Abstract
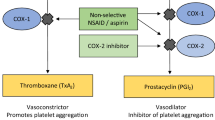
Background and objective: Impaired mobility and pain mean a loss of quality of life for patients with rheumatic diseases. Therefore the initial aim of therapy is rapid and efficient analgesia in order to achieve the best possible result for these patients. Lornoxicam is a strong analgesic and anti-inflammatory NSAID with balanced cyclo-oxygenase (COX)-1/COX-2 inhibition and excellent tolerability. In the course of the development of selective COX-2 inhibitors, it was maintained that COX-2 inhibitors decrease the risk of injury to the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract with a similar efficacy to that of classic NSAIDs. However, a clinical trial comparing both substances has never been performed. In the present study we investigated the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis with lornoxicam in comparison with treatment with the selective COX-2 inhibitor rofecoxib. This multicentre clinical investigation focused on efficacy and tolerability.
Patients and methods: A total of 2520 patients (most of them with osteoarthritis) were treated over 25 days on average. Before and after treatment patients documented their individual scores for pain on movement, at rest and during the night, and their individual duration of morning stiffness as well as the consequent grade of restriction. At the end of the study all individuals involved judged the efficacy and safety of the therapy.
Results: All improvements in each efficacy parameter were clinically relevant in each treatment group and significantly superior (p < 0.001) in the lornoxicam group. Pain on movement (−45.3%), at rest (−42.0%) and at night (−42.5%) was reduced by rofecoxib, whereas improvements after treatment with lornoxicam exceeded those effects significantly (−55.8%, −55.8% and −59.9%, respectively). Shortening of the duration of morning stiffness was significantly (p < 0.001) more pronounced with lornoxicam (−66.6%) than with rofecoxib (-50.2%). Nearly three times as many patients discontinued rofecoxib treatment because of lack of efficacy compared with lornoxicam treatment (8.9% versus 3.4%). Physicians judged lornoxicam to be markedly superior to rofecoxib, since excellent efficacy was observed in 40.9% of all cases versus 20.1% with rofecoxib. Serious adverse events did not occur. Adverse events were reported in 5.4% of all lornoxicam patients compared with 12.0% of the rofecoxib recipients (p < 0.001). GI symptoms showed a slight trend of being less frequent following rofecoxib therapy.
Conclusions: The results of this study confirmed the efficacy and safety of both drugs. Lornoxicam and rofecoxib are effective in the treatment of patients with activated osteoarthritis; the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of lornoxicam are significantly superior to those of rofecoxib without inferiority in tolerability.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The use of trade names is for product identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Pruss TP, Stroissnig H, Radhofer-Weite S, et al. Overview of the pharmacological properties, pharmacokinetics and animal safety assessment of lornoxicam. Postgrad Med J 1990; 66Suppl. 4: S18–21
Ferber HP, Maleschitz P, Binder D. Chlortenoxicam, a new NSAID, prevents the arachidonic acid-induced toxicity [abstract A387]. 2nd World Conference on Inflammation, Antirheumatics, Analgesics, Immunomodulators; 1986 Mar 19–20, Monte Carlo
Adams SS. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, plasma half-lives and adverse reactions [letter]. Lancet 1987; II: 1204–5
Futaki N, Takahashi S, Kitagawa T, et al. Anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic and cyclooxygenase inhibitory effects of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent lornoxicam (in Japanese). Jpn Pharmacol Ther 1997; 25: 55–71
Berg J, Christoph T, Widerna M, et al. Isoenzyme-specific cyclooxygenase inhibitors: a whole cell assay system using the human erythroleukemic cell line HEL and the human mono-cytic cell line Mono Mac 6. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 1997; 37: 179–86
Brune K, Hinz B. Selektive Cyclooxygenase-2-Hemmer: Glaube, Hoffnung, Realität. Akt Rheumatol 1998; 23: 1–5
Beejay U, Wolfe MM. Cyclooxygenase-2-selective inhibitors: panacea or flash in the pan? Gastroenterology 1999; 117: 1002–5
Balfour JA, Fitton A, Barradell LB. Lornoxicam. A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic potential in the management of painful and inflammatory conditions. Drugs 1996 Apr; 51(4): 639–57
Berry H, Ollier S. Lornoxicam in clinical practice. Postgrad Med J 1990; 66Suppl. 4: S41–5
Bias P. Efficacy and safety of lornoxicam (8mg b.i.d.) in comparison with placebo in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a four-week, randomized, prospective multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase IIb study (study CT 94). Nycomed Pharma A/S, 1995 (Data on file)
Caruso I, Montrone F, Boari L. et al. Lornoxicam versus diclofenac in rheumatoid arthritis: a double-blind, multicenter study. Adv Ther 1994; 11: 132–8
Krimmer J. A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, parallel group design study comparing the effects of multiple doses of lornoxicam versus diclofenac in patients with rheumatoid arthritis during a three month period followed by a continuation of treatment in an open design in those patients receiving lornoxicam for a period of nine months (study CT 39). Nycomed Pharma A/S, 1993 (Data on file)
Norholt SE, Sindet-Petersen S, Bugge C, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response study of the analgesic effect of lornoxicam after surgical removal of man-dibular third molars. J Clin Pharmacol 1995 Jun; 35: 606–14
Geba GP, Weaver AL, Polis AB, et al. Efficacy of rofecoxib, celecoxib, and acetaminophen in osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized trial. JAMA 2002; 287(1): 64–71
Kidd B, Frenzel W. A multicenter, randomized, double blind study comparing lornoxicam with diclofenac in osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 1996; 23(9): 1605–11
Cannon GW, Caldwell JR, Holt P, et al. Rofecoxib, a specific inhibitor of cyclooxygenase 2, with clinical efficacy comparable with that of diclofenac sodium. Athritis Rheum 2000; 43: 978–87
Day R, Morrison B, Luza A, et al. A randomized trial of the efficacy and tolerability of the COX-2 inhibitor rofecoxib vs ibuprofen in patients with osteoarthritis: Rofecoxib/Ibuprofen Comparator Study Group. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160(12): 1781–7
Buttgereit F, Burmester GR, Simon LS. Gastrointestinal toxic side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cyclooxygenase-2-specific inhibitors. Am J Med 2001; 110: 13–9
Whelton A, Fort JG, Puma JA, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2-specific inhibitors and cardiorenal function: a randomized, controlled trial of celexocib and rofecoxib in older hypertensive osteoarthritis patients. Am J Ther 2001; 8(2): 85–95
Graves JW, Hunder IA. Worsening of hypertension by cyclo-oxygenase-2-inhibitors. J Clin Hypertens 2000; 2(6): 396–8
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by Merckle GmbH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rose, P., Steinhauser, C. Comparison of Lornoxicam and Rofecoxib in Patients with Activated Osteoarthritis (COLOR Study). Clin. Drug Investig. 24, 227–236 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-200424040-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-200424040-00004