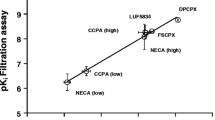
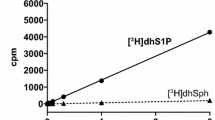
Abstract
Scintillation proximity assay (SPA), characterized by its speed, sensitivity, reliability, and the fact that no separation step is required, has become an important technique in high-throughput screening (HTS) for new drugs, and for investigating their biological interactions. The SPA technique now plays a key role in HTS, in that it can be used in many assay formats including radioimmunoassays (RIAs), ligand-receptor binding assays, and enzyme assays. The SPA-based enzyme assay is usually designed in three formats corresponding to different enzymes: signal removal format for hydrolytic enzymes, signal addition format for polymerase and transferase enzymes, and product capture format for antibodies, DNA probes, receptors or other specific binding proteins. The use of SPA in RIAs has been facilitated by new carriers, such as membranes that can be configured in various shapes and sizes, allowing the assay to be performed on samples from many sources including tissue, serum, plasma or cells. This review presents the principles of SPA, discusses supporting materials and quenching effects, as well as detailed examples of the latest advances.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The use of trade names is for product identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Liu BL, Li SJ, Hu J. Technological advances in high-throughput screening. Am J Pharmacogenomics 2004; 4: 263–76
Hart HE, Greenwald EB. Scintillation proximity assay (SPA): a new method of immunoassay. Direct and inhibition mode detection with human albumin and rabbit antihuman albumin. Mol Immunol 1979; 16: 265–7
Cook ND. Scintillation proximity assay: a versatile high-throughput screening technology. Drug Discov Today 1996; 1(7): 287–94
Arya P, Roth HJ. Combinatorial chemistry. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2005; 9: 229–31
Weber L. In vitro combinatorial chemistry to create drug candidates. Drug Discov Today 2004; 1: 261–7
Ganesan A. Natural products as a hunting ground for combinatorial chemistry. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2004; 15: 584–90
Ratti E, Trist D. The continuing evolution of the drug discovery process in the pharmaceutical industry. Farmaco 2001; 56: 13–9
Hurko O. Genetics and genomics in neuropsychopharmacology: the impact on drug discovery and development. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2001; 11: 491–9
Ryu DDY, Nam DH. Biomolecular engineering: a new frontier in biotechnology. J Mol Catal B Enzym 2000; 10: 23–37
Grippo JF, Burn P. Obesity genes: molecular genetic approaches to drug target identification. Farmaco 1998; 53: 262–5
Sittampalam GS, Kahl SD, Janzen WP. High-throughput screening: advances in assay technologies. Curr Opin Chem Biol 1997; 1: 384–91
Kominami G, Nakamura M, Chomei N, et al. Radioimmunoassay for a novel benzodiazepine inverse agonist, S-8510, in human plasma and urine. J Pharmaceut Biomed 1999 Jun; 20(1-2): 145–53
Mansfield RK, Bhattacharyya D, Hartman NG, et al. Scintillation proximity radioimmunoassay with microporous membranes. Appl Radiat Isot 1996; 47(3): 323–8
Crane K, Shih DT. Development of a homogeneous binding assay for histamine receptors. Anal Biochem 2004; 335: 42–9
Dautzenberg FM, Huber G, Higelin J, et al. Evidence for the abundant expression of arginine 185 containing human CRF2CC receptors and the role of position 185 for receptor-ligand selectivity. Neuropharmacology 2000; 39: 1368–76
Mádi A, Kárpáti L, Kovacs A, et al. High-throughput scintillation proximity assay for transglutaminase activity measurement. Anal Biochem 2005 Aug 15; 343(2): 256–62
Latour D, Fung K, Michelotti E, et al. 991 Development of a homogeneous scintillation proximity assay (SPA) for determining activity of HCV polymerase and screening for enzyme inhibitors. Hepatology 2003; 38: 633–9
Kumar CC, Yin ZZ, Liu YH, et al. Expression, purification, characterization and homology modeling of active Akt/PKB, a key enzyme involved in cell survival signaling. BBA-Gen Subjects 2001; 1526: 257–8
Liu JW, Feldman PA, Lippy JS, et al. A scintillation proximity assay for RNA detection. Anal Biochem 2001; 289(2): 239–45
Skorey KI, Kennedy BP, Friesen RW, et al. Development of a robust scintillation proximity assay for protein tyrosine phosphatase IB using the catalytically inactive (C215S) mutant. Anal Biochem 2001; 291: 269–78
Mueller JP, Reynolds KA. Development of a scintillation proximity assay for b-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III. Anal Biochem 2000; 282: 107–14
Whitfield J, Harada K, Bardelle C, et al. High-throughput methods to detect dimerization of Bcl-2 family proteins. Anal Biochem 2003; 322(2): 170–8
