Abstract
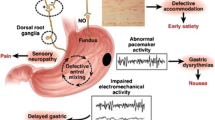
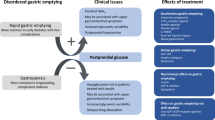
Gastric emptying is frequently abnormal in patients with long-standing type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Symptoms commonly associated with disordered gastric emptying include nausea, vomiting, bloating and epigastric pain, while patients are also at risk of malnutrition, weight loss, impaired drug absorption, disordered glycaemic control and poor quality of life. Although often attributed to the presence of irreversible autonomic neuropathy, acute hyperglycaemia represents a potentially reversible cause of gastric dysfunction in diabetes. Scintigraphy represents the gold standard for measuring gastric emptying. The management of diabetic gastroparesis is less than optimal, partly because the pathogenesis has not been clearly defined. Treatment approaches include dietary modification and optimization of glycaemia, and the use of prokinetic drugs, while novel therapies such as gastric electrical stimulation are the subject of ongoing investigation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkman HP, Hasler WL, Fisher RS. American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the diagnosis and treatment of gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2004; 127(5): 1592–622
Wang YR, Fisher RS, Parkman HP. Gastroparesis-related hospitalizations in the United States: trends, characteristics, and outcomes, 1995–2004. Am J Gastroenterol 2008; 103(2): 313–22
Abell TL, Bernstein RK, Cutts T, et al. Treatment of gastroparesis: a multidisciplinary clinical review. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2006; 18(4): 263–83
Camilleri M. Clinical practice. Diabetic gastroparesis. N Engl J Med 2007; 356(8): 820–9
Schvarcz E, Palmer M, Ingberg CM, et al. Increased prevalence of upper gastrointestinal symptoms in long-term type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 1996; 13(5): 478–81
Ricci JA, Siddique R, Stewart WF, et al. Upper gastrointestinal symptoms in a US national sample of adults with diabetes. Scand J Gastroenterol 2000; 35(2): 152–9
Horowitz M, Maddox AF, Wishart JM, et al. Relationships between oesophageal transit and solid and liquid gastric emptying in diabetes mellitus. Eur J Nucl Med 1991; 18(4): 229–34
Ferroir J. The diabetic stomach. Thesis in medicine. Paris, France, 1937
Horowitz M, Wishart JM, Jones KL, et al. Gastric emptying in diabetes: an overview. Diabet Med 1996; 13 (9 Suppl. 5): S16–22
Horowitz M, Su YC, Rayner CK, et al. Gastroparesis: prevalence, clinical significance and treatment. Can J Gastroenterol 2001; 15(12): 805–13
Jones KL, Horowitz M, Wishart MJ, et al. Relationships between gastric emptying, intragastric meal distribution and blood glucose concentrations in diabetes mellitus. J Nucl Med 1995; 36(12): 2220–8
Moldovan C, Dumitrascu DL, Demian L, et al. Gastroparesis in diabetes mellitus: an ultrasonographic study. Rom J Gastroenterol 2005; 14(1): 19–22
Phillips WT, Schwartz JG, McMahan CA. Rapid gastric emptying of an oral glucose solution in type 2 diabetic patients. J Nucl Med 1992; 33(8): 1496–500
Jones KL, Horowitz M, Carney BI, et al. Gastric emptying in early noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Nucl Med 1996; 37(10): 1643–8
Nowak TV, Johnson CP, Kalbfleisch JH, et al. Highly variable gastric emptying in patients with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Gut 1995; 37(1): 23–9
Horowitz M, Jones KL, Akkermans LM, et al. Gastric function. In: Horowitz M, Samsom M, editors. Gastrointestinal function in diabetes mellitus. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2004: 117–76
Horowitz M, Dent J, Fraser R, et al. Role and integration of mechanisms controlling gastric emptying. Dig Dis Sci 1994; 39 (12Suppl.): 7–13S
Camilleri M. Integrated upper gastrointestinal response to food intake. Gastroenterology 2006; 131(2): 640–58
Samsom M, Roelofs JM, Akkermans LM, et al. Proximal gastric motor activity in response to a liquid meal in type I diabetes mellitus with autonomic neuropathy. Dig Dis Sci 1998; 43(3): 491–6
