Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of losartan versus diltiazem on blood pressure, albuminuria, insulin sensitivity and lipid profile in a randomised, open study. p ]Patients: 40 type 2 diabetic patients (57 ± 12 years) from the Endocrinology clinic, with mild hypertension, persistent microalbuminuria and normal renal function, were randomly administered losartan 50 mg/day (n = 20) or diltiazem 300 mg/day (n = 20) for 12 weeks. After 1 month, hydrochlorothiazide 12.5mg was added if blood pressure was >130/85mm Hg.
Outcome Measures: At baseline and after 3 months, plasma glucose, glycated haemoglobin (HbA1C), uric acid, lipid profile, albumin excretion rate and creatinine clearance were measured by routine methods. Insulin sensitivity was estimated by an insulin suppression test, and ambulatory blood pressure was monitored for 24 hours.
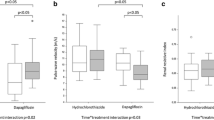
Results: Mean systolic blood pressure decreased from 151 ± 15 to 133 ± 11mm Hg with losartan (p < 0.05) and from 153 ± 17 to 130 ± 18mm Hg with diltiazem (p < 0.05). Mean diastolic blood pressure decreased from 82 ± 12 to 74 ± 13mm Hg with losartan (p < 0.05) and from 85 ± 13 to 72 ± 16mm Hg with diltiazem (p < 0.05). Albuminuria decreased from 147 ± 56 to 121 ± 57 μg/min with losartan (p < 0.05) and from 143 ± 76 to 119 ± 49 μg/min with diltiazem (p < 0.05). Differences between the two treatments were not significant. Insulin sensitivity and lipid profile were not modified by any of the treatments and no adverse effects were reported.
Conclusion: Both drugs were well tolerated and effectively reduced blood pressure and albuminuria, but did not modify insulin sensitivity or lipid profile.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lillioja S, Mott DM, Howard BV. Impaired glucose tolerance as a disorder of insulin action: longitudinal and cross-sectional studies in Pima Indians. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 1217–25
Saad MF, Pettit DJ, Mott DM, et al. Sequential changes in serum insulin concentration during development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet 1989; I: 1356–9
Reaven GM. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988; 37: 1595–1607
De Fronzo RA. Insulin resistance: the metabolic link between non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Cardiol 1990; 5: 286–93
Struthers AD. The choice of antihypertensive therapy in the diabetic patient. Postgrad Med J 1985; 61: 563–9
Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. The fifth report of the Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC-V). Arch Intern Med 1993; 153: 154–83
ADA Consensus Statement. Treatment of hypertension in diabetes. Diabetes Care 1993; 16: 1394–1401
The National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group report of hypertension in diabetes. Hypertension 1994; 23: 145–58
Recommendations de l’ALFEDIAM. Hypertension et diabète. Diabète Metab 1996; 22: 64–76
Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med 1984; 310: 356–60
Mattock MB, Morrish NJ, Viberti JC, et al. Prospective study of microalbuminuria as predictor of mortality in NIDDM. Diabetes 1992; 41: 736–41
Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Hiatt WR, et al. The effect of nisoldipine as compared with enalapril on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with non insulin dependent diabetes and hypertension. N Engl J Med 1988; 338: 645–52
Tatti P, Pahor RP, Byington P, et al. Outcome results of the Fosinopril versus Amlodipine Cardiovascular Events randomized Trial (FACET) in patients with hypertension and NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1988; 21: 597–603
Harris PG, Navar LG. Tubular transport responses to angiotensin. Am J Physiol 1985; 248: F261–88
Pollare T, Lithell H, Berne C. A comparison of the effects of hydrochlorothiazide and captopril on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with hypertension. N Engl J Med 1989; 321: 868–73
Ravid M, Lang R, Rachmani R, et al. Long-term renoprotective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. A 7-year follow-up study. Arch Intern Med 1996; 156: 286–9
Tikkanen Y, Omvic P, Jensen HA. Comparison of the angiotensin II antagonist losartan with the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor enalapril in patients with essential hypertension. J Hypertens 1995; 13: 1343–51
Mora-Maciá J, Ocón Pujadas J, Agraz Pamplona I, et al. Validación del monitor de presión ambulatoria ACP 2200. Hypertension 1996; 13: 8–11
Harano Y, Ohgaku S, Hidaka H, et al. Glucose, insulin and somatostatin infusion for the determination of insulin sensitivity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1977; 45: 1124–7
Martinez FJ, Villa E, Serrano J, et al. Diagnosis of insulin resistance. Drugs 1993; 46(2): 165–71
Wiegmann TB, Herron KG, Chonko AM, et al. Recognition of hypertension and abnormal blood pressure burden with ambulatory blood pressure recording in type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1990; 39: 1556–60
