Summary
This article reviews the available literature on the validity and reliability of the non-invasive techniques, commonly known as CO2 rebreathing, for estimating cardiac output. The differing indirect methodologies are described and illustrated.
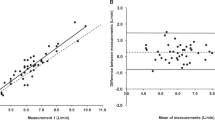
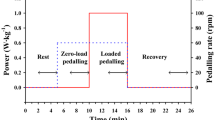
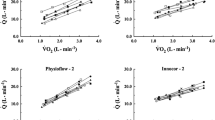
A table, constructed from the available literature, comparing criterion versus estimated cardiac outputs is presented. The varying combinations of methods employed, differing measurement conditions, i.e. rest and exercise, and divergent populations are illustrated and discussed. The correlation between criterion and estimated cardiac output for these studies ranged from r = 0.09 to 0.96, with a % standard deviation of the differences of 1.5 to 176.8%.
The Collier and end-tidal methods, in conjunction with either the Comroe or McHardy CO2 dissociation curve appears to be the most established, valid and reliable combination of methods for estimating resting cardiac output. These methods appear to be comparable to the combination of the Defares, end-tidal and Comroe curve methods for estimating cardiac output during exercise.
Because of the potential for large errors, caution is urged when interpreting cardiac output results based on indirect estimation for individual assessment, or for subjects with certain types of pulmonary or heart diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman. P.L; Gibson, J.F.; and Wang, C.C.: Handbook of Respiration (W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, 1958).
Ashton, C.H. and McHardy, J.R.: A rebreathing method for determining mixed venous PCO during exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 18: 668–671 (1963).
Asmussen, E. and Neilson, M.: The cardiac output in rest and work determined simultaneously by the acetylene and dye injection method. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 27: 217–230 (1953).
Asmussen, E. and Neilson, M: Physiological dead space and alveolar gas pressure at rest and during muscular exercise. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 38: 1–21 (1956).
Auchincloss, J.H.; Gilbert, R.; Kuppinger, M. and Peppi, D.: Mixed venous tension during exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 48(6): 933–938 (1980)
Bar-Or, O. and Shephard, R.J.: Cardiac output determination in exercising children — methodology and feasibility. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 217: Suppl 49–52 (1971a).
Bar-Or, O.; Shephard, R.J. and Allen, C.L.: Cardiac output of 10 to 13-year-old boys and girls during submaximal exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 30 (2): 219–223 (1971b).
Beekman, R.H.; Katch, V.L. and Marks, C.R.: Validity of CO — rebreathing cardiac output during rest and exercise in young adults. Medicine and Science in Sports 16(3): 306–310 (1984).
Cerretell, J.P.; Cruz, J.C.; Farhi, L.E. and Rahn, H.: Determination of mixed O and CO tensions and cardiac output by a rebreathing method. Respiration Physiology 1: 258–264 (1966).
Chen, H.; Silverton, N.P. and Hainsworth, R.: Evaluation of a method for estimating cardiac output from a single breath in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology 53(4): 1034–1038 (1982).
Clausen, J.P.; Larsen, O.A. and Trap-Jensen, J.: Cardiac output in middle-aged patients determined with CO rebreathing method. Journal of Applied Physiology 28(3): 337–342 (1970).
Collier, C.R.: Determination of mixed venous CO tension by rebreathing. Journal of Applied Physiology 9: 25–29 (1956).
Comroe, J.H.; Forester, R.E.; Dubois, A.G.; Briscoe, W.A. and Carlsten, E.: The lung: Clinical physiology and pulmonary function tests (Year Book, Chicago 1957).
Consolazio, F.C.; Johnson, R.E. and Pecora, L.J.: Physiological measurements of metabolic functions in man. (McGraw-Hill Inc., New York 1963).
Cumming, G.R.: Recirculation times in exercising children. Journal of Applied Physiology 45 (6): 1005–1008 (1978).
Dawson, W.T. and Johnson Jr, R.L.: Cardiac output measurement using N20 uptake: A method to subtract cardiogenic oscillations. Journal of Applied Physiology 54(5): 1427–1433 (1983).
Defares, J.G.: A study of the carbon dioxide time course during rebreathing. Drukkerij vlh kemink en zoon N.V. (Domplein 2. Utrecht 1956).