Samsom M, Salet GA, Roelofs JM, et al. Compliance of the proximal stomach and dyspeptic symptoms in patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Dig Dis Sci 1995; 40(9): 2037–42
Samsom M, Jebbink RJ, Akkermans LM, et al. Abnormalities of antroduodenal motility in type I diabetes. Diabetes Care 1996; 19(1): 21–7
Wehrmann T, Lembcke B, Caspary WF. Influence of cisapride on antroduodenal motor function in healthy subjects and diabetics with autonomic neuropathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1991; 5(6): 599–608
Kawagishi T, Nishizawa Y, Okuno Y, et al. Antroduodenal motility and transpyloric fluid movement in patients with diabetes studied using duplex sonography. Gastroenterology 1994; 107(2): 403–9
Mearin F, Camilleri M, Malagelada JR. Pyloric dysfunction in diabetics with recurrent nausea and vomiting. Gastroenterology 1986; 90(6): 1919–25
Koch KL. Electrogastrography: physiological basis and clinical application in diabetic gastropathy. Diabetes Technol Ther 2001; 3(1): 51–62
Nohara S, Iwase M, Imoto H, et al. Gastric emptying in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetes associated with mitochondrial DNA 3243 mutation using 13C-octanoic acid breath test. J Diabetes Complications 2006; 20(5): 295–301
Kumar A, Attaluri A, Hashmi S, et al. Visceral hypersensitivity and impaired accommodation in refractory diabetic gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2008; 20(6): 635–42
Rayner CK, Verhagen MA, Hebbard GS, et al. Proximal gastric compliance and perception of distension in type 1 diabetes mellitus: effects of hyperglycemia. Am J Gastroenterol 2000; 95(5): 1175–83
Rayner CK, Horowitz M. Gastrointestinal motility and glycemic control in diabetes: the chicken and the egg revisited? J Clin Invest 2006; 116(2): 299–302
Schmidt RE. Neuropathology and pathogenesis of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Int Rev Neurobiol 2002; 50: 257–92
Schmidt RE, Plurad SB, Olack BJ, et al. The effect of pancreatic islet transplantation and insulin therapy on experimental diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes 1983; 32(6): 532–40
Horvath VJ, Vittal H, Ordog T. Reduced insulin and IGF-I signaling, not hyperglycemia, underlies the diabetes-associated depletion of interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine stomach. Diabetes 2005; 54(5): 1528–33
Horvath VJ, Vittal H, Lorincz A, et al. Reduced stem cell factor links smooth myopathy and loss of interstitial cells of cajal in murine diabetic gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2006; 130(3): 759–70
Watkins CC, Sawa A, Jaffrey S, et al. Insulin restores neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression and function that is lost in diabetic gastropathy. J Clin Invest 2000; 106(3): 373–84
Gangula PR, Maner WL, Micci MA, et al. Diabetes induces sex-dependent changes in neuronal nitric oxide synthase dimerization and function in the rat gastric antrum. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2007; 292(3): G725–33
Asakawa H, Onishi M, Hayashi I, et al. Comparison between coefficient of R-R interval variation and gastric emptying in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 20(9): 1358–64
Yoshida MM, Schuffler MD, Sumi SM. There are no morphologic abnormalities of the gastric wall or abdominal vagus in patients with diabetic gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 1988; 94(4): 907–14
Forster J, Damjanov I, Lin Z, et al. Absence of the interstitial cells of Cajal in patients with gastroparesis and correlation with clinical findings. J Gastrointest Surg 2005; 9(1): 102–8
Pasricha PJ, Pehlivanov ND, Gomez G, et al. Changes in the gastric enteric nervous system and muscle: a case report on two patients with diabetic gastroparesis. BMC Gastroenterol 2008; 8: 21
Ejskjaer NT, Bradley JL, Buxton-Thomas MS, et al. Novel surgical treatment and gastric pathology in diabetic gastroparesis. Diabet Med 1999; 16(6): 488–95
Rayner CK, Samsom M, Jones KL, et al. Relationships of upper gastrointestinal motor and sensory function with glycemic control. Diabetes Care 2001; 24(2): 371–81
