Summary
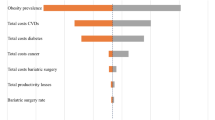
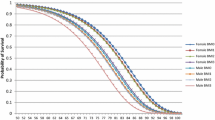
Obesity is a known risk factor for a number of diseases with serious mortality and morbidity implications. Thus, obesity is an economic burden to communities, since it reduces quality of life and leads to premature mortality; in addition, healthcare resources are used to manage obesity-related disease. It was estimated that in 1989, management of disease due to obesity (defined as body mass index > 30) cost A$395 million. This estimate covers the healthcare costs for the management of obesity, non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), gallstones, hypertension, coronary heart disease (CHD), breast cancer (among postmenopausal women), and colon cancer. As this estimate excludes the costs of some disease attributable to obesity, it is an underestimate of the true costs. Nonetheless, the estimated cost of the management of obesity-related conditions represents 86% of the healthcare costs used for the management of alcohol-related diseases in Australia. Healthcare costs attributable to obesity have not yet been estimated for countries elsewhere in Asia and the Pacific. However, it is acknowledged that obesity is a major problem in the Pacific, with exceptionally high prevalence rates and concomitant high rates of diseases for which obesity is a major risk factor, particularly NIDDM and CHD. It would, therefore, be useful to explore the cost of disease attributable to obesity in healthcare systems in these communities, and the potential for preventive programmes to reduce these costs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colditz GAL. The economic costs of obesity. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 55: 5053–5075, 1992
Collins V, Dowse G, Zimmet P. Prevalence of obesity in Pacific and Indian Ocean populations. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 10: S29–S32, 1990
Conway LM, Pinyopusarek M, Carter RC, Penm R, Stevenson C. The public health significance of drug and alcohol abuse in Australia. Discussion paper, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, 1993
Crowley S, Antioch K, Carter R, Waters AM, Conway L, et al. The cost of diet related disease in Australia. Discussion paper, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare and National Centre for Health Program Evaluation, 1992
Dowse G, Zimmet P, Collins V, Finch C. Obesity in Pacific populations. In Bjorntorp et al. (Eds) Obesity, pp. 619–639, JB Lippincott, Philadelphia, 1992
Dowse GK, Zimmet PZ, Gareeboo H, et al. Abdominal obesity and physical inactivity as risk factors for NIDDM and impaired glucose tolerance in Indian, Creole, and Chinese Mauritians. Diabetes Care 14: 271–282, 1991
Enzi G. Socioeconomic consequences of obesity: effect of obesity on the individual. PharmacoEconomics 5 (Suppl. 1): 54–57, 1994
Garrow J. Importance of obesity. British Medical Journal 303: 704–706, 1991
Lissner L. Causes, diagnosis and risks of obesity. PharmacoEconomics 5 (Suppl. 1): 8–17, 1994
National Heart Foundation, Australia. Risk Factor Prevalence Study, National Heart Foundation, Canberra, Australia, 1989
Vart Veer, et al. Dietary fat and the risk of breast cancer. International Journal of Epidemiology 19: 12–18, 1990
Zimmet P, Dowse G, Serjeantson S, King H. The epidemiology and natural history of NIDDM — lessons from the South Pacific. Diabetes/Metabolism Reviews 6: 91–124, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Segal, L., Carter, R. & Zimmet, P. The Cost of Obesity. Pharmacoeconomics 5 (Suppl 1), 45–52 (1994). https://doi.org/10.2165/00019053-199400051-00009
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00019053-199400051-00009