Defares, J.G.: Determination of PvCO from the exponential CO2 rise during rebreathing. Journal of Applied Physiology 13(2): 159–164 (1958)
DuBois, A.B.; Britt, A.G. and Fern, W.O.: Alveolar Co during the respiratory cycle. Journal of Applied Physiology 4: 335 (1952a).
DuBois, A.B.; Fowler, R.C.; Soffer, A. and Fenn, W.O.: Alvelar CO measured by expiration into the infrared gas analyzer. Journal of Applied Physiology 4: 526 (1952b).
Farhi, L.E.; Nesarahah, M.S.; Olszowka, A.J.; Metildi, L.A. and Ellis, A.K.: Cardiac output determination by simple one-step rebreating technique. Respiration Physiology 28(1): 141–159 (1976).
Ferguson, R.J.; Faulkner, J.A.; Julius, S. and Conway, J.: Comparison of cardiac output determined by CO rebreathing and dye-dilution methods. Journal of Applied Physiology 25(4): 450–454 (1968).
Franciosa, J.A.: Evaluation of the CO rebreathing cardiac output method in seriously ill patients. Circulation 55(3): 449 (1977).
Franciosa, J.A.; Ragan, D.O. and Rubenstone, S.J.: Validation of the CO rebreathing method for measuring cardiac output in patients with hypertension or heart failure. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 88(4): 672 (1976).
Godfrey, S. and Davies, C.T.M.: Estimation of arterial PCO and their effect on the calculated values of cardiac output and dead space on exercise. Clinical Science 39: 529–537 (1970).
Godfrey, S. and Wolfe, E.: An evaluation of rebreathing methods for measuring mixed venous PCO during exercise. Clinical Science 42: 345–353 (1972).
Guyton, A.C.: Basic Human Physiology: Normal Function and Mechanisms of Disease (W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia 1971).
Hargreaves, M. and Jennings, G.: Evaluation of the CO rebreathing method for the non-invasive measurement of resting cardiac output in man. Clinical Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 10(5): 609–614 (1983).
Heigenhauser, G.J.F. and Jones, N.L.: Comparison of two rebreathing methods for the determination of mixed venous partial pressure of carbon dioxide during exercise. Clinical Science 56: 433 (1979).
Henry, F.M.: Reliability, measurement error and intra-individual difference. Resource Quarterly 30(1): 21–24 (1959).
Jernerus, R.; Lundin, G.; and Thomson, D.: Cardiac output in healthy subjects determined with a CO rebreathing method. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 59: 390–399 (1963).
Jones, N.L.; Campbell, E.J.M., McHardy, G.J.R.; Higgs, B.E. and Clode, M.: The estimation of carbon dioxide pressure of mixed venous blood during exercise. Clinical Science 32: 311–327 (1967).
Jones, N.L.; Robertson, D.G. and Kane, J.W.: Difference between end-tidal and arterial PCO in exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 47(5): 954–960 (1979).
Jones, N.L.; Robertson, D.G.; Kane, J.W. and Campbell, J.M.: Effect of PCO on alveolar-arterial PCO difference during rebreathing. Journal of Applied Physiology 32(6): 782–787 (1972).
Klausen, K.: Comparison of CO rebreathing and acetylene methods for cardiac output. Journal of Applied Physiology 20: 763–766 (1965).
Leoppky, J.A.; Hoekenga, D.E.; Greene, E.R. and Luft, U.C.: Comparison of non-invasive pulsed Doppler and Fick measurements of stroke volume in cardiac patients. American Heart Journal 107(2): 339–346 (1984).
Lundin, L.G. and Thomson, D.: Determination of the mixed venous CO pressure with a rebreathing method. Correction for volume changes of the lung bag system. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 64: 448–452 (1965).
Magel, J.R. and Anderson, K.L.: Cardiac output in muscular exercise measured by the rebreathing procedure; in Deolin, Kanigk, Messin and Degre (Eds) Ergometry in Cardiology pp. 147–157 (Boehringer Mannheim GMBH 1968).
Marks, C.R.; Katch, V.L. and Beekman, R.: Arterial and venous CO pressure and content differences in exercising children with heart disease; A validation study. (Abstract.) Midwest chapter ACSM winter meeting, Boyne, Michigan (1982).