Fraser RJ, Horowitz M, Maddox AF, et al. Hyperglycaemia slows gastric emptying in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1990; 33(11): 675–80
Schvarcz E, Palmer M, Aman J, et al. Physiological hyperglycemia slows gastric emptying in normal subjects and patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 1997; 113(1): 60–6
Russo A, Stevens JE, Chen R, et al. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia accelerates gastric emptying of solids and liquids in long-standing type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90(8): 4489–95
Schvarcz E, Palmer M, Aman J, et al. Hypoglycemia increases the gastric emptying rate in healthy subjects. Diabetes Care 1995; 18(5): 674–6
Schvarcz E, Palmer M, Aman J, et al. Hypoglycaemia increases the gastric emptying rate in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 1993; 10(7): 660–3
Hasler WL, Soudah HC, Dulai G, et al. Mediation of hyperglycemia-evoked gastric slow-wave dysrhythmias by endogenous prostaglandins. Gastroenterology 1995; 108(3): 727–36
Jebbink RJ, Samsom M, Bruijs PP, et al. Hyperglycemia induces abnormalities of gastric myoelectrical activity in patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 1994; 107(5): 1390–7
Barnett JL, Owyang C. Serum glucose concentration as a modulator of interdigestive gastric motility. Gastroenterology 1988; 94(3): 739–44
Horowitz M, Harding PE, Maddox AF, et al. Gastric and oesophageal emptying in patients with type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1989; 32(3): 151–9
Gallar P, Oliet A, Vigil A, et al. Gastroparesis: an important cause of hospitalization in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients and the role of erythromycin. Perit Dial Int 1993; 13 Suppl. 2: S183–6
Bell RA, Jones-Vessey K, Summerson JH. Hospitalizations and outcomes for diabetic gastroparesis in North Carolina. South Med J 2002; 95(11): 1297–9
Whitson BA, Asolati M, Kandaswamy R, et al. Diabetic gastroparesis-associated bezoar resolution via ‘cola-lysis’. Clin Transplant 2008; 22(2): 242–4
Horowitz M, O’Donovan D, Jones KL, et al. Gastric emptying in diabetes: clinical significance and treatment. Diabet Med 2002; 19(3): 177–94
Bytzer P, Talley NJ, Leemon M, et al. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: a population-based survey of 15 000 adults. Arch Intern Med 2001; 161(16): 1989–96
Jones KL, Russo A, Stevens JE, et al. Predictors of delayed gastric emptying in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001; 24(7): 1264–9
Quan C, Talley NJ, Jones MP, et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms and glycemic control in diabetes mellitus: a longitudinal population study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 20(9): 888–97
Talley SJ, Bytzer P, Hammer J, et al. Psychological distress is linked to gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetes mellitus. Am J Gastroenterol 2001; 96(4): 1033–8
Koch CA, Uwaifo GI. Are gastrointestinal symptoms related to diabetes mellitus and glycemic control? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 20(9): 822–5
Horowitz M, Edelbroek MA, Wishart JM, et al. Relationship between oral glucose tolerance and gastric emptying in normal healthy subjects. Diabetologia 1993; 36(9): 857–62
Chaikomin R, Doran S, Jones KL, et al. Initially more rapid small intestinal glucose delivery increases plasma insulin, GIP, and GLP-1 but does not improve overall glycemia in healthy subjects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2005; 289(3): E504–7
O’Donovan DG, Doran S, Feinle-Bisset C, et al. Effect of variations in small intestinal glucose delivery on plasma glucose, insulin, and incretin hormones in healthy subjects and type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89(7): 3431–5
Gonlachanvit S, Hsu CW, Boden GH, et al. Effect of altering gastric emptying on postprandial plasma glucose concentrations following a physiologic meal in type-II diabetic patients. Dig Dis Sci 2003; 48(3): 488–97
