoumarin melanin concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonists. J Med Chem 2005; 48 (19): 5888–91
Blackburn C, LaMarche MJ, Brown J, et al. Identification and characterization of amino-piperidinequinolones and quinazolinones as MCHr1 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (10): 2621–7
Lynch JK, Freeman JC, Judd AS, et al. Optimization of chromone-2-carboxamide melanin concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonists: assessment of potency, efficacy, and cardiovascular safety. J Med Chem 2006; 49 (22): 6569–84
Ma V, Bannon AW, Baumgartner J, et al. Solid-phase synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel biarylethers as melanin-concentrating hormone receptor-1 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006; 16 (19): 5066–72
Beck JP, Wakefeidl BD, Cordier FL, et al., inventors. Eli Lilly & Co., assignee. Novel MCH receptor antangonists. WO 2006/066173 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.wipo.int/pctdb/en/search.jsp
Amegadzie AK, Beck JP, Gardinier KM, et al., inventors. Eli Lilly & Co., assignee. Thiazolopyridinone derivates as MCH receptor antagonists. WO 2006/066174 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.wipo.int/pctdb/en/search.jsp
Guo T, Gu H, Hobbs DW, inventors. Pharmacopeia Drug Discovery Inc., assignee. Bicyclic compounds as selective melanin concentrating hormone receptor antagonists for the treatment of obesity and related disorders. WO 2006/044293 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.wipo.int/pctdb/en/search.jsp
Sekiguchi Y, Kanuma K, Omodera K, et al., inventors. Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, assignee. Pyridine derivatives and their use as medicaments for treating diseases related to MCH receptor. WO 2006/035967 [online]. Available from URL
Egner B, Giordanetto F, Inghardt T, inventors. Astrazeneca, assignee. Heterocyclic MCHrl antagonists and their use in therapy. WO 2006/068594 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.wipo.int/pctdb/en/search.jsp
Browning A, Scobie M, inventors. Biovitrum, assignee. Substituted octahydroisoindoles as antagonists of melanin concentrating hormone receptor 1 (MCH1R). WO 2006/114402 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.wipo.int/pctdb/en/search.jsp
Mashiko S, Ishihara A, Gomori A, et al. Antiobesity effect of a melanin-concentrating hormone 1 receptor antagonist in diet-induced obese mice. Endocrinology 2005; 146 (7): 3080–6
Borowsky B, Durkin MM, Ogozalek K, et al. Antidepressant, anxiolytic and anorectic effects of a melanin-concentrating hormone-1 receptor antagonist. Nat Med 2002; 8 (8): 825–30
Huang CQ, Baker T, Schwarz D, et al. l- (4-Amino-phenyl)-pyrrolidin-3-yl-amine and 6- (3-amino-pyrrolidin-l-yl)-pyridin-3-yl-amine derivatives as melanin-concentrating hormone receptor-1 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2005; 15 (16): 3701–6
Souers AJ, Gao J, Brune M, et al. Identification of 2- (4-benzyloxyphenyl)-N-[l- (2-pyrrolidin-l-yl-ethyl) -1H-indazol-6-yl]acetamide, an orally efficacious melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonist for the treatment of obesity. J Med Chem 2005; 48 (5): 1318–21
Takekawa S, Asami A, Ishihara Y, et al. T-226296: a novel, orally active and selective melanin-concentrating hormone receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 2002; 438 (3): 129–35
Kowalski TJ, Spar BD, Weig B, et al. Effects of a selective melanin-concentrating hormone 1 receptor antagonist on food intake and energy homeostasis in dietinduced obese mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2006; 535 (1–3): 182–91
Kowalski TJ, Farley C, Cohen-Williams ME, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone-1 receptor antagonism decreases feeding by reducing meal size. Eur J Pharmacol 2004; 497 (1): 41–7
McBriar MD, Guzik H, Shapiro S, et al. Discovery of orally efficacious melanin-concentrating hormone receptor-1 antagonists as antiobesity agents: synthesis, SAR, and biological evaluation of bicyclo[3.1.0]hexyl ureas. J Med Chem 2006; 49 (7): 2294–310