McHardy, G.J.R.: The relationship between the differences in pressure and content of carbon dioxide in arterial and venous blood. Clinical Science 32: 299–309 (1967).
McNemar, Q.: Psychological Statistics, 4th ed. (John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York 1969).
Miyamura, M. and Honda, Y.: CO dissociation curves of oxygenated whole blood obtained at rest and in exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology 39(1): 37–45 (1978).
Muiesan, G.; Sorbini, C.A.; Solinas, E.; Grassi, V.; Casucci, G. and Petz, E.: Comparison of CO rebreathing and direct Fick methods for determining cardiac output. Journal of Applied Physiology 24(3): 424–429 (1968).
Ohlsson, J.; Hlatala, M.P.; Tranesjo, J. and Wranne, B.: Non-invasive determination of effect stroke volume: Evaluation of a CO2-rebreathing method in normal subjects and patients. Clinical Physiology 3(1): 9–18 (1983).
Parnat, J.; Seliger, V.; Trefny, Z. and Pauer, M.: Determination of cardiac output by the CO2-rebreating method in fifteen-year-old boys subjected to graduated loading. Physiologia Bohemoslovaca 26: 85–93 (1977).
Paterson, D.H. and Cunningham, D.A.: Comparison of methods to calculate cardiac output using the CO2 rebreathing method, ropean Journal of Applied Physiology 35: 223–230 (1976).
Paterson, D.H.; Cunningham, D.A.; Plyley, M.J.; Blimkie, C.J.R. and Donner, A.P.: The consistency of cardiac output measurement (CO2 rebreathing) in children during exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology 49(1): 37–44 (1982).
Pengelly, L.D.: Curve-fitting analysis of pressure-volume characteristics of the lungs. Journal of Applied Physiology 42(1): 111–116 (1977).
Rahn, H.: Concept of mean alveolar air and ventilation-blood flow relationships during pulmonary gas exchange. American Journal of Physiology 158: 21–30 (1949).
Raimondi, G.A.; Puy, R.J.M.; Raimondi, A.J.; Manique, J.L. and Marchissio, M.L.: Influence of estimates of arterial PCO2 on the Fick CO2 values of cardiac output on exercise. Acta Physiologica Latinoamericana 24: 258–264 (1974).
Reybrouck, T.; Amery, A.; Billiet, L.; Fagard, R. and Stijns, H.: Comparison of cardiac output determined by a carbon dioxide-rebreathing and direct Fick method at rest and during exercise. Clinical Science and Molecular Medicine 55: 445–452 (1978).
Rode, A. and Shephard, R.J.: Cardiac output, blood volume, and total hemoglobin of the Canadian Eskimo. Journal of Applied Physiology 34(1): 91–96 (1973).
Sady, S.P.; Freedson, S.P. and Gilliam, T.B.: Calculation of submaximal and maximal cardiac output in children using the CO2 rebreathing technique. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness 21(3): 245–255 (1981).
Shephard, R.J. and Bar-Or, O.: Alveolar ventilation in near maximum exercise. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2: 83–92 (1970).
Stewart, R.I. and Lewis, C.M.: The reliability of the carbon dioxide-rebreathing, indirect Fick method of output determination in patients with pulmonary disease. Clinical Science 64(3): 289–293 (1983).
Svensson, S.E.; Lomsky, M.; Olsson, L.; Persson, S.; Strauss, H.W. and Westins, H.: Non-invasive determination of distribution of cardiac output in man at rest and exercise. Clinical Physiology 2(6): 467–477 (1982).
Wise, M.E. and Defares, J.G.: Venous PCO2 and cardiac output obtained from rebreathing curves: Extrapolation or by plateau method? Clinical Science 43: 303–307 (1972).
Zeidifard, E.; Silverman, M. and Godfrey, S.: Reproducibility of indirect (CO2) Fick method for calculation of cardiac output. Journal of Applied Physiology 33 (1): 141–143 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marks, C., Katch, V., Rocchini, A. et al. Validity and Reliability of Cardiac Output by CO2 Rebreathing. Sports Medicine 2, 432–446 (1985). https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-198502060-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-198502060-00004