Ishii M, Nakamura T, Kasai F, et al. Altered postprandial insulin requirement in IDDM patients with gastroparesis. Diabetes Care 1994; 17(8): 901–3
Horowitz M, Jones KL, Rayner CK, et al. ‘Gastric’ hypoglycaemia: an important concept in diabetes management. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2006; 18(6): 405–7
Ohlsson B, Melander O, Thorsson O, et al. Oesophageal dysmotility, delayed gastric emptying and autonomic neuropathy correlate to disturbed glucose homeostasis. Diabetologia 2006; 49(9): 2010–4
Chandalia M, Garg A, Lutjohann D, et al. Beneficial effects of high dietary fiber intake in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 2000; 342(19): 1392–8
Russo A, Stevens JE, Wilson T, et al. Guar attenuates fall in postprandial blood pressure and slows gastric emptying of oral glucose in type 2 diabetes. Dig Dis Sci 2003; 48(7): 1221–9
Gentilcore D, Chaikomin R, Jones KL, et al. Effects of fat on gastric emptying of and the glycemic, insulin, and incretin responses to a carbohydrate meal in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91(6): 2062–7
Cunningham KM, Read NW. The effect of incorporating fat into different components of a meal on gastric emptying and postprandial blood glucose and insulin responses. Br J Nutr 1989; 61(2): 285–90
Cervera A, Wajcberg E, Sriwijitkamol A, et al. Mechanism of action of exenatide to reduce postprandial hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2008; 294(5): E846–52
Linnebjerg H, Park S, Kothare PA, et al. Effect of exenatide on gastric emptying and relationship to postprandial glycemia in type 2 diabetes. Regul Pept 2008; 151(1–3): 123–9
Hebbard GS, Sun WM, Bochner F, et al. Pharmacokinetic considerations in gastrointestinal motor disorders. Clin Pharmacokinet 1995; 28(1): 41–66
Groop LC, Luzi L, DeFronzo RA, et al. Hyperglycaemia and absorption of sulphonylurea drugs. Lancet 1989; II(8655): 129–30
Wright RA, Clemente R, Wathen R. Diabetic gastroparesis: an abnormality of gastric emptying of solids. Am J Med Sci 1985; 289(6): 240–2
Maurer AH, Parkman HP. Update on gastrointestinal scintigraphy. Semin Nucl Med 2006; 36(2): 110–8
Camilleri M, Hasler WL, Parkman HP, et al. Measurement of gastrointestinal motility in the GI laboratory. Gastroenterology 1998; 115(3): 747–62
Abell TL, Camilleri M, Donohoe K, et al. Consensus recommendations for gastric emptying scintigraphy: a joint report of the American Neurogastroenterology and Motility Society and the Society of Nuclear Medicine. J Nucl Med Technol 2008; 36(1): 44–54
Guo JP, Maurer AH, Fisher RS, et al. Extending gastric emptying scintigraphy from two to four hours detects more patients with gastroparesis. Dig Dis Sci 2001; 46(1): 24–9
Ziessman HA, Bonta DV, Goetze S, et al. Experience with a simplified, standardized 4-hour gastric-emptying protocol. J Nucl Med 2007; 48(4): 568–72
Bures J, Kopacova M, Vorisek V, et al. Examination of gastric emptying rate by means of 13C-octanoic acid breath test. Methods of the test for adults and results of the investigation of healthy volunteers. Cas Lek Cesk 2005; 144 Suppl. 3: 18–22
Chew CG, Bartholomeusz FD, Bellon M, et al. Simultaneous 13C/14C dual isotope breath test measurement of gastric emptying of solid and liquid in normal subjects and patients: comparison with scintigraphy. Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur 2003; 6(1): 29–33
Sanaka M, Urita Y, Sugimoto M, et al. Comparison between gastric scintigraphy and the [13C]-acetate breath test with Wagner-Nelson analysis in humans. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2006; 33(12): 1239–43
Sanaka M, Nakada K, Nosaka C, et al. The Wagner-Nelson method makes the [13C]-breath test comparable to radioscintigraphy in measuring gastric emptying of a solid/liquid mixed meal in humans. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2007; 34(7): 641–4
Zahn A, Langhans CD, Hoffner S, et al. Measurement of gastric emptying by 13C-octanoic acid breath test versus scintigraphy in diabetics. Z Gastroenterol 2003; 41(5): 383–90
