Abstract
Objective
To compare loratadine with fexofenadine and placebo in relieving symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR).
Design
A randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study.
Study Participants
Participants were aged 12 to 60 years with spring/summer SAR and total symptom severity scores (TSS) of at least 8 (maximum score 15) on six of 14 pre-baseline time-points.
Interventions
Loratadine 10mg once daily, fexofenadine 60mg twice daily, or placebo for 7 days.
Main Outcome Measures and Results
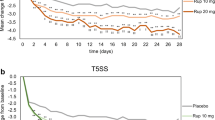
The primary end-point was the reduction from baseline in am and pm reflective and instantaneous TSS at final assessment. Times to 25% and maximum reductions in am reflective TSS were also analysed. Drug administration with either loratadine or fexofenadine provided significant relief versus placebo: both agents provided similar reductions from baseline in am and pm reflective and instantaneous TSS at final assessment. Compared with fexofenadine, loratadine demonstrated a statistically greater percentage reduction in am and pm reflective TSS in four of the initial five assessments (p < 0.05 for day 1 pm, day 2 pm, and day 3 am and pm assessments), achieving significance versus fexofenadine as early as 12 hours following the first dose (day 1 pm). Median times to a 25% reduction and maximum reduction in am reflective TSS also occurred significantly earlier in patients receiving loratadine.
Conclusions
Compared with placebo, both loratadine and fexofenadine provided significant relief of the symptoms of SAR. At the first assessment following the first dose, however, loratadine demonstrated a significant reduction from baseline in TSS compared with fexofenadine. In addition, time-to-event analysis indicated that the reduction in symptoms occurred significantly earlier with loratadine.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rachelefsky GS. National guidelines needed to manage rhinitis and prevent complications. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1999; 82: 296–305
Simons FE. Learning impairment and allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc 1996; 17: 185–9
Marshall PS, Colon EA. Effects of allergy season on mood and cognitive function. Ann Allergy 1993; 71: 251–8
Dykewicz MS, Fineman S, Skoner DP, et al. Diagnosis and management of rhinitis: complete guidelines of the Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters in Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1998; 81: 478–518
Gonzalez MA, Estes KS. Pharmacokinetic overview of oral second-generation H1 antihistamines. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 1998; 36: 292–300
Van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C, Passalacqua G, et al. Consensus statement on the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Allergy 2000; 55: 116–34
Claritin (loratadine) prescribing information. Physicians’ Desk Reference. Montvale, NJ: Medical Economics, 2000: 2781–3
Allegra (fexofenadine) prescribing information. Physicians’ Desk Reference. Montvale, NJ: Medical Economics, 2000: 1343–4
Gutkowski A, Bedard PM, Del Carpio J, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of loratadine, terfenadine, and placebo in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1988; 81 (5 Pt 1): 902–7
Del Carpio J, Kabbash L, Turenne Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of loratadine (10 mg once daily), terfenadine (60 mg twice daily), and placebo in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1989; 84: 741–6
Casale TB, Andrade C, Qu R. Safety and efficacy of once-daily fexofenadine HCl in the treatment of autumn seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc 1999; 20: 193–8
Bronsky E, Falliers CJ, Kaiser HB, et al. Effectiveness and safety of fexofenadine, a new nonsedating H1-receptor antagonist, in the treatment of fall allergies. Allergy Asthma Proc 1998; 19:135–41
Van Cauwenberge P, Juniper EF. Comparison of the efficacy, safety and quality of life provided by fexofenadine hydrochloride 120 mg, loratadine 10 mg and placebo administered once daily for the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy 2000; 30: 891–9
Prenner BM, Capano D, Harris AG. Efficacy and tolerability of loratadine versus fexofenadine in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis: a double-blind comparison with crossover treatment of nonresponders. Clin Ther 2000; 22: 760–9
Day JH, Briscoe MP, Welsh A, et al. Onset of action, efficacy, and safety of a single dose of fexofenadine hydrochloride for ragweed allergy using an environmental exposure unit. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1997; 79: 533–40
Day JH, Briscoe MP, Clark RH, et al. Onset of action and efficacy of terfenadine, astemizole, cetirizine, and loratadine for the relief of symptoms of allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1997; 79: 163–72
Bedard PM, Del Carpio J, Drouin MA, et al. Onset of action of loratadine and placebo and other efficacy variables in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Clin Ther 1992; 14: 269–75
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by Integrated Therapeutics Group Inc. (a subsidiary of Schering-Plough), Kenilworth, New Jersey, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaiser, H.B., Rooklin, A., Spangler, D. et al. Efficacy of Loratadine Compared with Fexofenadine or Placebo for the Treatment of Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis. Clin. Drug Investig. 21, 571–578 (2001). https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-200121080-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-200121080-00006