Summary
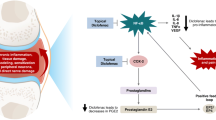
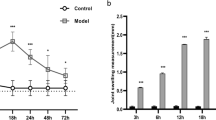
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease of the articular cartilage associated with synovial inflammation. Hyperplasia of synovial cells and infiltrating macrophages increase local synthesis of prostaglandins (mainly PGE2) and cytokines. Excess synthesis of PGE2 by osteoarthritic chondrocytes is also among the factors contributing to the degradation of the cartilage matrix. We evaluated the effect of a new NSAID, aceclofenac, at therapeutic concentrations (2, 4 and 8 mg/L) on the level of PGE2 in osteoarthritic synovial membrane and cartilage and on the levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in osteoarthritic synovial membranes following lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [20 mg/L] treatment, and compared it with diclofenac (125 and 250 µg/L). Results showed that aceclofenac and diclofenac almost completely abrogated the PGE2 synthesis at all concentrations tested on osteoarthritic synovial membranes and cartilages. Moreover, both NSAIDs demonstrated a statistically significant inhibition of LPS-stimulated IL-1β and TNF-α synthesis.
The destruction of articular joint tissue is a key element in the osteoarthritic process. Upregulation of catabolic factors contribute to this degradation. Investigation of drugs that are able to reduce the synthesis of some of these factors is of the utmost importance. We reported that NSAIDs, such as aceclofenac and diclofenac, can significantly decrease the synthesis of three major factors, PGE2, IL-1β and TNF-α, in joint articular tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J, Altman RD, et al. Collagenase and collagenolytic activity in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheum 1983; 26: 63–8
Dodge GR, Poole AR. Immunohistochemical detection and immunochemical analysis of type II collagen degradation in human normal, rheumatoid, and osteoarthritic articular cartilages and in expiants of bovine articular cartilage cultured with interleukin-1. J Clin Invest 1989; 83: 647–61
Hollander AP, Heathfield TF, Webber C, et al. Increased damage to type II collagen in osteoarthritic articular cartilage detected by a new immunoassay. J Clin Invest 1994; 93: 1722–32
Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP, Malemud CJ. Activation of metalloproteases in human osteoarthritic knee cartilage. Evidence for degradation in the core protein of sulfated proteoglycans. Ann Rheum Dis 1988; 47: 801–8
Zafarullah M, Martel-Pelletier J, Cloutier J-M, et al. Expression of c-fos, c-jun, jun-B, metallothionein and metalloproteinase genes in human chondrocytes. FEBS Lett 1992; 306: 169–72
Zafarullah M, Pelletier JP, Cloutier J-M, et al. Elevated metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase mRNA in human osteoarthritic synovia. J Rheumatol 1993; 20: 693–7
Pelletier JP, Roughley P, DiBattista JA, et al. Are cytokines involved in osteoarthritis pathophysiology? Semin Arthritis Rheum 1991; 20 Suppl. 2: 12–25
Dayer JM, de Rochemonteix B, Burrus B, et al. Human recombinant interleukin-1 stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells. J Clin Invest 1986; 77: 645–8
Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, et al. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum 1986; 29: 1039–49
Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J. Evidence for the involvement of interleukin-1 in human OA cartilage degradation: protective effect of NSAIDs. J Rheumatol 1989; 16 Suppl. 18: 19–27
Fowler PD, Shadforth MF, Crook PR, et al. Plasma and synovial fluid concentrations of diclofenac sodium and its major hydroxylated metabolites during long term treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1983; 25: 389–94
Honorato J, Caballero R, Giorgiani G, et al. Dose-analgesic response study and aceclofenac plasma levels in humans. Curr Ther Res 1990; 47: 605–11
González E, de la Cruz C, de Nicolás R, et al. Long term effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the production of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators by blood cells of patients with osteoarthritis. Agents Actions 1994; 41: 171–8
Pelletier JP, Cloutier JM, Martel-Pelletier J. In vitro effects of NSAIDs and corticosteroids on the synthesis and secretion of interleukin-1 by human osteoarthritic synovial membranes. Agents Actions 1993; 39 Suppl.: 181–93
Pelletier JP, McCollum R, Cloutier J-M, et al. Synthesis of metalloproteases and IL-6 in human osteoarthritic synovial membrane is an IL-1 mediated process. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1995; 43: 109–14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martel-Pelletier, J., Cloutier, JM. & Pelletier, JP. Effects of Aceclofenac and Diclofenac on Synovial Inflammatory Factors in Human Osteoarthritis. Clin. Drug Invest. 14, 226–232 (1997). https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199714030-00011
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199714030-00011