Abstract
Objective: Repinotan hydrochloride (repinotan) is a selective, high-affinity, full serotonin receptor agonist at the 5-HT1a subtype that is undergoing clinical development in acute stroke. To investigate whether gender is an important covariable for repinotan pharmacokinetics, two studies were performed in subjects of different age and gender who had been phenotyped as extensive metabolisers for cytochrome P450 (CYP)2D6 using dextromethorphan as model substrate.
Subjects and methods: Both studies were placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomised, parallel-group studies. Study I was conducted in six healthy young males, five healthy elderly males, and four healthy elderly females receiving a continuous intravenous (IV) infusion of repinotan 0.45 μg/kg/h or placebo for a duration of 12 hours. Study II was performed in healthy elderly male and female volunteers aged ≥65 years with 67 subjects receiving repinotan and 34 receiving placebo. Subjects received a 12-hour infusion of repinotan at doses of 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 or 3.0 μg/kg/h.
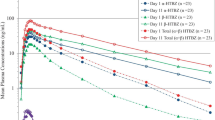
Results: Following IV infusion, the steady-state plasma concentration (Css) for repinotan was reached after 4–6 hours consistent with its half-life of 0.8–1.8 hours. In both male and female subjects, the volume of distribution at steady-state and plasma clearance (CL) were independent of dose, indicating linear pharmacokinetics and dose-proportionality for area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) and peak plasma concentration (Cmax) over the dose range of 0.1–3.0 μg/kg/h. Compared with elderly subjects, repinotan CL was unchanged in a subgroup of young subjects. The pooled evaluation of elderly subjects (n = 67) showed that gender had no influence on the pharmacokinetics of repinotan. The ratios male : female and their 90% CIs were: 0.91 (0.789, 1.052) for dose/ bodyweight-normalised Cmax (Cmax, norm), 0.95 (0.808, 1.110) for half-life, 0.97 (0.900, 1.044) for Vss, and 1.11 (0.923, 1.336) for CL.
Conclusion: These results indicate that gender does not affect the pharmacokinetics of repinotan in healthy subjects whose age (≥65 years) was representative of the target patient population for repinotan in acute stroke.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horvath E, Augstein K-H, Wittka R. Neuroprotective effect of the novel 5-HT1a receptor agonist BAY × 3702 in a rat model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain injury [abstract]. Soc Neurosci 1997; 23: 1923
Horvath E, Augstein K-H. Neuroprotection by the novel 5-HT1a receptor agonist BAY × 3702 in the rat model of acute subdural hematoma [abstract]. J Neurotrauma 1997; 14: 800
Boettcher, M. Pupillography in clinical pharmacology. In: Kuhlmann J, Boettcher M, editors Pupillography: principles, methods and applications. Zuckschwerdt Verlag, München, 1999; 13: 13–26
Ohman J, Braakman R, Legout V, et al. Repinotan (BAY × 3702): A 5HT1a agonist in traumatically brain injured patients. J Neurotrauma 2001; 12: 1313–22
Teal P, BRAINS, a phase II study of the neuroprotectant, BAY × 3702 in patients with ischemic stroke [abstract]. Cerebrovasc Dis 1998; 8 Suppl. 4: 20
Bertilsson L, Dahl ML. Polymorphic drug oxidation. CNS Drugs 1996; 5: 200–23
Meibohm B, Beierle I, Derendorf H. How important are gender differences in pharmacokinetics? Clin Pharmacokinet 2002; 41: 329–42
Laurent-Kenesi MA, Jacqz-Aigrain E, Lejonc JL, et al. Assessment of CYP 2D6 activity in very elderly healthy subjects. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 1996; 10: 158–9
Pollock BG, Perel JM, Altieri LP, et al. Debrisoquine hydroxylation phenotyping in geriatric psychopharmacology. Psychopharmacol Bull 1992; 28: 163–8
Shulman R, Özdemir V. Psychotropic medications and cytochrome P450 2D6: pharmacokinetic considerations in the elderly. Can J Psychiatry 1997; 42 Suppl. 1: 4S–9S
Yamada H, Dahl ML, Lannfelt L, et al. CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes in an elderly Swedish population. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1998; 54: 479–81
Ohara K, Tanabu S, Ishibashi K, et al. Effects of age and cytochrome P450 2D6*10 allele on the plasma haloperidol concentration/dose ratio. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2003; 27: 945–9
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Bayer HealthCare AG, Wuppertal, Germany.
Safety data for one of the present studies has been previously published as an abstract (Fleckenstein L, Roche L, Sundaresan PR, et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1998; 63: 190).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinig, R., Sundaresan, P., Shah, A. et al. Effect of Gender and Age on the Pharmacokinetics of Repinotan. Clin. Drug Investig. 25, 125–134 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-200525020-00005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-200525020-00005