Pfaffenbach B, Wegener M, Adamek RJ, et al. Non-invasive 13C octanoic acid breath test for measuring stomach emptying of a solid test meal-correlation with scintigraphy in diabetic patients and reproducibility in healthy probands. Z Gastroenterol 1995; 33(3): 141–5
Viramontes BE, Kim DY, Camilleri M, et al. Validation of a stable isotope gastric emptying test for normal, accelerated or delayed gastric emptying. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2001; 13(6): 567–74
Haruma K, Kusunoki H, Manabe N, et al. Real-time assessment of gastroduodenal motility by ultrasonography. Digestion 2008; 77 Suppl. 1: 48–51
Gentilcore D, Hausken T, Horowitz M, et al. Measurements of gastric emptying of low- and high-nutrient liquids using 3D ultrasonography and scintigraphy in healthy subjects. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2006; 18(12): 1062–8
Gilja OH, Detmer PR, Jong JM, et al. Intragastric distribution and gastric emptying assessed by three-dimensional ultrasonography. Gastroenterology 1997; 113(1): 38–49
Hveem K, Jones KL, Chatterton BE, et al. Scintigraphic measurement of gastric emptying and ultrasonographic assessment of antral area: relation to appetite. Gut 1996; 38(6): 816–21
Stevens JE, Gilja OH, Gentilcore D, et al. Validation of 3D ultrasonography to measure gastric emptying of a high-nutrient drink in diabetic gastroparesis [abstract]. Gastroenterology 2008; 134 (4 Suppl. 1): A340
Kara S, Dirgenali F, Okkesim S. Detection of gastric dysrhythmia using WT and ANN in diabetic gastroparesis patients. Comput Biol Med 2006; 36(3): 276–90
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998; 352(9131): 837–53
O’Donovan D, Feinle-Bisset C, Jones K, et al. Idiopathic and diabetic gastroparesis. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol 2003; 6(4): 299–309
Gentilcore D, O’Donovan D, Jones KL, et al. Nutrition therapy for diabetic gastroparesis. Curr Diab Rep 2003; 3(5): 418–26
Olausson EA, Alpsten M, Larsson A, et al. Small particle size of a solid meal increases gastric emptying and late postprandial glycaemic response in diabetic subjects with gastroparesis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2008; 80(2): 231–7
Talley NJ. Diabetic gastropathy and prokinetics. Am J Gastroenterol 2003; 98(2): 264–71
Horowitz M, Jones KL, Harding PE, et al. Relationship between the effects of cisapride on gastric emptying and plasma glucose concentrations in diabetic gastroparesis. Digestion 2002; 65(1): 41–6
Petrakis IE, Vrachassotakis N, Sciacca V, et al. Hyperglycaemia attenuates erythromycin-induced acceleration of solid-phase gastric emptying in idiopathic and diabetic gastroparesis. Scand J Gastroenterol 1999; 34(4): 396–403
Sturm A, Holtmann G, Goebell H, et al. Prokinetics in patients with gastroparesis: a systematic analysis. Digestion 1999; 60(5): 422–7
Janssens J, Peeters TL, Vantrappen G, et al. Improvement of gastric emptying in diabetic gastroparesis by erythromycin: preliminary studies. N Engl J Med 1990; 322(15): 1028–31
Ehrenpreis ED, Zaitman D, Nellans H. Which form of erythromycin should be used to treat gastroparesis? A pharmacokinetic analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1998; 12(4): 373–6
Rayner CK, Horowitz M. New management approaches for gastroparesis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 2(10): 454–62
Richards RD, Davenport K, McCallum RW. The treatment of idiopathic and diabetic gastroparesis with acute intravenous and chronic oral erythromycin. Am J Gastroenterol 1993; 88(2): 203–7
Dhir R, Richter JE. Erythromycin in the short- and long-term control of dyspepsia symptoms in patients with gastroparesis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2004; 38(3): 237–42
Ray WA, Murray KT, Meredith S, et al. Oral erythromycin and the risk of sudden death from cardiac causes. N Engl J Med 2004; 351(11): 1089–96
Sengupta S, Modak P, McCauley N, et al. Effect of oral clarithromycin on gall-bladder motility in normal subjects and those with gall-stones. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006; 24(1): 95–9
Sutera L, Dominguez LJ, Belvedere M, et al. Azithromycin in an older woman with diabetic gastroparesis. Am J Ther 2008; 15(1): 85–8