Palani A, Shapiro S, McBriar MD, et al. Biaryl ureas as potent and orally efficacious melanin concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonists for the treatment of obesity. J Med Chem 2005; 48 (15): 4746–9
McBriar MD, Guzik H, Xu R, et al. Discovery of bicycloalkyl urea melanin concentrating hormone receptor antagonists: orally efficacious antiobesity therapeutics. J Med Chem 2005; 48 (7): 2274–7
Chaki S, Funakoshi T, Hirota-Okuno S, et al. Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like profile of ATC0065 and ATC0175: nonpeptidic and orally active melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005; 313 (2): 831–9
Tavares FX, Al-Barazanji KA, Bishop MJ, et al. 6- (4-Chlorophenyl)-3-substituted-thieno[3,2-d] pyrimidin-4 (3H)-one-based melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonist. J Med Chem 2006; 49 (24): 7108–18
Tavares FX, Al-Barazanji KA, Bigham EC, et al. Potent, selective, and orally efficacious antagonists of melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1. J Med Chem 2006; 49 (24): 7095–107
Vasudevan A, Souers AJ, Freeman JC, et al. Aminopiperidine indazoles as orally efficacious melanin concentrating hormone receptor-1 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2005; 15 (23): 5293–7
Dyck B, Markison S, Zhao L, et al. A thienopyridazinone-based melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonist with potent in vivo anorectic properties. J Med Chem 2006; 49 (13): 3753–6
Smith DG, Davis RJ, Rorick-Kehn L, et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone-1 receptor modulates neuroendocrine, behavioral, and corticolimbic neurochemical stress responses in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006; 31 (6): 1135–45
Roy M, David NK, Danao JV, et al. Genetic inactivation of melanin-concentrating hormone receptor subtype 1 (MCHR1) in mice exerts anxiolytic-like behavioral effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006; 31 (1): 112–20
Hervieu GJ. Further insights into the neurobiology of melanin-concentrating hormone in energy and mood balances. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2006; 10 (2): 211–29
Monzon ME, Varas MM, De Barioglio SR. Anxiogenesis induced by nitric oxide synthase inhibition and anxiolytic effect of melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) in rat brain. Peptides 2001; 22 (7): 1043–7
Gonzalez MI, Vaziri S, Wilson CA. Behavioral effects of alpha-MSH and MCH after central administration in the female rat. Peptides 1996; 17 (1): 171–7
Basso AM, Bratcher NA, Gallagher KB, et al. Lack of efficacy of melanin-concentrating hormone-1 receptor antagonists in models of depression and anxiety. Eur J Pharmacol 2006; 540 (1–3): 115–20
Fanghanel G, Cortinas L, Sanchez-Reyes L, et al. Second phase of a double-blind study clinical trial on sibutramine for the treatment of patients suffering essential obesity: 6 months after treatment cross-over. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25 (5): 741–7
Mathus-Vliegen EM, van de Voorde K, Kok AM, et al. Dexfenfluramine in the treatment of severe obesity: a placebo-controlled investigation of the effects on weight loss, cardiovascular risk factors, food intake and eating behaviour. J Intern Med 1992; 232 (2): 119–27
Pi-Sunyer FX, Aronne LJ, Heshmati HM, et al. Effect of rimonabant, a cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker, on weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight or obese patients: RIO-North America: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006; 295 (7): 761–75
Acknowledgments
The authors are employees of Schering-Plough Research Institute, the research and development arm of Schering-Plough Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kowalski, T.J., Sasikumar, T. Melanin-Concentrating Hormone Receptor-1 Antagonists as Antiobesity Therapeutics. BioDrugs 21, 311–321 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2165/00063030-200721050-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00063030-200721050-00003