Higelin J, Lang GP, Paternoster C, et al. 125I-Antisauvagine-30: a novel and specific high-affinity radioligand for the characterization of corticotropin-releasing factor type 2 receptors. Neuropharmacology 2000; 40(1): 114–22
Zhou V, Han S, Brinker A, et al. A time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based HTS assay and a surface plasmon resonance-based binding assay for heat shock protein 90 inhibitors. Anal Biochem 2004; 331(2): 349–57
Baum EZ, Johnston SH, Bebernitz GA, et al. Development of a scintillation proximity assay for human cytomegalovirus protease using 33Phosphorous. Anal Biochem 1996; 237(1): 129–34
Zaworski PG, Alberts GL, Pregenzer JF, et al. Efficient functional coupling of the human D3 dopamine receptor to G(o) subtype of G proteins in SH-SY5Y cells. Br J Pharmacol 1999; 128(6): 1181–8
Yang QD, Qureshi SA, Xie D, et al. Detection of glucagon-dependent GTPgam-maS binding in high-throughput format. Anal Biochem 2002 Feb 1; 301(1): 156–9
Simpson PR, Yu XH, Redza ZM, et al. Quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA using competitive PCR and a scintillation proximity assay. J Virol Methods 1997; 69(1-2): 197–208
Pachter JA, Zhang RM, Mayerezell R. Scintillation proximity assay to measure binding of soluble fibronectin to antibody-captured 51 integrin. Anal Biochem 1995; 230: 101–7
McDonald OB, Chen WJ, Ellis B, et al. A scintillation proximity assay for the Raf/ MEK/ERK kinase cascade: high-throughput screening and identification of selective enzyme inhibitors. Anal Biochem 1999; 268(2): 318–29
Pai JJK, Kirkup MP, Frank EA, et al. Compounds capable of generating singlet oxygen represent a source of artifactual data in scintillation proximity assays measuring phosphopeptide binding to SH2 domains [published erratum appears in Anal Biochem 1999 Dec 15; 276(2): 262. Anal Biochem 1999 May 15; 270 (1): 33–4
Dayton BD, Chiou WJ, Opgenorth TJ, et al. Direct determination of endothelin receptor antagonist levels in plasma using a scintillation proximity assay. Life Sci 2000; 66: 937–45
Zhang J, Wu P, Kuvelkar R, et al. A scintillation proximity assay for human interleukin-5 (hIL-5) high-affinity binding in insect cells coexpressing hIL-5 receptor a and β subunits. Anal Biochem 1999; 268(1): 134–42
Jeffery JA, Sharom JR, Fazekas M, et al. An ATPase assay using scintillation proximity beads for high-throughput screening or kinetic analysis. Anal Biochem 2002; 304(1): 55–62
Sonatore LM, Wisniewski D, Frank LJ, et al. The utility of FK506-binding protein as a fusion partner in scintillation proximity assays: application to SH2 domains. Anal Biochem 1996; 240: 289–97
Antonsson B, Marshall CJ, Montessuit S, et al. An in vitro 96-well plate assay of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Anal Biochem 1999; 267: 294–9
Nichols JS, Parks DJ, Consler TG, et al. Development of a scintillation proximity assay for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ψ ligand binding domain [published erratum appears in Anal Biochem 1998 Oct 1; 263(1): 126. Anal Biochem 1998; 257 (2): 112–
Patel S, Harris A, O’Beirne G, et al. Kinetic analysis of inositol trisphosphate binding to pure inositol trisphosphate receptors using scintillation proximity assay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 221: 821–5
Sun SX, Almaden J, Carlson TJ, et al. Assay development and data analysis of receptor-ligand binding based on scintillation proximity assay. Metab Eng 2005; 7(1): 38–44
Yang F, Dicker IB, Kurilla MG, et al. PolC-type polymerase III of Streptococcus pyogenes and its use in screening for chemical inhibitors. Anal Biochem 2002; 304(1): 110–6
Tanitame A, Oyamada Y, Ofuji K, et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel and potent DNA gyrase inhibitors with azole ring. Bioorg Med Chem 2004; 12: 5515–24
DeLapp NW, McKinzie JH, Sawyer BD, et al. Determination of [35S] guanosine-5′-O- (3-thio) triphosphate binding mediated by cholinergic muscarinic receptors in membranes from Chinese hamster ovary cells and rat striatum using an anti-G protein scintillation proximity assay. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1999; 289(2): 946–55
Porter AC, Sauer JM, Knierman MD, et al. Characterization of a novel endocan-nabinoid, virodhamine, with antagonist activity at the CB1 receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2002; 301(3): 1020–4
Bymaster FP, Falcone JF, Bauzon D, et al. Potent antagonism of 5-HT3 and 5-HT6 receptors by olanzapine. Eur J Pharmacol 2001; 430(2-3): 341–9
Cussac D, Pasteau V, Millan MJ. Characterisation of Gs activation by dopamine Dl receptors using an antibody capture assay: antagonist properties of clozapine. Eur J Pharmacol 2004; 485(1-3): 111–7