Puig JG, Ruilope LM, Ortega R on behalf of the Spanish Multicenter Study Group. Antihypertensive treatment efficacy in type II diabetes mellitus. Dissociation between casual and 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure. Hypertension 1995; 26: 1093–9
Navarro-Cid J, Maeso R, Pérez-Vizcaíno F, et al. Effects of losartan on blood pressure, metabolic alterations, and vascular reactivity in the fructose-induced hypertensive rat. Hypertension 1995; 26: 1074–8
Rosenthal T, Erlich Y, Cohen A. Effects of enalapril, losartan and verapamil on blood pressure and glucose metabolism in the Cohen-Rosenthal diabetic hypertensive rat. Hypertension 1997; 29: 1260–4
Moan A, Htieggen A, Nordby G, et al. Effects of losartan on insulin sensitivity in severe hypertension: connections through sympathetic nervous system activity? J Hum Hypertens 1995; 9 (5 Suppl.): S45–50
Moan A, Risanger T, Eide I, et al. The effect of angiotensin II receptor blockade on insulin sensitivity and sympathetic nervous system activity in primary hypertension. Blood Press 1994; 3: 185–8
Moan A, Hoigzen A, Seljeflot I, et al. The effect of angiotensin II receptor blockade with losartan on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. J Hypertens 1996; 14: 1093–7
Laakso M, Karjalainen L, Lempiainen-Kousa P. Effects of losartan on insulin sensitivity in hypertensive subjects. Hypertension 1996; 28: 392–6
Fliser D, Keller C, Bahrmann P, et al. Altered action of angiotensin II in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus of recent onset. J Hypertens 1997; 15: 293–9
Jauch KW, Hartl W, Günther M. Captopril enhances insulin responsiveness of forearm muscle tissue in non insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Invest 1987; 17: 448–54
Martinez FJ, Diaz AB, Aguilar JA, et al. Trandolapril enhances insulin sensitivity and decreases microalbuminuria in hypertensive NIDDM patients. Diabetologia 1995; 38 (1 Suppl.): A226
Isami S, Kishikawa H, Araki E, et al. Bradykinin enhances GLUT-4 translocation through the increase of insulin receptor tyrosin-kinase in primary adipocytes: evidence that bradykinin stimulates the insulin signalling pathway. Diabetologia 1996; 39: 412–20
Malstrom R, Packard CJ, Caslake M, et al. Defective regulation of triglyceride metabolism by insulin in the liver in NIDDM. Diabetologia 1997; 40: 454–62
Martinez J, de Pablos P, Aguilar JA, et al. Treatment of hypertensive type 2 diabetes with a fixed combination of trandolapril and verapamil: effects on insulin sensitivity and lipid profile. Atherosclerosis 1997; 134: 312
Chan JC, Critchley JA, Tomlinson B, et al. Antihypertensive and anti-albuminuric effects of losartan potassium and felodipine in Chinese elderly hypertensive patients with or without non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Nephrol 1997; 17: 72–80
Nakashima M, Uematsu T, Kosuge K, et al. Pilot study of the uricosuric effect of DuP753, a new angiotensin-II receptor antagonist in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1992; 42: 333–5
Parving HH, Andersen AR, Smith QM, et al. Effect of antihypertensive treatment on kidney function in diabetic nephropathy. BMJ 1987; 294: 1443–7
Viberti G, Mogensen CE, Leif C, et al. Effect of captopril on progression to clinical proteinuria in patients with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria. JAMA 1994; 271: 275–9
Murray KM. Calcium channel blockers for treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Clin Pharm 1991; 10: 862–5
Fioretto P, Frigato F, Velussi M, et al. Effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and calcium antagonists on atrial natriuretic peptide release and action and on albumin excretion rate in hypertensive insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Am J Hypertens 1992; 5: 837–46
Forsblom C, Trenkwalder P, Dahl K, et al. Candesartan cilexetil, a novel angiotensin II antagonist, reduces microalbuminuria in patients with type II diabetes mellitus and mild hypertension. Am J Hypertens 1997; 10: 86A
Andersson OK, Neldam S. Candesartan cilexetil 16mg provides greater antihypertensive effect than losartan 50mg in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Am J Hypertens 1997; 10: 125A
Nielsen S, Dollerup J, Nielsen B, et al. Losartan reduces albuminuria in patients with essential hypertension: an enalapril controlled 3 months study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1997; 12Suppl. 2: 19–23
Weber MA, Byyny RL, Pratt JH, et al. Effects of losartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, on blood pressure. Arch Intern Med 1995; 155: 405–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Pablos Velasco, P.L., Martín, F.J.M. Effects of Losartan and Diltiazem on Blood Pressure, Insulin Sensitivity, Lipid Profile and Microalbuminuria in Hypertensive Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Clin. Drug Investig. 16, 361–370 (1998). https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199816050-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199816050-00003