Summary
Paediatric respiratory tract infections are one of the most common reasons for physician visits and hospitalisation, and are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The role of physicians and other healthcare professionals has expanded from merely treating disease to implementing measures aimed at health maintenance and disease prevention. Therefore, children with recurrent respiratory tract infections represent a great challenge for the paediatrician, from both therapeutic and preventive standpoints.
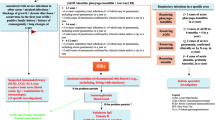
The paediatrician must first determine whether these recurrent infections are because of host-derived factors or are the result of increased environmental exposure. Host-derived factors may be nonimmunological or related to host immunodeficiency. The leading cause of recurrent respiratory tract infections throughout the world is increased environmental exposure in children attending nursery school or daycare centres. Acute otitis media in children is of particular concern because of its high incidence, frequent recurrence, and serious long term sequelae, e.g. hearing loss.
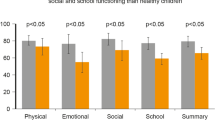
The socioeconomic impact of these recurrent infections is staggering, and there remains much scope for devising methods for their treatment and prevention. Recent approaches have included the encouragement of breastfeeding, the use of intravenous immunoglobulin and respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin, as well as methods of stimulating immunity, such as ribosomal immunotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paradise JL, Rockette HE, Colburn DK, et al. Otitis media in 2253 Pittsburgh-area infants: prevalence and risk factors during the first two years of life. Pediatrics 1997; 99: 318–33
Schwartz B, Giebink GS, Henderson FW, et al. Respiratory infections in day care. Pediatrics 1994; 94: 1018–20
Daly KA. Epidemiology of otitis media. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 1991; 24: 775–86
Wald ER, Dashefsky B, Beyers C, et al. Frequency and severity of infections in day care. J Pediatr 1986; 112: 4540–6
Appelbaum PC. Antimicrobial resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae: an overview. Clin Infect Dis 1992; 15: 77–82
Osterholm MT. Infectious disease in child day care: an overview. Pediatrics 1994; 94: 987–90
Subramanian KNS. Prophylaxis for respiratory syncytial virus infection with immune globulin. In: Bellanti JA, Bracci R, Prindull G, et al., editors. Neonatal hematology and immunology III. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science BV, 1996: 97–102
Collet J-P, Floret D, Ducruet T, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of Imocur in reducing recurrent respiratory infections in children attending day care centers [abstract 1320]. Meeting of the European Respiratory Disease Society. Brussels, September 1991
Vautel JM, Cauquil J, Perruchet AM, et al. Prevention of recurrent ear, nose, and throat infections in young children with Ribomunyl®: double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Curr Ther Res 1993; 63(6): 722–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellanti, J.A. Recurrent Respiratory Tract Infections in Paediatric Patients. Drugs 54 (Suppl 1), 1–4 (1997). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199700541-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199700541-00003