Mei HY, Mack DP, Galan AA, et al. Discovery of selective, small-molecule inhibitors of RNA complexes: 1. The Tat protein/TAR RNA complexes required for HIV-1 transcription. Bioorg Med Chem 1997; 5(6): 1173–84
Laurin P, Ferroud D, Schio L, et al. Structure-activity relationship in two series of aminoalkyl substituted coumarin inhibitors of gyrase B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1999; 9(19): 2875–80
Laurin P, Ferroud D, Klich M, et al. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of novel highly potent coumarin inhibitors of gyrase B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1999; 9(14): 2079–84
Kyono K, Miyashiro M, Taguchi I. Detection of hepatitis C virus helicase activity using the scintillation proximity assay system. Anal Biochem 1998 Mar 15; 257(2): 120–6
Gevi M, Domenici E. A scintillation proximity assay amenable for screening and characterization of DNA gyrase B subunit inhibitors. Anal Biochem 2002 Jan 1; 300(1): 34–9
Tadepalli SM, Quinn RP. Scintillation proximity radioimmunoassay for the measurement of Acyclovir. J Pharm Biomed Anal 1996; 15: 157–63
Serres MD, McNully MJ, Christensen L, et al. Development of a novel scintillation proximity competitive hybridization assay for the determination of phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotide plasma concentrations in a toxicokinetic study. Anal Biochem 1996; 233: 228–33
Zheng W, Carroll SS, Inglese J, et al. Miniaturization of a hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase assay using a −102°C cooled CCD camera-based imaging system. Anal Biochem 2001; 290(2): 214–20
Nare B, Allocco JJ, Kuningas R, et al. Development of a scintillation proximity assay for histone deacetylase using a biotinylated peptide derived from histone-H4. Anal Biochem 1999; 267(2): 390–6
Hood CM, Kelly VA, Bird MI, et al. Measurement of a (1-3) fucosyltransferase activity using scintillation proximity. Anal Biochem 1998; 255(1): 8–12
Zhang Y, Yang F, Kao YC, et al. Homogenous assays for Escherichia coli DnaB-stimulated DnaG primase and DnaB helicase and their use in screening for chemical inhibitors. Anal Biochem 2002; 304(2): 174–9
Macarron R, Mensah L, Cid C, et al. A homogeneous method to measure aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase aminoacylation activity using scintillation proximity assay technology. Anal Biochem 2000; 284(2): 183–90
Sawyer BD, Silbernagel A, McKinzie JB, et al. Comparison of GTP-ψ-35S and 3H-NMS binding in CHO cells stably expressing human M1–M5 muscarinic receptors using scintillation proximity assays. Life Sci 1999; 64: 568
Milligan G. Principles: extending the utility of [35S] GTPψS binding assays. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2003; 24: 87–90
Wang XY, Bergdahl K, Heijbel A, et al. Analysis of in vitro interactions of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B with insulin receptors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2001; 173(1-2): 109–20
DeLapp NW, McClure D, McKinzie J, et al. A study of M1 receptor coupling to inhibitory G proteins in CHO cells via GTPψS binding determined with anti-G protein antibodies. Life Sci 1999; 64: 569
DeLapp NW. The antibody-capture [35S] GTPψS scintillation proximity assay: a powerful emerging technique for analysis of GPCR pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2004; 25: 400–1
Williams JB, Mallorga PJ, Lemaire W, et al. Development of a scintillation proximity assay for analysis of Na+/Cl—dependent neurotransmitter transporter activity. Anal Biochem 2003; 321(1): 31–7
Mattingly CD, Mansfield RK, Bhattacharyya D, et al. Membrane-based scintillation proximity assays: I. Detection and quantification of 14CO2. J Memb Sci 1995; 98: 275–80
Culliford SJ, McCauley P, Sutherland AJ, et al. A novel cell-based scintillation proximity assay for studying protein function and activity in vitro using membrane-soluble scintillants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 296(4): 857–63
Chapman RL, Stanley TB, Hazen R, et al. Small molecule modulators of HIV Rev/ Rev response element interaction identified by random screening. Antiviral Res 2002; 54(3): 149–62
McCairn MC, Culliford SJ, Kozlowski RZ, et al. Synthesis, evaluation and incorporation into liposomes of 4-functionalised-2, 5-diphenyloxazole derivatives for application in scintillation proximity assays. Tetrahedron Lett 2004; 45: 2163–6
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20574071).
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to the contents of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Liu, B. Application of Scintillation Proximity Assay in Drug Discovery. BioDrugs 19, 383–392 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2165/00063030-200519060-00005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00063030-200519060-00005