Rabine JC, Barnett JL. Management of the patient with gastroparesis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2001; 32(1): 11–8
McCallum RW, Valenzuela G, Polepalle S, et al. Subcutaneous metoclopramide in the treatment of symptomatic gastroparesis: clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1991; 258(1): 136–42
McHugh S, Lico S, Diamant NE. Cisapride vs metoclopramide: an acute study in diabetic gastroparesis. Dig Dis Sci 1992; 37(7): 997–1001
Tonini M, Cipollina L, Poluzzi E, et al. Review article: clinical implications of enteric and central D2 receptor blockade by antidopaminergic gastrointestinal prokinetics. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004; 19(4): 379–90
Franzese A, Borrelli O, Corrado G, et al. Domperidone is more effective than cisapride in children with diabetic gastroparesis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002; 16(5): 951–7
Tatsuta M, Iishi H, Nakaizumi A, et al. Effect of treatment with cisapride alone or in combination with domperidone on gastric emptying and gastrointestinal symptoms in dyspeptic patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1992; 6(2): 221–8
Abell TL, Camilleri M, DiMagno EP, et al. Long-term efficacy of oral cisapride in symptomatic upper gut dysmotility. Dig Dis Sci 1991; 36(5): 616–20
Veysey MJ, Malcolm P, Mallet AI, et al. Effects of cisapride on gall bladder emptying, intestinal transit, and serum deoxycholate: a prospective, randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial. Gut 2001; 49(6): 828–34
Horowitz M, Maddern GJ, Maddox A, et al. Effects of cisapride on gastric and esophageal emptying in progressive systemic sclerosis. Gastroenterology 1987; 93(2): 311–5
Kendall BJ, Kendall ET, Soykan I, et al. Cisapride in the long-term treatment of chronic gastroparesis: a 2-year open-label study. J Int Med Res 1997; 25(4): 182–9
Braden B, Enghofer M, Schaub M, et al. Long-term cisapride treatment improves diabetic gastroparesis but not glycaemic control. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002; 16(7): 1341–6
Tonini M, De Ponti F, Di Nucci A, et al. Review article: cardiac adverse effects of gastrointestinal prokinetics. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1999; 13(12): 1585–91
Hasler WL. Gastroparesis: symptoms, evaluation, and treatment. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2007; 36(3): 619–47, ix
Itoh Z. Motilin and clinical application. Peptides 1997; 18(4): 593–608
Verhagen MA, Samsom M, Maes B, et al. Effects of a new motilide, ABT-229, on gastric emptying and postprandial antroduodenal motility in healthy volunteers. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997; 11(6): 1077–86
Thielemans L, Depoortere I, Perret J, et al. Desensitization of the human motilin receptor by motilides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005; 313(3): 1397–405
Tack J, Peeters T. What comes after macrolides and other motilin stimulants? Gut 2001; 49(3): 317–8
McCallum RW, Cynshi O. Clinical trial: effect of mitemcinal (a motilin agonist) on gastric emptying in patients with gastroparesis. A randomized, multicentre, placebo-controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007; 26(8): 1121–30
McCallum RW, Cynshi O. Efficacy of mitemcinal, a motilin agonist, on gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with symptoms suggesting diabetic gastropathy: a randomized, multi-center, placebo-controlled trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007; 26(1): 107–16
Iwanaga Y, Kimura T, Miyashita N, et al. Characterization of acetylcholinesterase-inhibition by itopride. Jpn J Pharmacol 1994; 66(3): 317–22
Holtmann G, Talley NJ, Liebregts T, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of itopride in functional dyspepsia. N Engl J Med 2006; 354(8): 832–40
Talley NJ, Tack J, Ptak T, et al. Itopride in functional dyspepsia: results of two phase III multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Gut 2008; 57(6): 740–6
Stevens JE, Russo A, Maddox AF, et al. Effect of itopride on gastric emptying in longstanding diabetes mellitus. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2008; 20(5): 456–63
Tack J, Depoortere I, Bisschops R, et al. Influence of ghrelin on gastric emptying and meal-related symptoms in idiopathic gastroparesis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22(9): 847–53
Murray CD, Martin NM, Patterson M, et al. Ghrelin enhances gastric emptying in diabetic gastroparesis: a double blind, placebo controlled, crossover study. Gut 2005; 54(12): 1693–8
Zheng Q, Qiu WC, Yan J, et al. Prokinetic effects of a ghrelin receptor agonist GHRP-6 in diabetic mice. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(30): 4795–9
Melga P, Mansi C, Ciuchi E, et al. Chronic administration of levosulpiride and glycemic control in IDDM patients with gastroparesis. Diabetes Care 1997; 20(1): 55–8
Mansi C, Savarino V, Vigneri S, et al. Gastrokinetic effects of levosulpiride in dyspeptic patients with diabetic gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol 1995; 90(11): 1989–93
Degen L, Petrig C, Studer D, et al. Effect of tegaserod on gut transit in male and female subjects. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2005; 17(6): 821–6
Morganroth J, Ruegg PC, Dunger-Baldauf C, et al. Tegaserod, a 5-hydroxytryptamine type 4 receptor partial agonist, is devoid of electrocardiographic effects. Am J Gastroenterol 2002; 97(9): 2321–7
Dishy V, Cohen Pour M, Feldman L, et al. The effect of sildenafil on gastric emptying in patients with end-stage renal failure and symptoms of gastroparesis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2004; 76(3): 281–6
Bianco A, Pitocco D, Valenza V, et al. Effect of sildenafil on diabetic gastropathy. Diabetes Care 2002; 25(10): 1888–9
Duby JJ, Campbell RK, Setter SM, et al. Diabetic neuropathy: an intensive review. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2004; 61(2): 160–73
Tolle T, Freynhagen R, Versavel M, et al. Pregabalin for relief of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind study. Eur J Pain 2008; 12(2): 203–13
Feinle C, Meier O, Otto B, et al. Role of duodenal lipid and cholecystokinin A receptors in the pathophysiology of functional dyspepsia. Gut 2001; 48(3): 347–55
Lin ZY, McCallum RW, Schirmer BD, et al. Effects of pacing parameters on entrainment of gastric slow waves in patients with gastroparesis. Am J Physiol 1998; 274(1 Pt 1): G186–91
McCallum RW, Chen JD, Lin Z, et al. Gastric pacing improves emptying and symptoms in patients with gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 1998; 114(3): 456–61
Lin Z, Forster J, Sarosiek I, et al. Effect of high-frequency gastric electrical stimulation on gastric myoelectric activity in gastroparetic patients. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2004; 16(2): 205–12
Lin Z, Hou Q, Sarosiek I, et al. Association between changes in symptoms and gastric emptying in gastroparetic patients treated with gastric electrical stimulation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2008; 20(5): 464–70
Abell TL, Van Cutsem E, Abrahamsson H, et al. Gastric electrical stimulation in intractable symptomatic gastroparesis. Digestion 2002; 66(4): 204–12
Zhang J, Chen JD. Systematic review: applications and future of gastric electrical stimulation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006; 24(7): 991–1002
Ayinala S, Batista O, Goyal A, et al. Temporary gastric electrical stimulation with orally or PEG-placed electrodes in patients with drug refractory gastroparesis. Gastrointest Endosc 2005; 61(3): 455–61
Elfvin A, Andersson S, Abrahamsson H, et al. Percutaneous implantation of gastric electrodes: a novel technique applied in animals and in patients. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2007; 19(2): 103–9
Sallam HS, Chen JD, Pasricha PJ. Feasibility of gastric electrical stimulation by percutaneous endoscopic transgastric electrodes. Gastrointest Endosc 2008; 68(4): 754–9
Xu X, Pasricha PJ, Chen JD. Feasibility of gastric electrical stimulation by use of endoscopically placed electrodes. Gastrointest Endosc 2007; 66(5): 981–6
Abell TL, Malinowski S, Minocha A. Nutrition aspects of gastroparesis and therapies for drug-refractory patients. Nutr Clin Pract 2006; 21(1): 23–33
Anand C, Al-Juburi A, Familoni B, et al. Gastric electrical stimulation is safe and effective: a long-term study in patients with drug-refractory gastroparesis in three regional centers. Digestion 2007; 75(2–3): 83–9
Cutts TF, Luo J, Starkebaum W, et al. Is gastric electrical stimulation superior to standard pharmacologic therapy in improving GI symptoms, healthcare resources, and long-term health care benefits? Neurogastroenterol Motil 2005; 17(1): 35–43
Maranki JL, Lytes V, Meilahn JE, et al. Predictive factors for clinical improvement with Enterra gastric electric stimulation treatment for refractory gastroparesis. Dig Dis Sci 2008; 53(8): 2072–8
McCallum RW, Dusing RW, Sarosiek I, et al. Mechanisms of high-frequency electrical stimulation of the stomach in gastroparetic patients. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2006; 1: 5400–3
Abell TL. Gastric electric stimulation is a viable option in gastroparesis treatment. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009; 6(3): E8–13
Jones MP. Is gastric electrical stimulation an effective therapy for patients with drug-refractory gastroparesis? Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 5(7): 368–70
Jankovic J, Brin MF. Therapeutic uses of botulinum toxin. N Engl J Med 1991; 324(17): 1186–94
Pasricha PJ, Ravich WJ, Hendrix TR, et al. Intrasphincteric botulinum toxin for the treatment of achalasia. N Engl J Med 1995; 332(12): 774–8
Lacy BE, Crowell MD, Schettler-Duncan A, et al. The treatment of diabetic gastroparesis with botulinum toxin injection of the pylorus. Diabetes Care 2004; 27(10): 2341–7
Miller LS, Szych GA, Kantor SB, et al. Treatment of idiopathic gastroparesis with injection of botulinum toxin into the pyloric sphincter muscle. Am J Gastroenterol 2002; 97(7): 1653–60
Ezzeddine D, Jit R, Katz N, et al. Pyloric injection of botulinum toxin for treatment of diabetic gastroparesis. Gastrointest Endosc 2002; 55(7): 920–3
Lacy BE, Zayat EN, Crowell MD, et al. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of gastroparesis: a preliminary report. Am J Gastroenterol 2002; 97(6): 1548–52
Arts J, Holvoet L, Caenepeel P, et al. Clinical trial: a randomized-controlled crossover study of intrapyloric injection of botulinum toxin in gastroparesis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007; 26(9): 1251–8
Friedenberg FK, Palit A, Parkman HP, et al. Botulinum toxin A for the treatment of delayed gastric emptying. Am J Gastroenterol 2008; 103(2): 416–23
Wang L. Clinical observation on acupuncture treatment in 35 cases of diabetic gastroparesis. J Tradit Chin Med 2004; 24(3): 163–5
Wang CP, Kao CH, Chen WK, et al. A single-blinded, randomized pilot study evaluating effects of electroacupuncture in diabetic patients with symptoms suggestive of gastroparesis. J Altern Complement Med 2008; 14(7): 833–9
Wang XY, Shi X, He L. Effect of electroacupuncture on gastrointestinal dynamics in acute pancreatitis patients and its mechanism. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2007; 32(3): 199–202
Jones MP, Maganti K. A systematic review of surgical therapy for gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol 2003; 98(10): 2122–9
Cashion AK, Holmes SL, Hathaway DK, et al. Gastroparesis following kidney/pancreas transplant. Clin Transplant 2004; 18(3): 306–11
Acknowledgements
The authors’ research work was been supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Royal Adelaide Hospital/Institute of Medical and Veterinary Science Research Committee, and the Rebecca L. Cooper Foundation. Dr Horowitz has been a member of advisory boards of Tranzyme Pharma, Amulet Pharma and Merck Sharpe & Dohme, and has received honoraria for these activities. The other authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Rayner, C.K., Jones, K.L. et al. Diabetic Gastroparesis. Drugs 69, 971–986 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200969080-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200969080-00003